Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 15, 2004; 10(14): 2019-2023
Published online Jul 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2019
Published online Jul 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2019
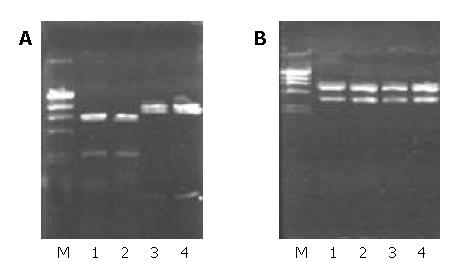
Figure 1 Identification of KAI1 recombinant plasmids digested by Sal I and Xba I.
M: λDNA/Hind III marker (23.13, 9.42, 6.56, 4.36, 2.32 and 2.02 kb), 1, 2: pCI-KAI1, 3, 4: pCI-anti-KAI1.
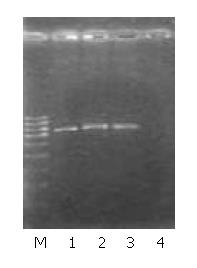
Figure 2 Identifications of gene integration by neo gene amplification.
M: Ladder marker (1.0, 0.9, 0.8, 0.7, 0.6, 0.5, 0.4 and 0.3 kb), 1: MHCC97-H-S (790 bp), 2: MHCC97-H-AS (790 bp), 3: MHCC97-H-pCI (790 bp), 4: MHCC97-H.
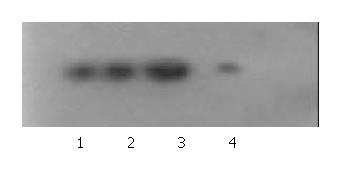
Figure 3 KAI1 protein expressions in different cells revealed by Western blot.
1: MHCC97-H, 2: MHCC97-H-pCI, 3: MHCC97-H-S, 4: MHCC97-H-AS.
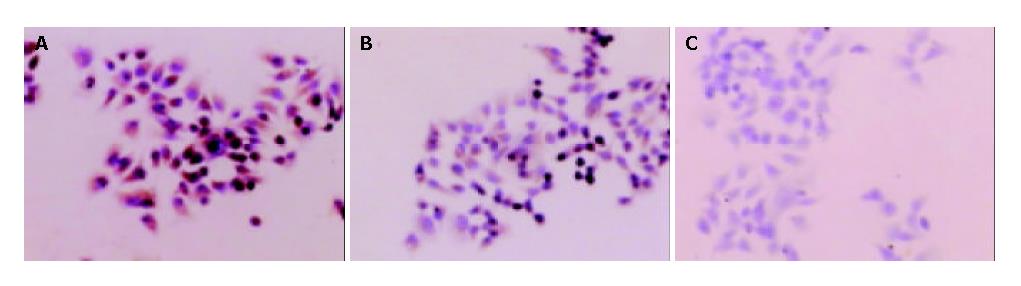
Figure 4 KAI1 protein expression in different cells revealed by immunocytochemistry (SP × 400).
A: MHCC97-H-S, B: MHCC97-H, C: MHCC97-H-AS.
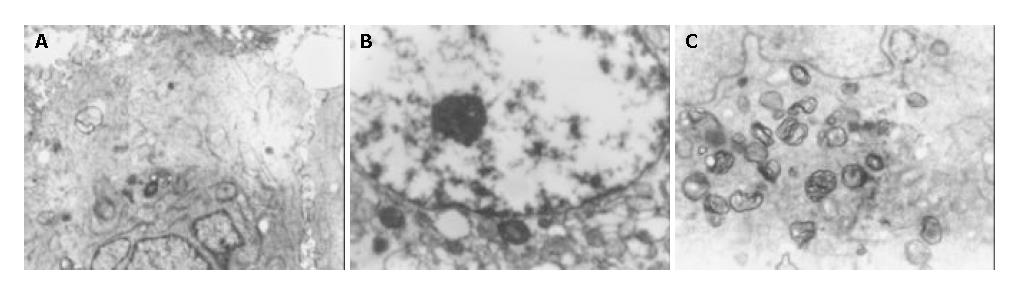
Figure 5 Ultrastrucrtural changes in transfected cells.
× 6200. A: MHCC97-H-S cells, fewer RER and mitochondria, B: MHCC97-H-AS cells, more mitochondria, expanded endoplasmic reticulum, C: MHCC97-H-AS cells, myelin-sheath-like changes of mitochondria.
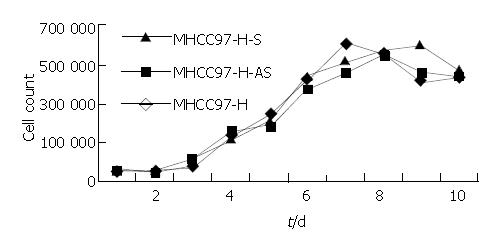
Figure 6 Growth curves of different cells.
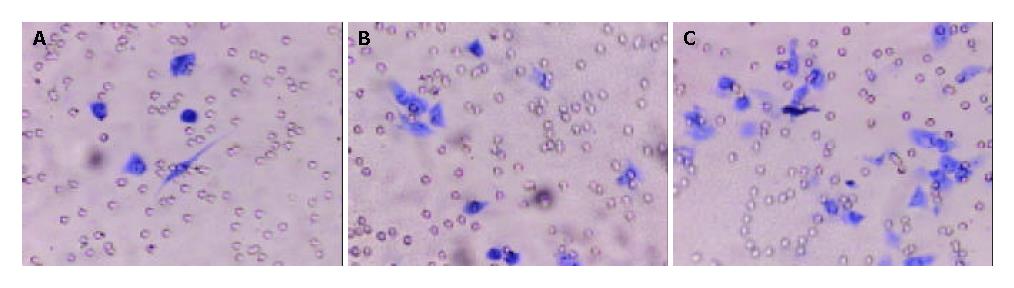
Figure 7 Penetrated cells (blue) in Boyden Chamber test.
Giemsa × 400. A: MHCC97-S, B: MHCC97-H, C: MHCC97-H-AS.
- Citation: Si SH, Yang JM, Peng ZH, Luo YH, Zhou P. Effects of KAI1 gene on growth and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma MHCC97-H cells. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(14): 2019-2023
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i14/2019.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2019