Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 15, 2004; 10(4): 491-496
Published online Feb 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i4.491
Published online Feb 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i4.491
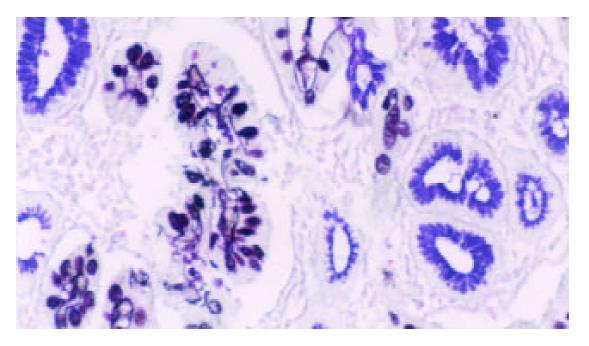
Figure 1 Type III intestinal metaplasia.
Blue and brown stained mucin in cells. HID/AB/PAS stain × 200.
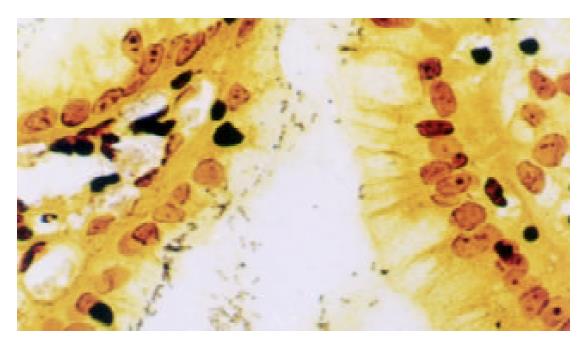
Figure 2 Dark-brown stained bacillary structures of positive H pylori in epithelium of mucosa.
Warthin-Starry stain × 400.
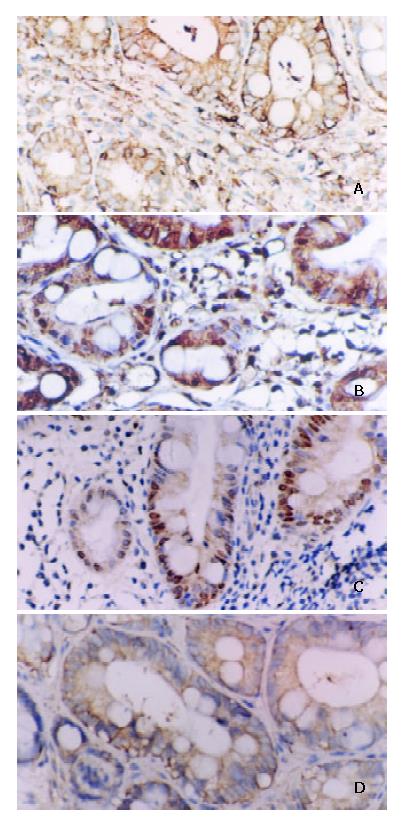
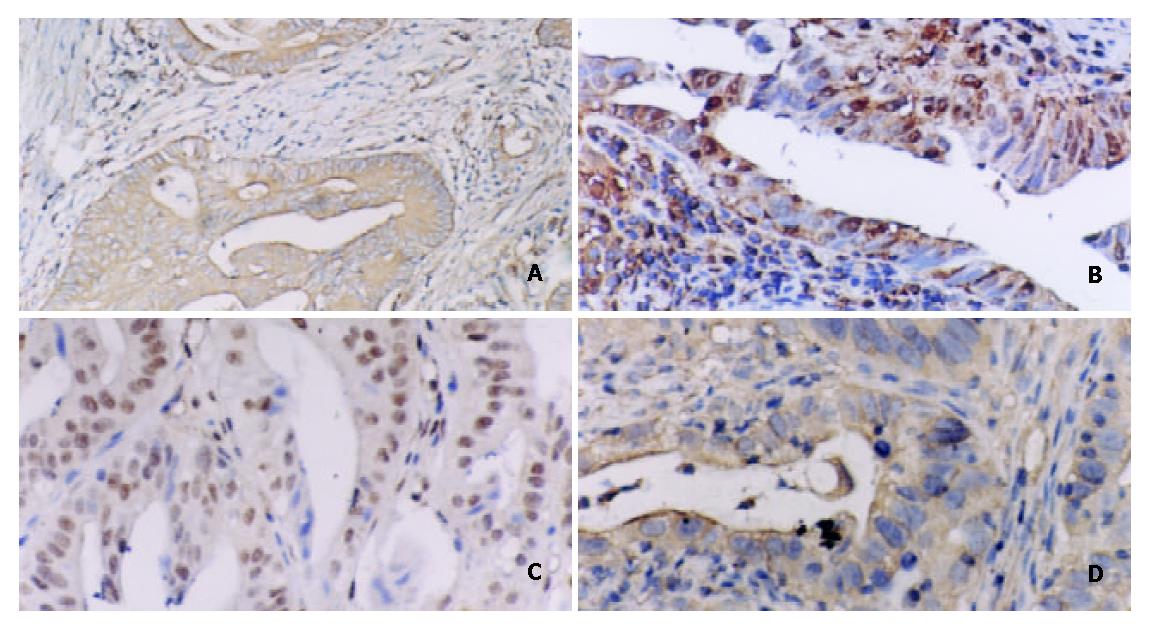
Figure 3 A: Positive expression of NF-κB/p65 in IM.
Some inflammatory cells showed plasmatic stain. Immunohistochemical stain × 200. B: Positive expression of cyclinD1 in IM. Some inflammatory cells showed nuclear and plasmatic stains. Immunohistochemical stain × 200. C: Positive expres-sion of c-myc in IM. Some inflammatory cells showed nuclear and plasmatic stains. Immunohistochemical stain × 200. D: Positive expression of bcl-xl in IM. Some inflammatory cells showed plasmatic stain. Immunohistochemical stain × 200.
