Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2013; 19(33): 5464-5472
Published online Sep 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i33.5464
Published online Sep 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i33.5464
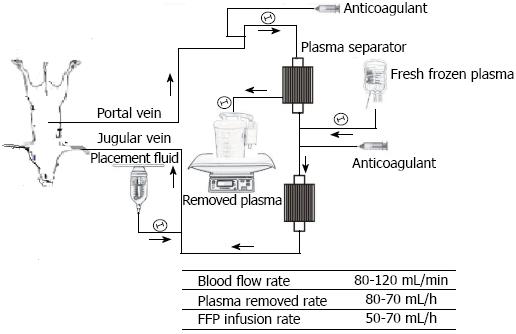
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the extracorporeal circuit indicating the plasmapheresis and conditions of slow plasma exchange.
The portal venous blood was aspirated through the portal catheter and into tubing connected to a centrifugal pump immediately post-hepatectomy (PH), and then passed through plasma-separation cartridges with a blood flow of 90-110 mL/min. From 24 h PH these pigs were converted to plasma exchange for 6 h. After that the blood was returned to the pig through a double-lumen catheter inserted into the internal jugular or subclavian vein, and then continued on extracorporeal continuous portal diversion until 48 h PH. FFP: Fresh frozen plasma.
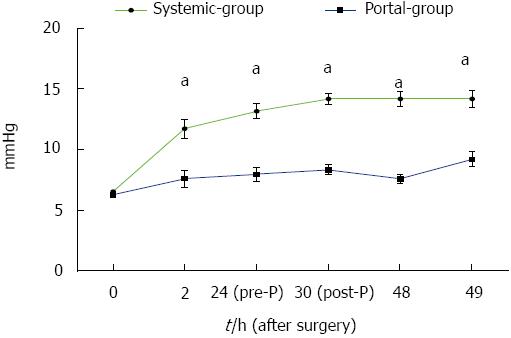
Figure 2 Portal vein pressure was significantly reduced in the Portal group compared with the Systemic group.
Portal vein pressure in the Portal group was significantly lower than that in the Systemic group from 2 to 49 h post-hepatectomy. aP < 0.05 indicates Portal group vs Systemic group.
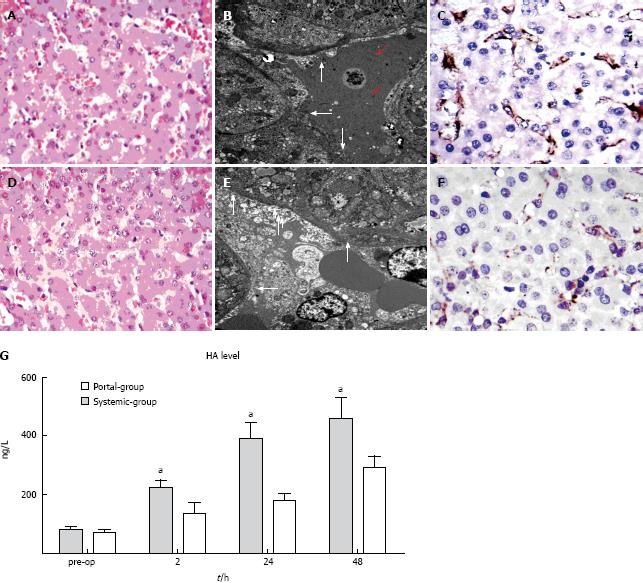
Figure 3 Portal group attenuated sinusoidal endothelial injury compared with the Systemic group.
A, D: Hematoxylin and eosin staining (× 400 magnification) in the Systemic group and Portal group, respectively; B, E: Transmission electron microscopic (TEM) photographs (× 6000 magnification) in the Systemic group and Portal group, respectively; C, F: CD31 immunohistochemical staining of tissue samples (× 400 magnification) taken at 1 h post-hepatectomy (PH) in the Systemic group and Portal group, respectively; G: Serial changes in the level of hyaluronic acid (HA) in the two groups. aP < 0.05 indicates Portal group vs Systemic group.
