Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2013; 19(11): 1718-1727
Published online Mar 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1718
Published online Mar 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1718
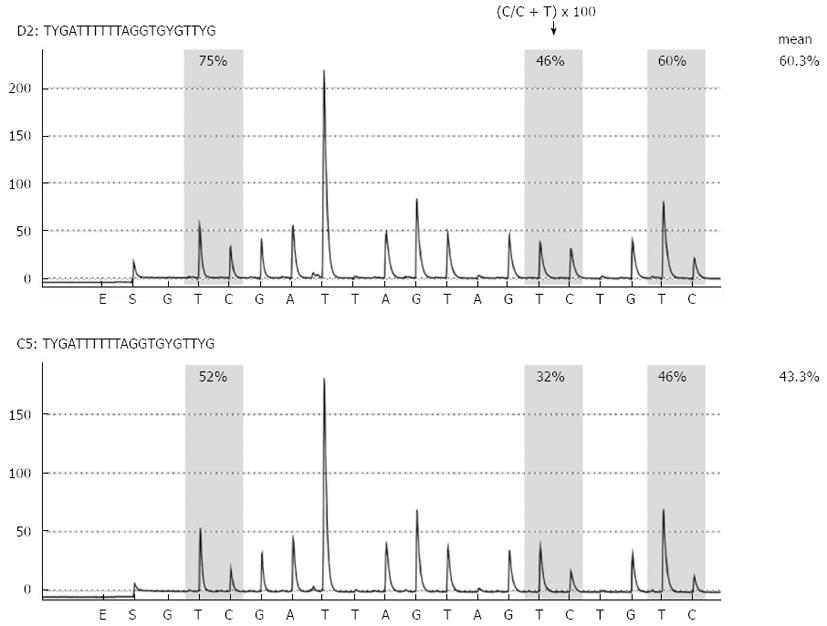
Figure 1 Representative long interspersed nuclear element-1 methylation analysis by pyrosequencing.
Long interspersed nuclear element-1 methylation analysis in biliary fluids from patients with noncancerous pancreatic disease (chronic pancreatitis, upper panel) and pancreatic cancer (lower panel) is shown.
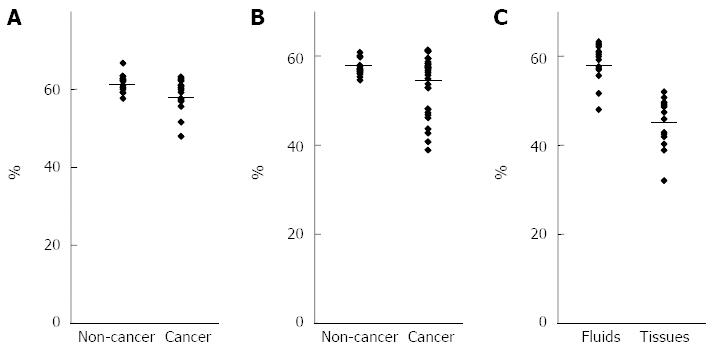
Figure 2 Analysis of long interspersed nuclear element-1 methylation levels using pancreatobiliary fluids.
A: Comparison of the long interspersed nuclear element-1 (LINE-1) methylation levels in pancreatic fluids between pancreatic cancer and noncancerous pancreatic disease; B: Comparison of the LINE-1 methylation levels in biliary fluids between pancreatobiliary cancer and noncancerous pancreatobiliary disease; C: Comparison of the LINE-1 methylation levels in pancreatic cancer between pancreatic fluids and tissues.
