Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2011; 17(23): 2829-2837
Published online Jun 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2829
Published online Jun 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2829
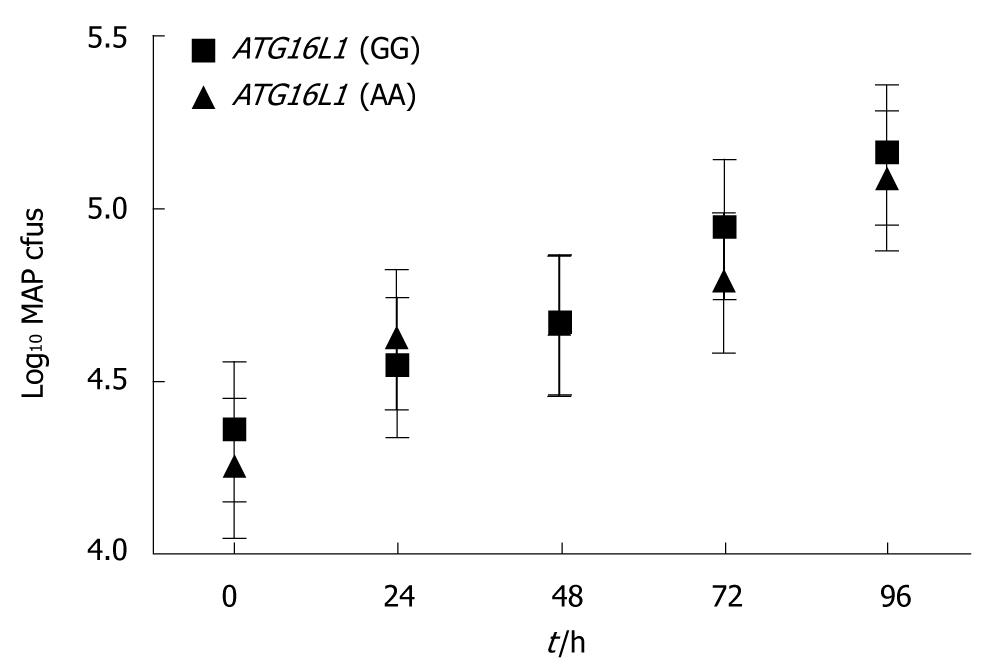
Figure 1 Effect of ATG16L1 T300A variant on mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis numbers.
Time course of mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP) growth in the context of the ATG16L1 1138 G > A variant. Monocytes were derived from subjects homozygous for either ATG16L1 allele and carrying NOD2 wild-type alleles (n = 6 for each group). MAP growth is expressed as colony forming units (cfu).
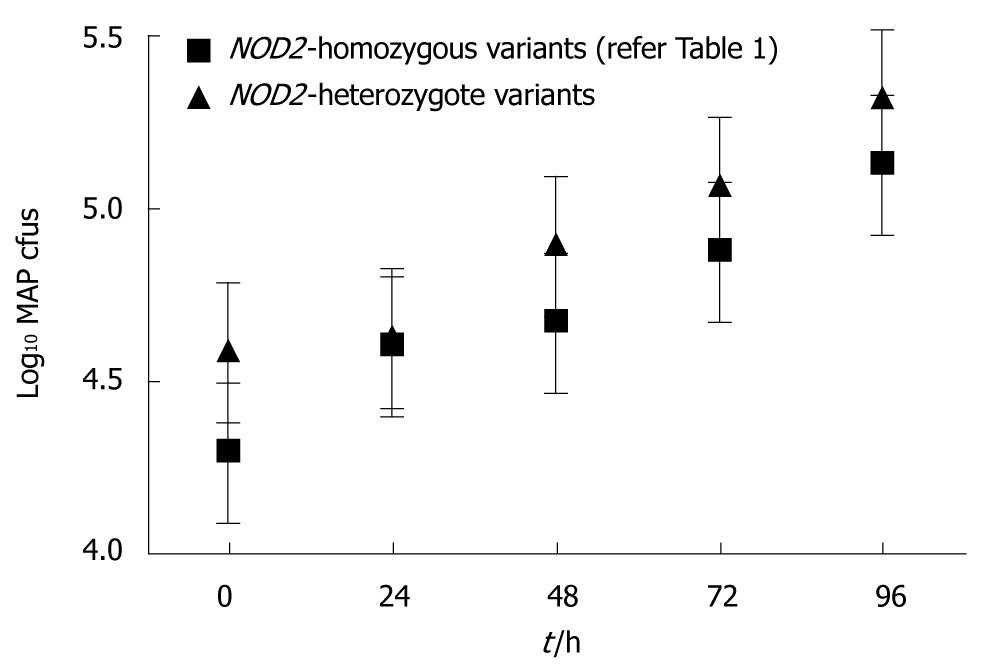
Figure 2 Effect of NOD2 variants on mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis numbers.
