Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2009; 15(14): 1677-1689
Published online Apr 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1677
Published online Apr 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1677
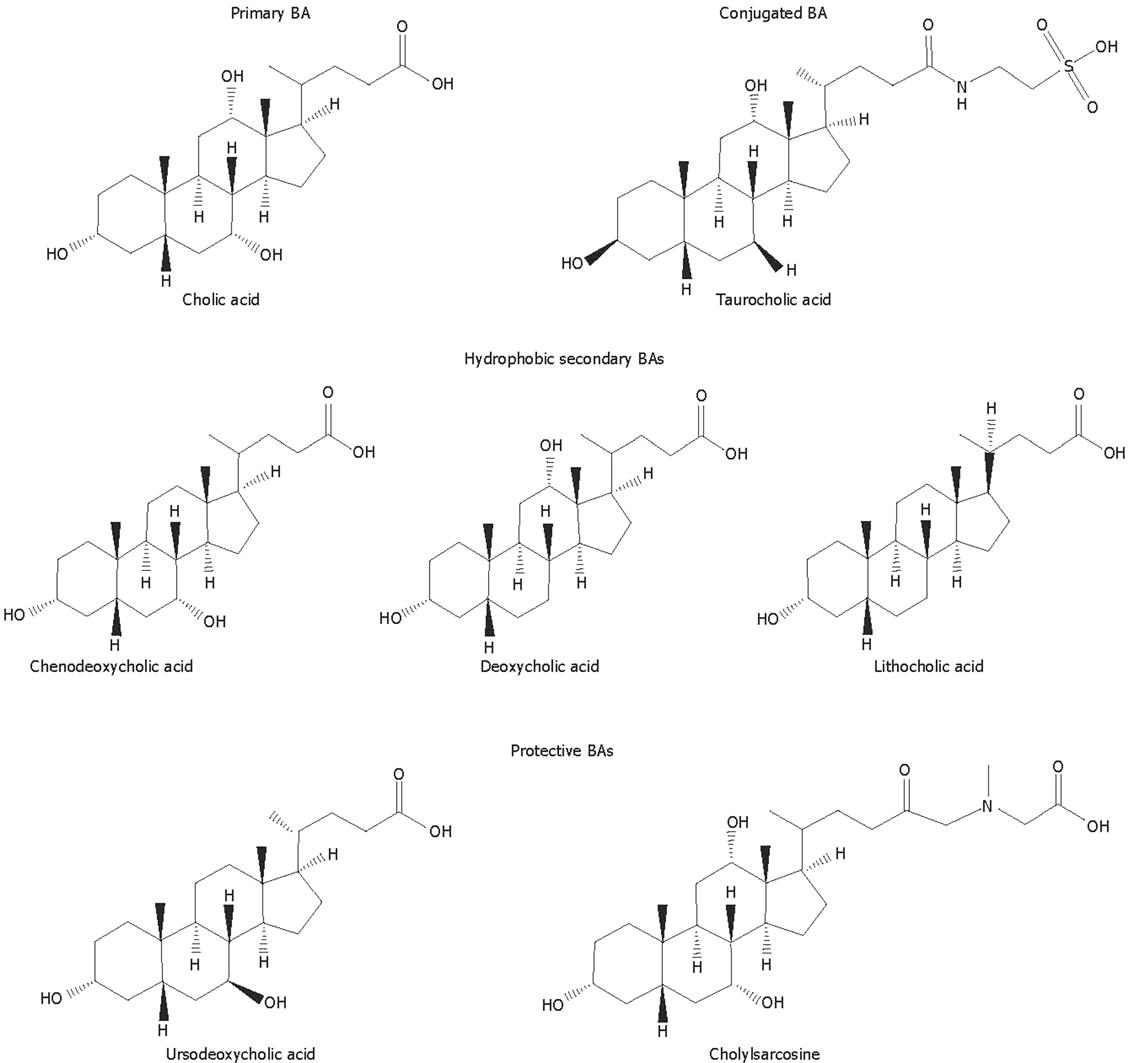
Figure 1 Molecular structures of different potentially toxic or protective natural bile acids and synthetic bile acid analogues.
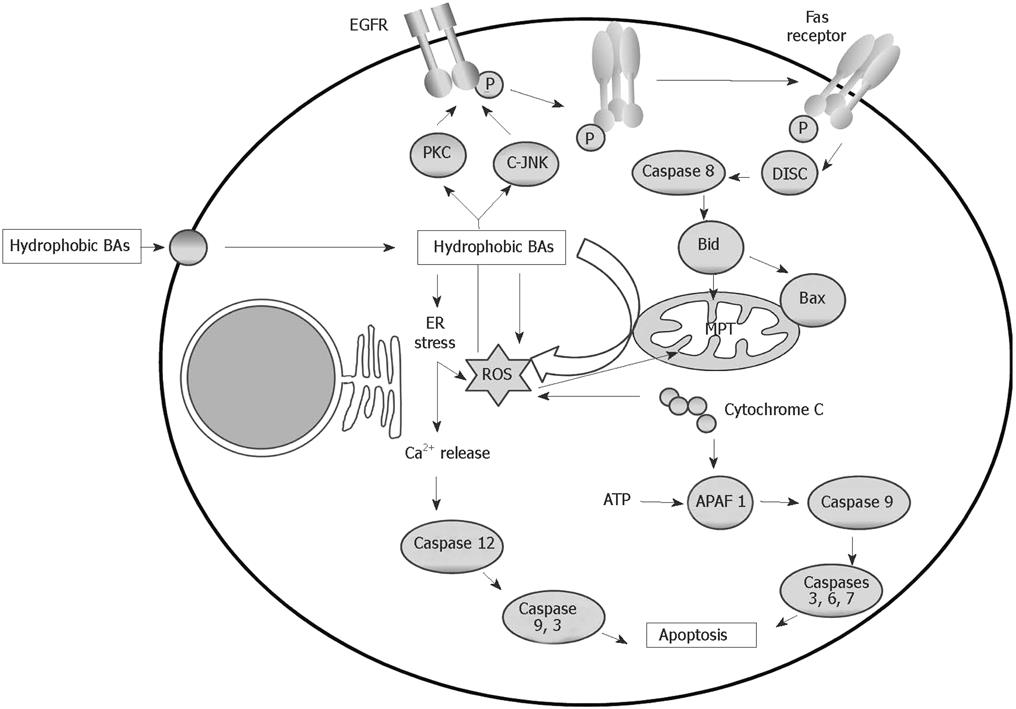
Figure 2 Intracellular mechanisms of bile acid-induced hepatocyte apoptosis.
In this schema, further transduction after activation of death receptors and formation of the DISC, direct mitochondrial toxicity and ER stress are implicated.
- Citation: Perez MJ, Briz O. Bile-acid-induced cell injury and protection. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(14): 1677-1689
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i14/1677.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.1677