Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2006; 12(14): 2293-2296
Published online Apr 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i14.2293
Published online Apr 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i14.2293
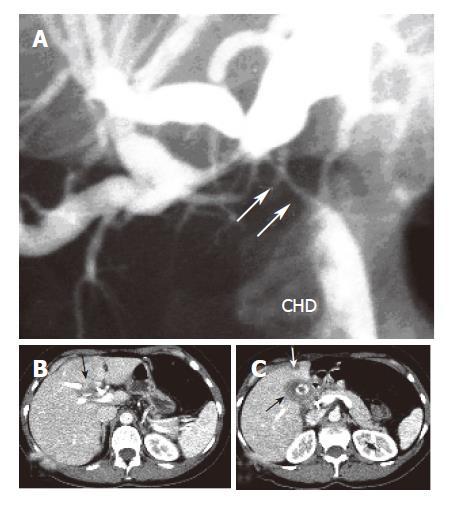
Figure 1 Proximal obstruction (arrows) of the common hepatic bile duct (CHD) with upstream dilatation of both left and right intrahepatic bile ducts (A), a soft tissue mass at the hepatic hilum (B), and thickened gallbladder wall (black arrow) with a concretion and hepatic lesion in liver segment 4 (C).
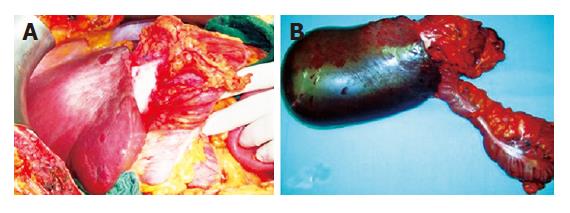
Figure 2 Intraoperative finding in situ (A) and surgical specimen ex situ (B).
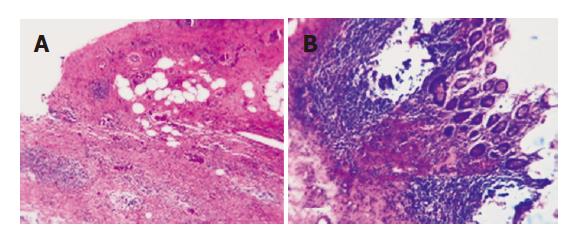
Figure 3 Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis (A) and xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis involving the wall of the transverse colon (B).
There is destruction of the submucosa and muscular coat of the transverse colon by extensive macrophage infiltrates, the mucosa is intact and exhibits no cellular atypia (HE, 200x).
- Citation: Spinelli A, Schumacher G, Pascher A, Lopez-Hanninen E, Al-Abadi H, Benckert C, Sauer IM, Pratschke J, Neumann UP, Jonas S, Langrehr JM, Neuhaus P. Extended surgical resection for xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis mimicking advanced gallbladder carcinoma: A case report and review of literature. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(14): 2293-2296
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i14/2293.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i14.2293