Time course of mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP) growth in the context of NOD2 genetic variation. Monocytes were derived from subjects homozygous for the ATG16L1 1138G allele and with/without NOD2 genetic variants (n = 6 for each group). MAP growth is expressed as colony forming units (cfu).
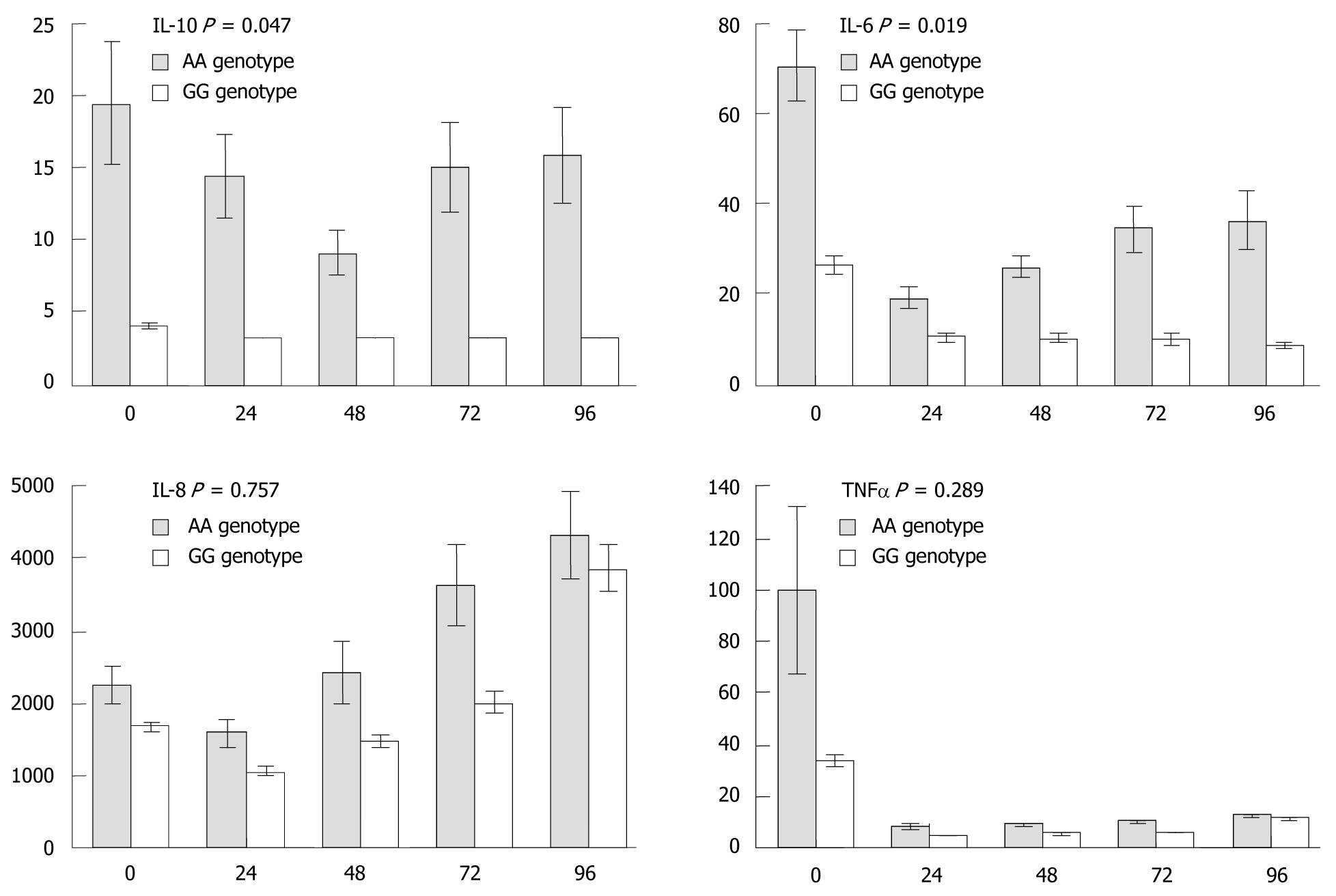
Figure 3 Effect of the ATG16L1 T300A polymorphism on expression of cytokines following challenge with mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis.
