Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 1, 2004; 10(11): 1555-1559
Published online Jun 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i11.1555
Published online Jun 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i11.1555
Figure 1 Putative amino-acid sequence of LAPTM4B.
The four transmembrane domains are shadowed with gray color. Two translation initiation sites are thick black. Putative SH3 ligand is indicated by thick underlining. The sequence containing 10 amino acid residues (28aa-37aa or 232aa-241aa) and used as immunogen is wavy underlined. PKC-P, cAMP-P, cGMP-P, CK2-P, Tyr-P: various phosphorylation sites; G: N-glycosylation site; M: myristylation site.
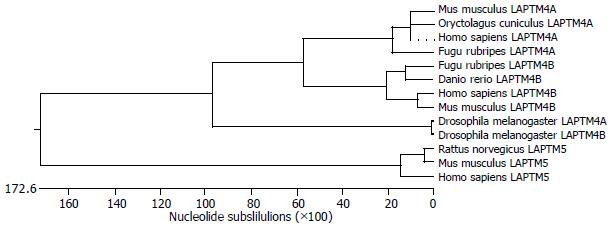
Figure 2 Phylogenic tree of LAPTM4B.
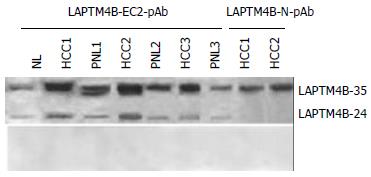
Figure 3 Expressions of LAPTM4B proteins in HCC tissues identified by Western blot with various antibodies.
Top: Western Blot profiles performed with anti serum. LAPTM4B-EC2-pAb: polyclonal antibody directing against the epitope localized at the EC2 domain between the 3rd and 4th transmembrane regions of LAPTM4B. LAPTM4B-N28-37-pAb: polyclonal antibody directing against the epitope localized at the N-terminal region of LAPTM4B. Bottom: Western blot profiles performed with pre-immune serum.
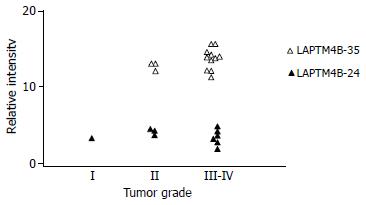
Figure 4 Correlation between LAPTM4B-35 protein expression and pathological grade of HCC.
Figure 5 Expression of LAPTM4B proteins in various cell lines shown via Western blot with LAPTM4B-EC2-pAb.
Top: Western blot profiles performed with LAPTM4B-EC2-pAb. Bottom: Western blot profiles performed with pre-immune serum.
- Citation: Liu XR, Zhou RL, Zhang QY, Zhang Y, Jin YY, Lin M, Rui JA, Ye DX. Structure analysis and expressions of a novel tetratransmembrane protein, lysosoma-associated protein transmembrane 4 β associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(11): 1555-1559
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i11/1555.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i11.1555