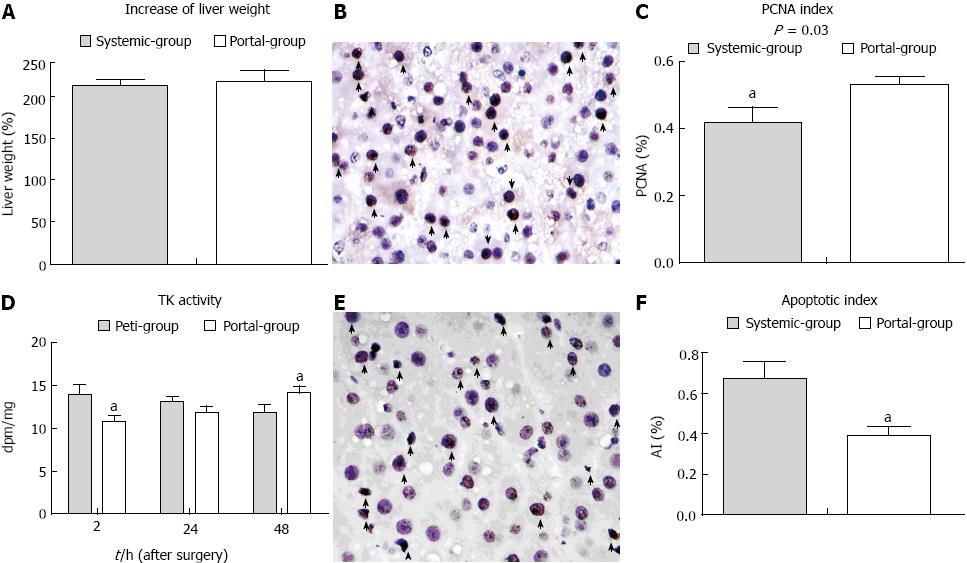
Figure 4 The rate of liver remnant regeneration was elevated and apoptosis was attenuated in the Portal group compared with the Systemic group.
A: The rate of increase of liver volume in the two groups; B: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) staining in the liver remnant (arrows indicate stained positive cells × 400 magnification). A large number of transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL)-positive cells (arrows) in the liver remnant (× 400 magnification); C: Microphotometric evaluation of the PCNA index in PCNA-stained tissue at 48 h PH; D: The change in thymidine kinase activity in the two groups; E: TUNEL staining at 48 h PH; F: Microphotometric evaluation of the apoptotic index (AI) in TUNEL-stained tissue at 48 h PH. aP < 0.05 indicates a significant difference between the groups.
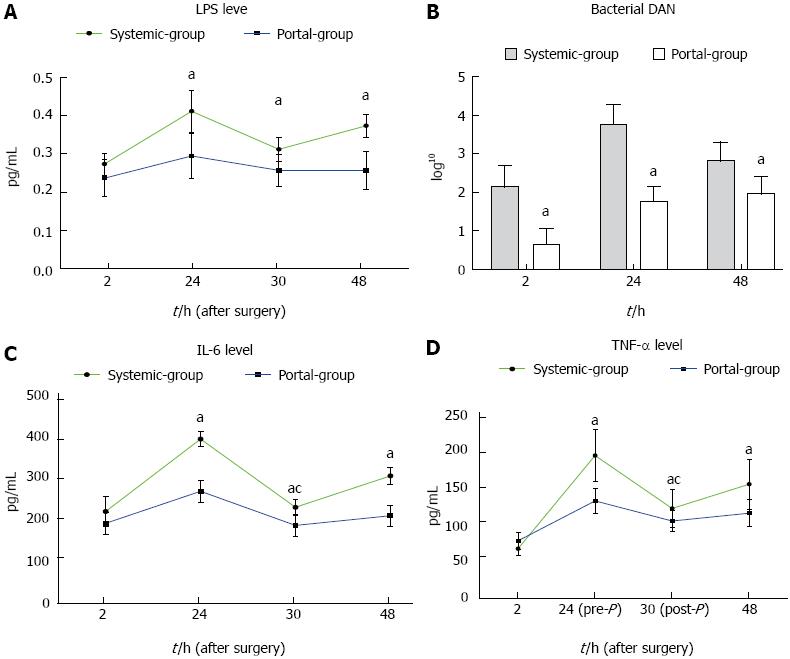
Figure 5 Bacterial translocation and endotoxin, as well as the inflammatory response, were significantly attenuated in the Portal group compared with the Systemic group.
A: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) level was reduced in the Portal group compared with the Systemic group from 24 h post-hepatectomy (PH) until 48 h PH; B: Bacterial DNA level was reduced in the Portal group compared with the Systemic group from 2 h PH until 48 h PH; C: Interleukin (IL)-6 level was reduced in the Portal group compared with the Systemic group from 24 h PH until 48 h PH. D: tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α level was reduced in the Portal group compared with the Systemic group from 24 h PH until 48 h PH. aP < 0.05 indicates Portal group vs Systemic group; cP < 0.05 indicates before plasma exchange vs after plasma exchange.
- Citation: Hou P, Chen C, Tu YL, Zhu ZM, Tan JW. Extracorporeal continuous portal diversion plus temporal plasmapheresis for “small-for-size” syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(33): 5464-5472
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i33/5464.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i33.5464