Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2006; 12(4): 588-594
Published online Jan 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i4.588
Published online Jan 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i4.588
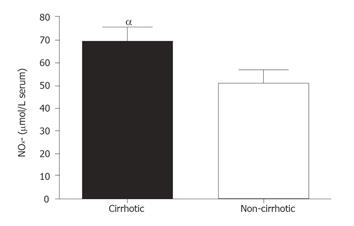
Figure 1 Total NO metabolites in plasma were measured from 20 cirrhotic patients and 20 non-cirrhotic controls.
Cirrhotic patients NOx- levels were markedly higher at 69.72 ± 6.31μmol/L serum; while non-cirrhotic patients NOx- levels were lower at 50.83 ± 5.67μmol/L serum. αP < 0.05.
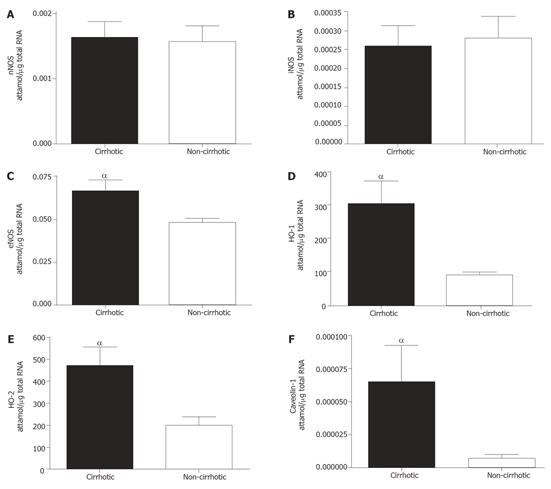
Figure 2 Differential mRNA expression in cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic patient livers were measured via competitive PCR.
A, B: nNOS and iNOS showed no significant change; C, D, E, F: eNOS, HO-1, HO-2 and Caveolin-1 respectively showed significant increase when compared to non-cirrhotic mRNA. αP < 0.05.
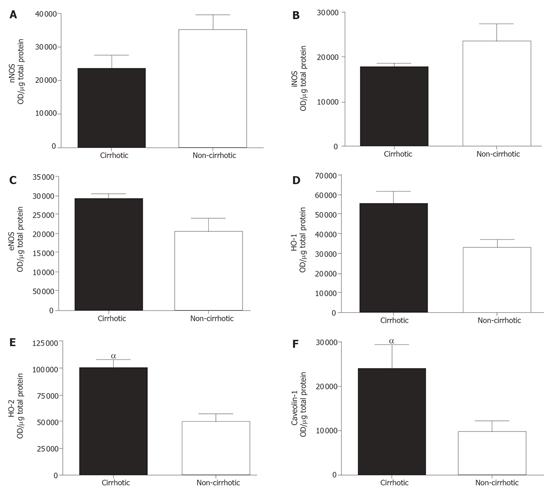
Figure 3 Protein expression in cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic patient livers were semi-quantitated via Western Blot.
Results were tabulated and presented. Both nNOS (A) and iNOS (B) were unchanged. eNOS (C), HO-1(D), HO-2(E) and Caveolin-1(F) protein expression were significantly increased in cirrhotic tissue. OD represents optical density. αP < 0.05.
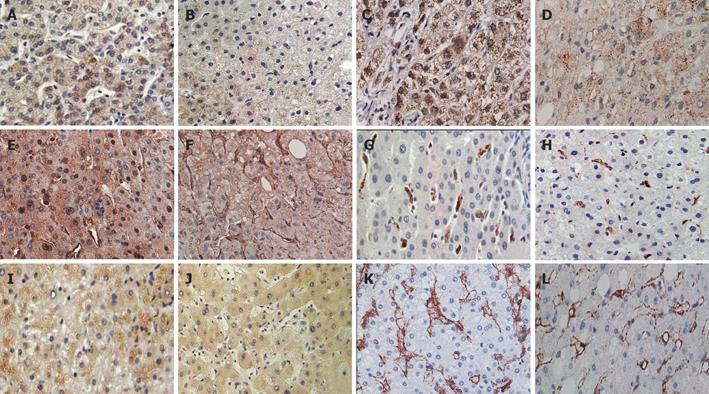
Figure 4 Immunohistochemistry of cirrhotic livers sections (left panel) and non-cirrhotic sections(right panel).
A and B, show no difference in nNOS localization; likewise with iNOS as shown in C and D. eNOS was found to have translocated mainly to the nuclei in cirrhotic sections as evidenced in E, but found in hepatocyte cytoplasm and endothelial cells in non-cirrthotic as in F. In G and H, HO-1 is clearly found in macrophages with marked increase in cirrhotic sections (G). HO-2 was more highly expressed in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes in cirrhotic (I) than non-cirrhotic (J) tissues. Cirrhotic liver in K shows higher immunoreactivity to caveolin-1 that that of non-cirrhotic liver in L. In all IHC, monoclonal antobodies were used.
- Citation: Goh BJ, Tan BT, Hon WM, Lee KH, Khoo HE. Nitric oxide synthase and heme oxygenase expressions in human liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(4): 588-594
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i4/588.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i4.588