Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2009; 15(25): 3161-3165
Published online Jul 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3161
Published online Jul 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3161
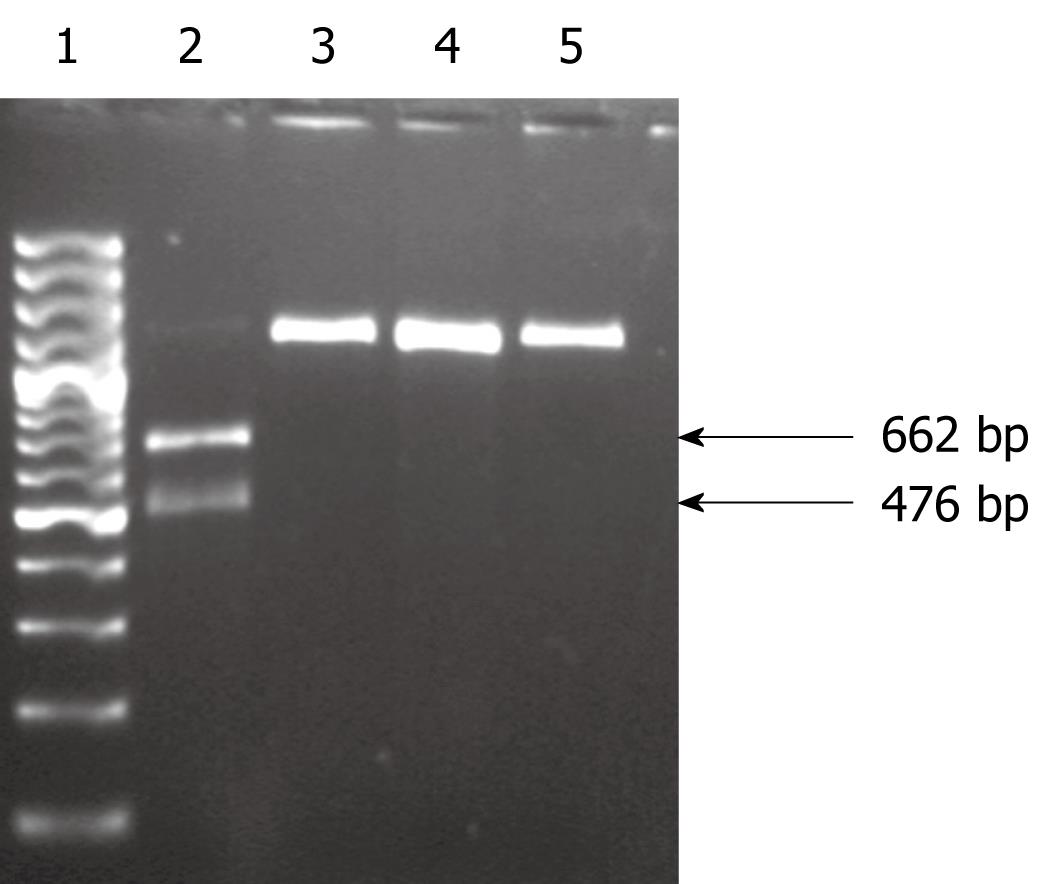
Figure 1 RFLP analysis of 23S rRNA to detect the A2142G mutation using MboII restriction enzyme.
Lane 1: 100 bp DNA ladder; Lane 2: Digestion product of resistant isolate with A2142G mutation, showing two fragments of 662 and 476 bp; Lanes 3 and 4: Digestion products of two clarithromycin-resistant isolates with A2143G mutation; Lane 5: Digestion product of a clarithromycin-sensitive isolate with T2182C mutation.
