Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2009; 15(45): 5746-5750
Published online Dec 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5746
Published online Dec 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5746
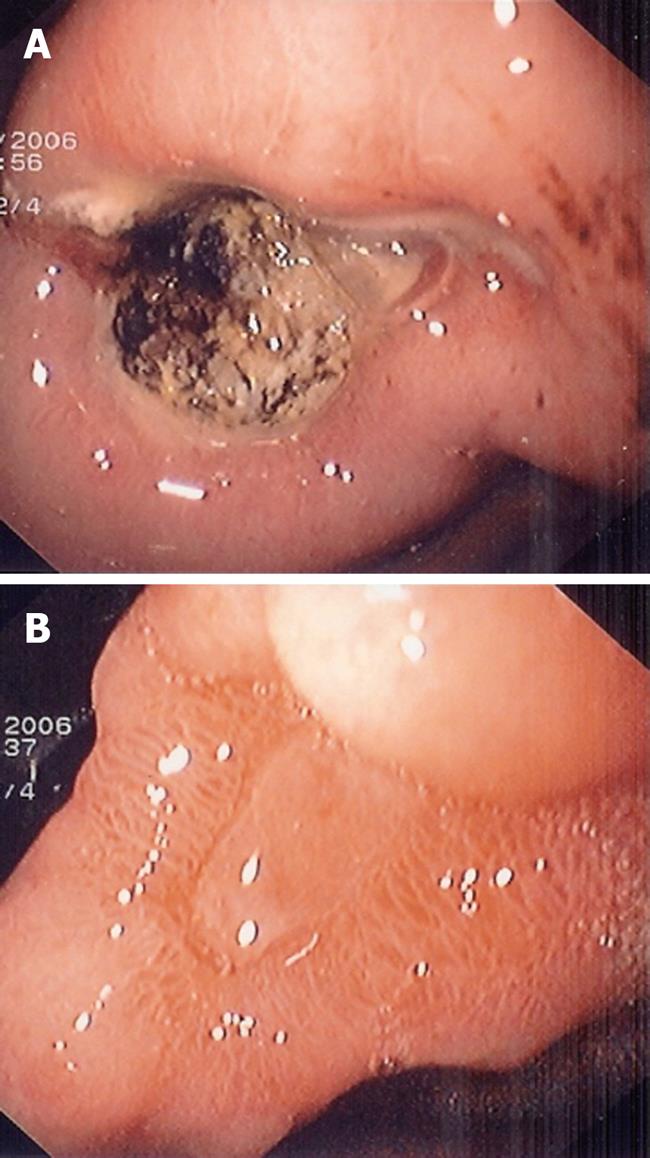
Figure 1 Endoscopic aspect of the gastric lesion before and after Helicobacter pylori (H pylori) eradication.
A: Oesophagogastroduodenoscopy shows a large ulcer at the angularis; B: Ulcer healing 3 mo after H pylori eradication.