Cytokine concentrations are in pg/mL. Results are the means (and standard error of the mean) of triplicate samples from patients in Table 1. P-values are derived from repeated measures ANOVA testing for the effect of genotype on cytokine expression. Fixed effects for time (categorical variable) and ATG16L1 genotype, random effect for subject. IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
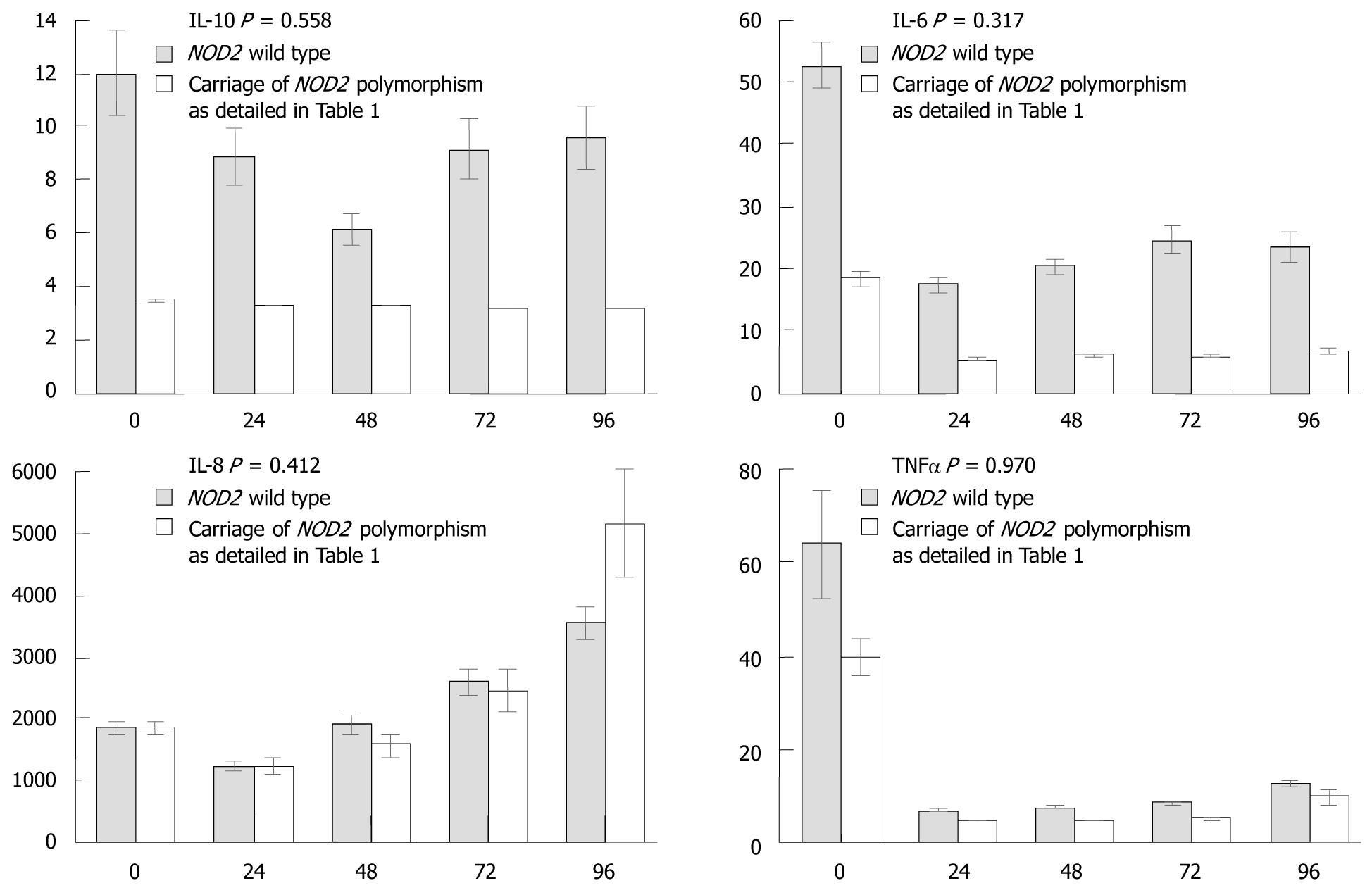
Figure 4 Effect of NOD2 polymorphisms on expression of cytokines following challenge with mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis.
Cytokine concentrations are in pg/mL. Results are the means (and standard error of the mean) of triplicate samples from patients in Table 1. P-values are derived from repeated measures ANOVA testing for the effect of genotype on cytokine expression. Fixed effects for time (categorical variable) and NOD2 genotype, random effect for subject. IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
-
Citation: Glubb DM, Gearry RB, Barclay ML, Roberts RL, Pearson J, Keenan JI, McKenzie J, Bentley RW.
NOD2 andATG16L1 polymorphisms affect monocyte responses in Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(23): 2829-2837 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i23/2829.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2829