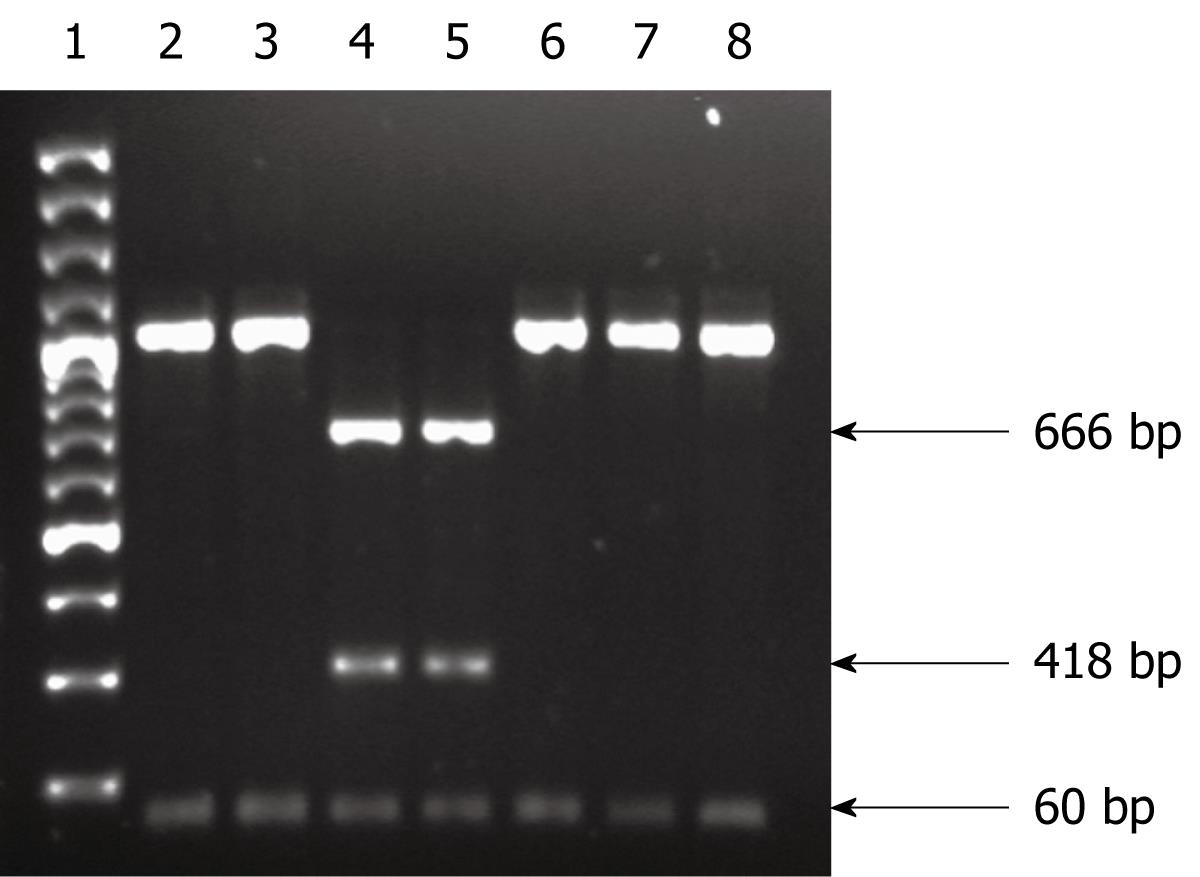
Figure 2 RFLP analysis of 23S rRNA to detect the A2143G using BsaI restriction enzyme.
Lane 1: 100 bp DNA ladder; Lanes 2 and 3: Digestion products of two clarithromycin-resistant isolates with A2142G mutation; Lanes 4 and 5: Restriction analysis of resistant isolates with A2143G mutation, showing three fragments of sizes 666, 418 and 60 bp; Lanes 6-8: Digestion products of clarithromycin-sensitive isolates.
-
Citation: Ahmad N, Zakaria WR, Abdullah SA, Mohamed R. Characterization of clarithromycin resistance in Malaysian isolates of
Helicobacter pylori . World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(25): 3161-3165 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i25/3161.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.3161