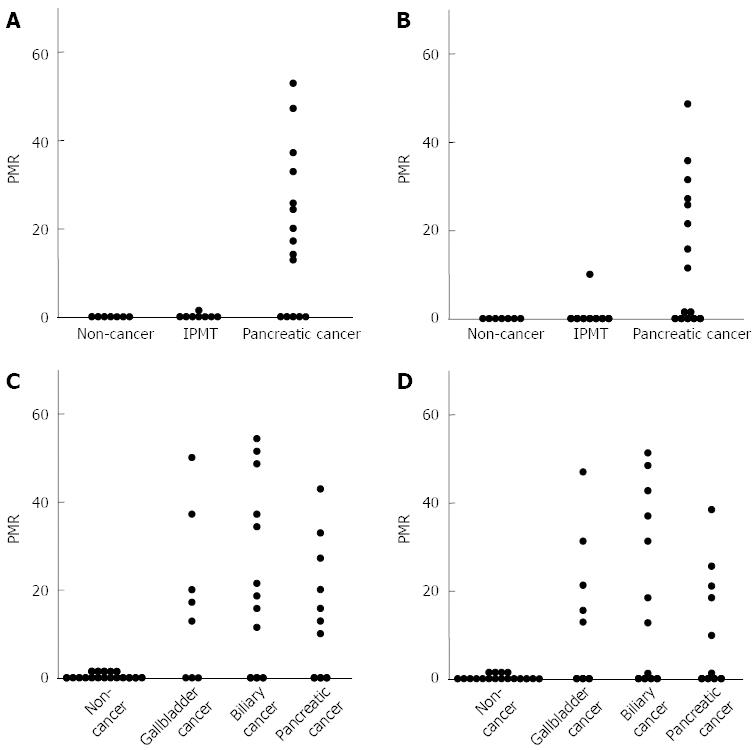
Figure 3 Analysis of methylation levels of ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal esterase L1 and runt-related transcription factor 3 using pancreatobiliary fluids.
Comparison of the ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal esterase L1 (UCHL1) (A) and runt-related transcription factor 3 (RUNX3) (B) methylation levels in pancreatic fluids between pancreatic cancer and noncancerous pancreatic disease; Comparison of the UCHL1 (C) and RUNX3 (D) methylation levels in biliary fluids between pancreatobiliary cancer and noncancerous pancreatobiliary disease. PMR: Percentage of methylated reference.
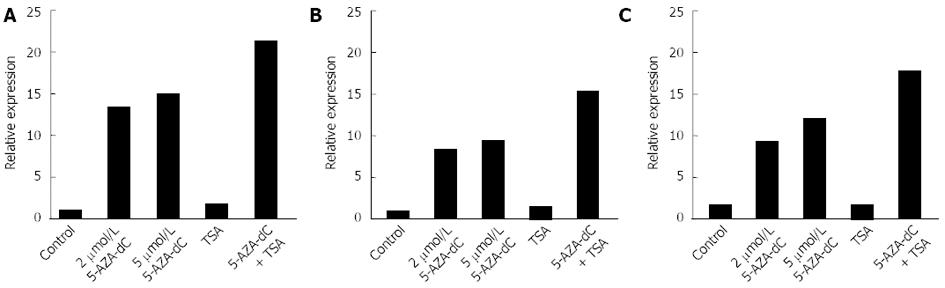
Figure 4 Reactivation of ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal esterase L1 by 5-AZA-2’-deoxycytidine and/or Trichostatin A treatment in pancreatic and biliary cancer cell lines.
A: PK-1 cells; B: PK45P cells; C: TGBC1TKB cells. To examine the roles of CpG methylation and histone deacetylation in the silencing of ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal esterase L1, cancer cells were treated with 2 or 5 μmol/L 5-AZA-2’-deoxycytidine (5-AZA-dC) for 72 h or 100 nmol/L Trichostatin A (TSA) for 24 h. The cells were also treated with 2 μmol/L 5-AZA-dC for 72 h, followed by 100 nmol/L TSA for an additional 24 h.
- Citation: Kato N, Yamamoto H, Adachi Y, Ohashi H, Taniguchi H, Suzuki H, Nakazawa M, Kaneto H, Sasaki S, Imai K, Shinomura Y. Cancer detection by ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal esterase L1 methylation in pancreatobiliary fluids. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(11): 1718-1727
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i11/1718.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1718