Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2009; 15(14): 1738-1743
Published online Apr 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1738
Published online Apr 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1738
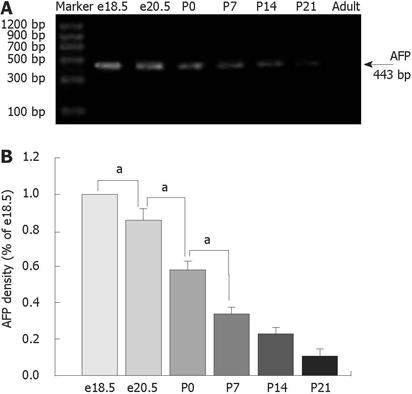
Figure 1 Expression of AFP mRNA using RT-PCR analysis in the developing rat colons as indicated in lanes e18.
5, e20.5, P0, P7, P14, P21 and adult rats. The position of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left. A: The highest levels of AFP mRNA were detected in colons of rats at e18.5 and declined steadily during rat development and were undetected in adult rats; B: Results are indicated in percentages above the e18.5 value and are representative of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05 vs e18.5, e20.5 and P0, respectively.
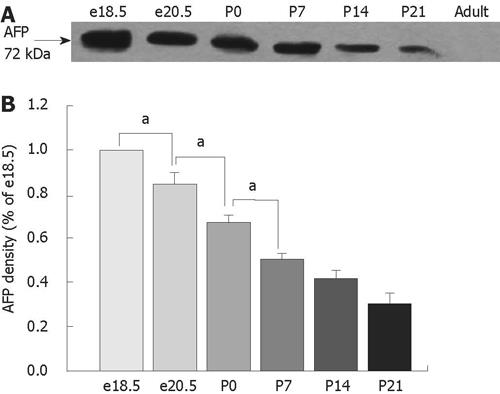
Figure 2 Expression of AFP protein using Western blot analysis in the developing rat colons as indicated in lanes e18.
5, e20.5, P0, P7, P14, P21 and adult rats. A: Western blot analysis using AFP (C-19), an affinity purified goat polyclonal antibody against a peptide mapping at the C-terminus of AFP, revealed a 72-kDa isoform. The highest levels of AFP protein were detected in colons of rats at e18.5 and declined steadily during rat development and were undetected in adult rats. B: Results are indicated in percentage above the e18.5 value and are representative of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05 vs e18.5, e20.5 and P0, respectively.
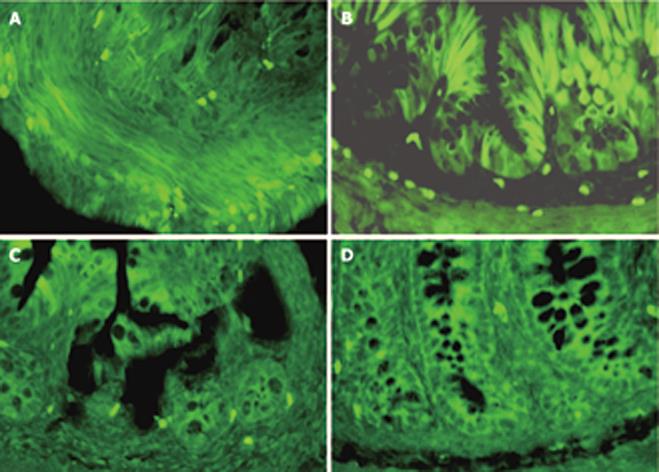
Figure 3 Immunofluorescence localization of AFP in the developing rat colons.
A: In e18.5, AFP positive staining can be detected in the epithelium and mesenchymal tissues; B: At P0, positive cells were located at the base of the crypts and scattered on the epithelium; C, D: Only a few positive cells restricted to the base of the crypts between 14 and 21 d, and no positive cells can be detected in adult rat colons. (× 200). C, D: Only a few positive cells restricted to the base of the crypts between 14 and 21 d, and no positive cells can be detected in adult rat colons. (× 200).
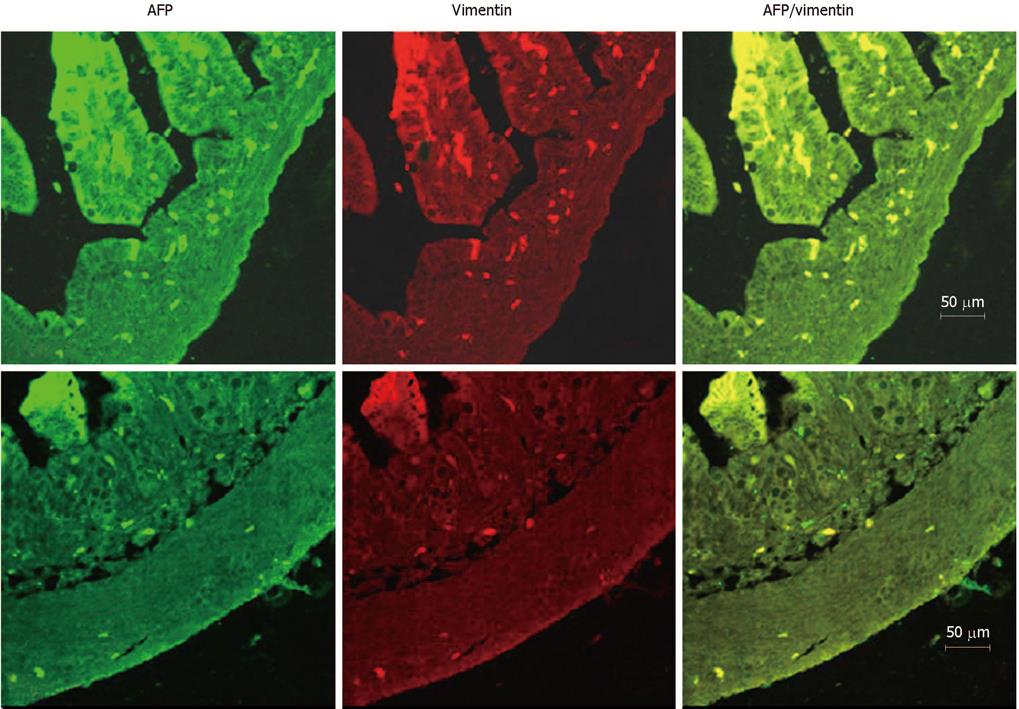
Figure 4 Immunofluorescence localization of AFP and vimentin in the developing rat colons.
Labeling by the AFP antibody was detected with an FITC (green)-labeled secondary antibody. Labeling of vimentin was detected with a rhodamine- (red)-labeled secondary antibody on the same section. The overlap of AFP (green) and vimentin (red) labeling appeared orange in color. Double-labeling revealed complete localization of AFP and vimentin in the same colon cells at both e20.5 and P7. A: e20.5; B: P7.
- Citation: Liu XY, Dong D, Sun P, Du J, Gu L, Ge YB. Expression and location of α-fetoprotein during rat colon development. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(14): 1738-1743
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i14/1738.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.1738