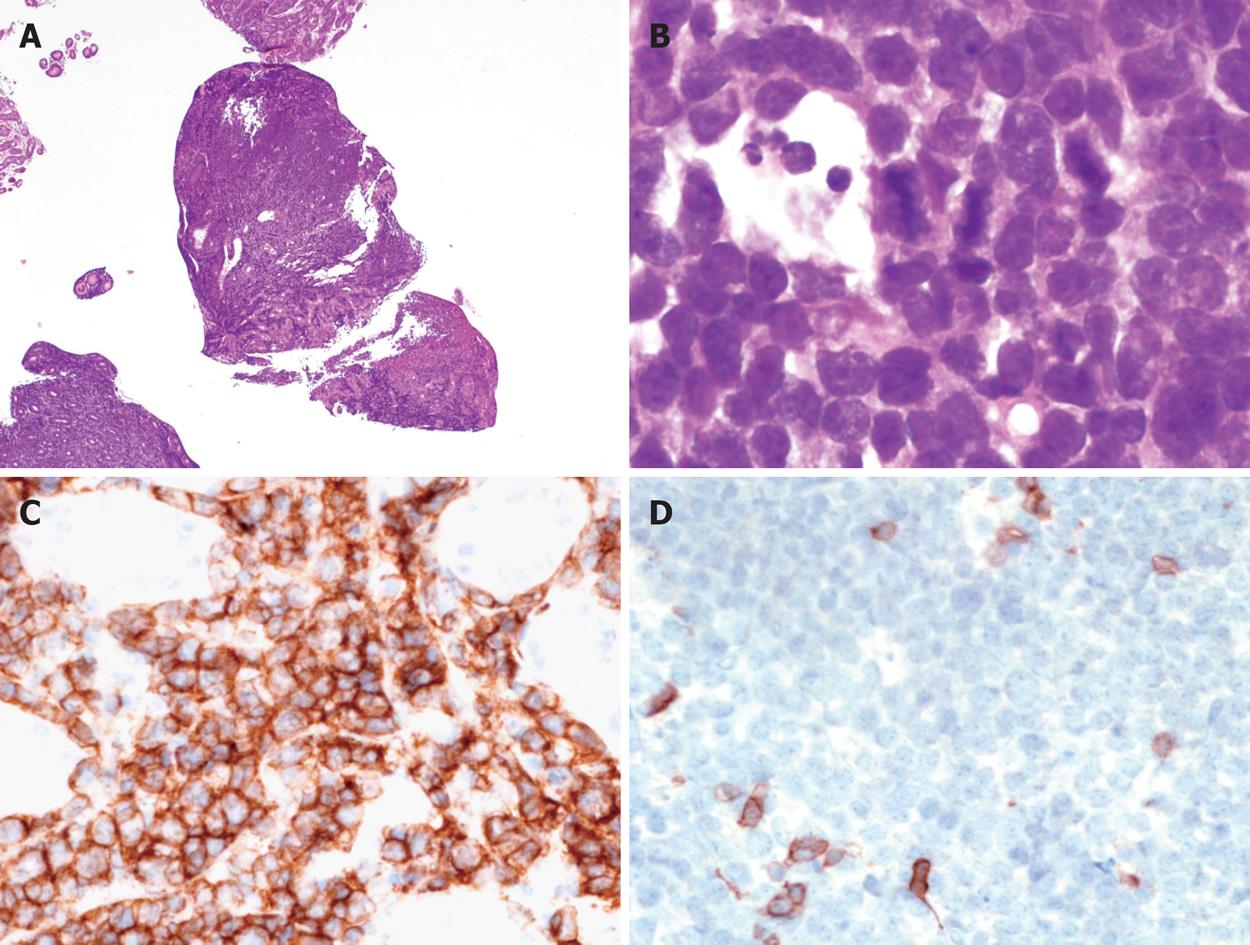
Figure 2 Morphological and immunohistochemical features of the disease.
A: At low magnification, the gastric mucosa is diffusely infiltrated by medium sized lymphoid cells (HE, × 25); B: Tumour cells are medium sized with scarce cytoplasm, round nuclei and fine chromatin; numerous mitoses are observed; tangible body macrophages are present (HE, × 1000); C: Immunohistochemistry shows that the tumour cells are CD20+, × 400; D: CD5-, × 400.