Figure 4 A: Positive expression of NF-κB/p65 in DYS.
Some inflammatory cells showed plasmatic stain. Immunohistochemical stain × 200. B: Positive expression of c-myc in DYS III. Some inflammatory cells showed nuclear and plasmatic stains. Immunohistochemical stain × 400.
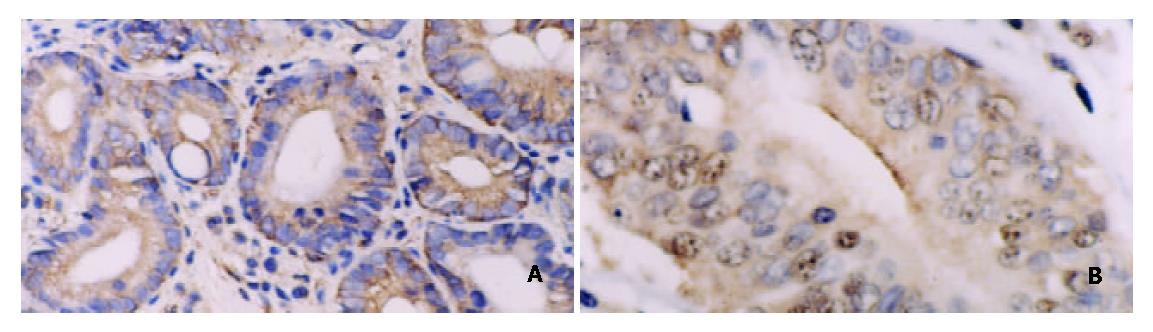
Figure 5 A: Positive expression of NF-κB/p65 in intestinal type gastric carcinoma.
Immunohistochemical stain × 200. B: Positive expression of c-myc in intestinal type gastric carcinoma. Immunohistochemical stain × 200. C: Positive expression of cyclinD1 in intestinal type gastric carcinoma. Immunohistochemical stain × 200. D: Positive expression of bcl-xl in intestinal type gastric carcinoma. Immunohistochemical stain × 400.
- Citation: Yang GF, Deng CS, Xiong YY, Gong LL, Wang BC, Luo J. Expression of nuclear factor-kappa B and target genes in gastric precancerous lesions and adenocarcinoma: Association with Helicobactor pylori cagA (+) infection. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(4): 491-496
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i4/491.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i4.491