Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2006; 12(30): 4859-4865
Published online Aug 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4859
Published online Aug 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4859
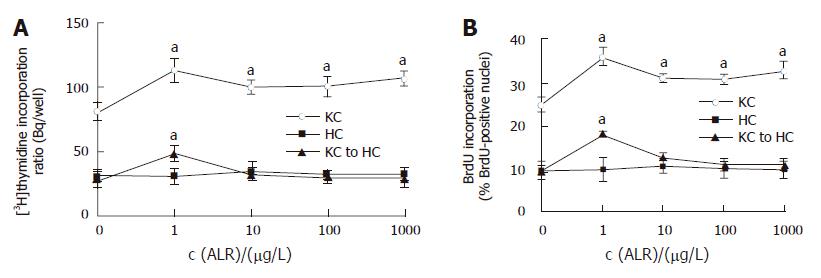
Figure 1 Effects of ALR on proliferation of Kupffer cells and hepatocytes.
A: DNA replication; B: BrdU-positive nuclei. KC: Kupffer cells; HC: Hepatocytes; KC to HC: Hepatocytes conditioned by Kupffer cells. aP < 0.05 vs control, n = 3.
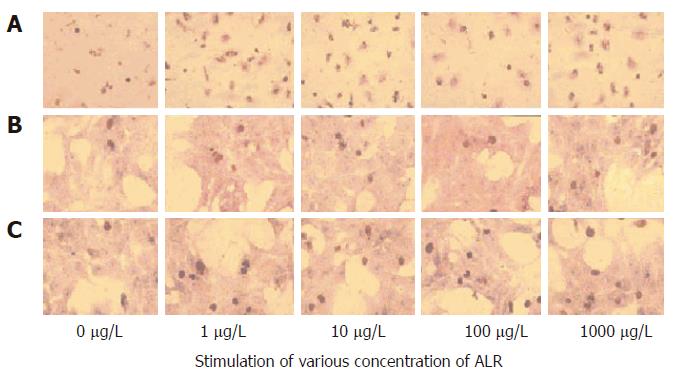
Figure 2 BrdU immunohistochemistry.
The nuclei of BrdU-positive cells were stained brown. A: Kupffer cells; B: Hepatocytes; C: Hepatocytes conditioned by Kupffer cells (× 100).
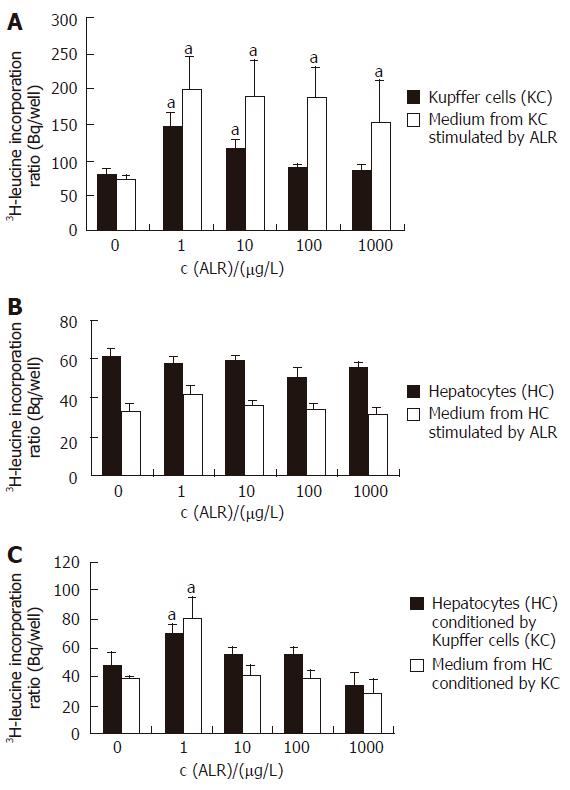
Figure 3 3H-leucine incorporation assay.
A: Kupffer cells and associated medium; B: Hepatocytes and associated medium; C: Hepatocytes conditioned by Kupffer cells and associated medium. aP < 0.05 vs control, n = 3.
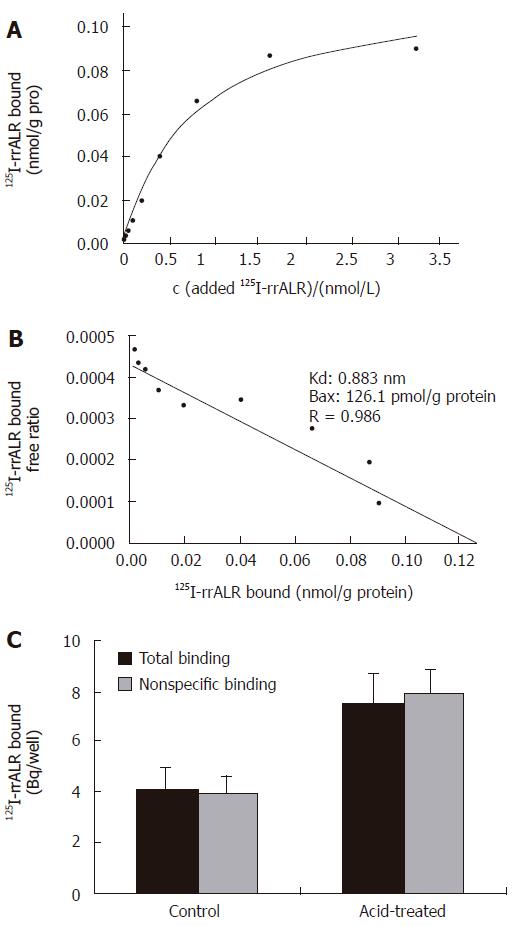
Figure 4 125I-rrALR binding assay.
A: Saturation cures of 125I-rrALR binding to its receptor on Kupffer cells; B: Scatchard plot of the ALR receptor on Kupffer cells; C: Binding of ALR to cultured hepatocytes (mean ± SD, n = 3).
- Citation: Wang CP, Zhou L, Su SH, Chen Y, Lu YY, Wang F, Jia HJ, Feng YY, Yang YP. Augmenter of liver regeneration promotes hepatocyte proliferation induced by Kupffer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(30): 4859-4865
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i30/4859.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4859