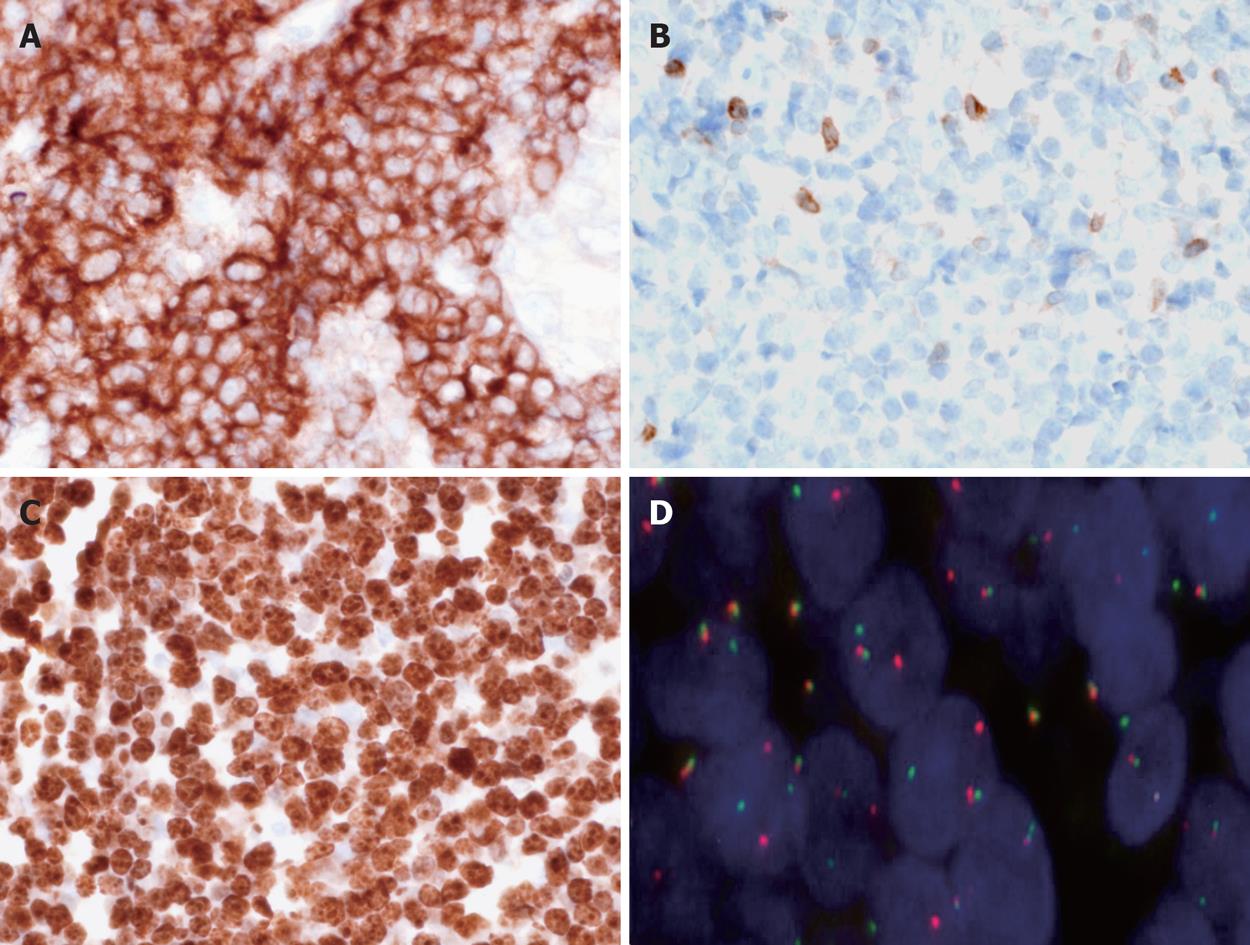
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical and cytogenetic features of the disease.
A: Tumour cells are CD10+, × 400; B: BCL2-, × 400; C: 100% of tumour cells are Ki67+, × 400; D: Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) performed with split signal FISH DNA probes for c-MYC revealed distinct red and green split signals in many nuclei, consistent with c-MYC gene rearrangement, beside yellow fusion signals for the non-rearranged alleles, × 1000.
-
Citation: Baumgaertner I, Copie-Bergman C, Levy M, Haioun C, Charachon A, Baia M, Sobhani I, Delchier JC. Complete remission of gastric Burkitt’s lymphoma after eradication of
Helicobacter pylori . World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(45): 5746-5750 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i45/5746.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.5746