Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Orthop. Nov 18, 2023; 14(11): 827-835
Published online Nov 18, 2023. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v14.i11.827
Published online Nov 18, 2023. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v14.i11.827
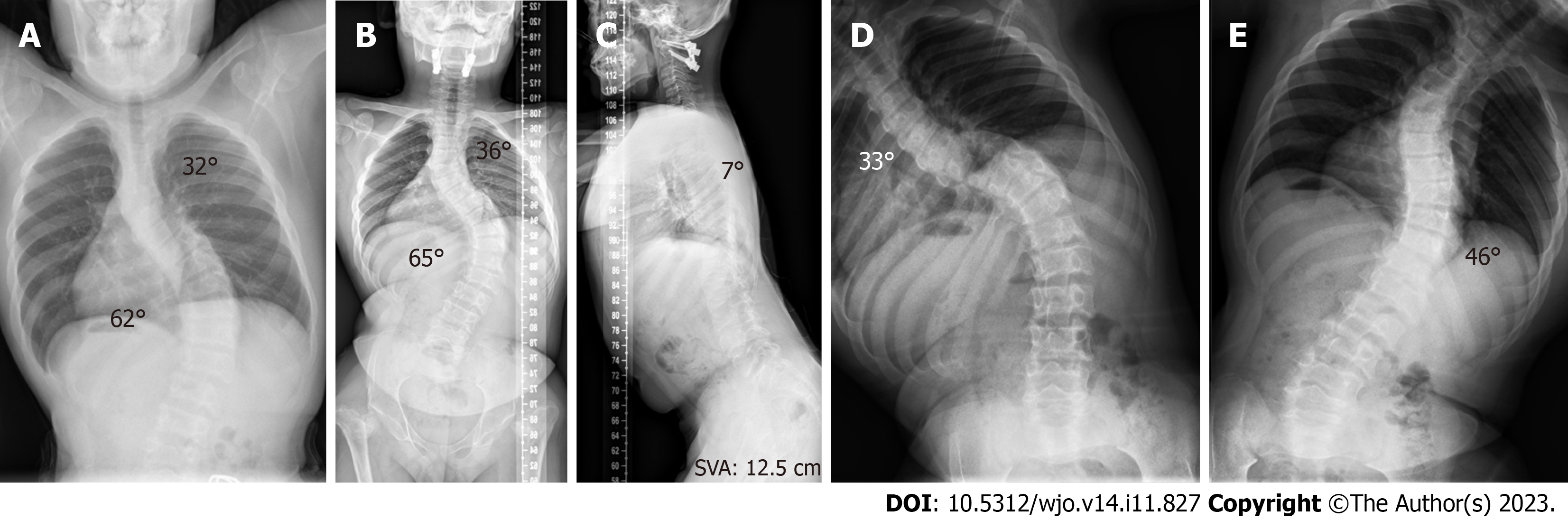
Figure 1 Preoperative X-ray data of the spine.
A: The spine X-ray taken during the first outpatient clinic indicates a leftward proximal thoracic curve (PTC) of 32° and a rightward main thoracic curve (MTC) of 65°; B: Before scoliosis correction, the standing spine X-ray reveals the PTC is 36° and the MTC is 65°; C: The thoracic kyphosis is 7° and the sagittal vertical axis is 12.5 cm; D and E: On the bending X-rays, the Cobb angle of the PTC is 33°and the MTC is 46°.
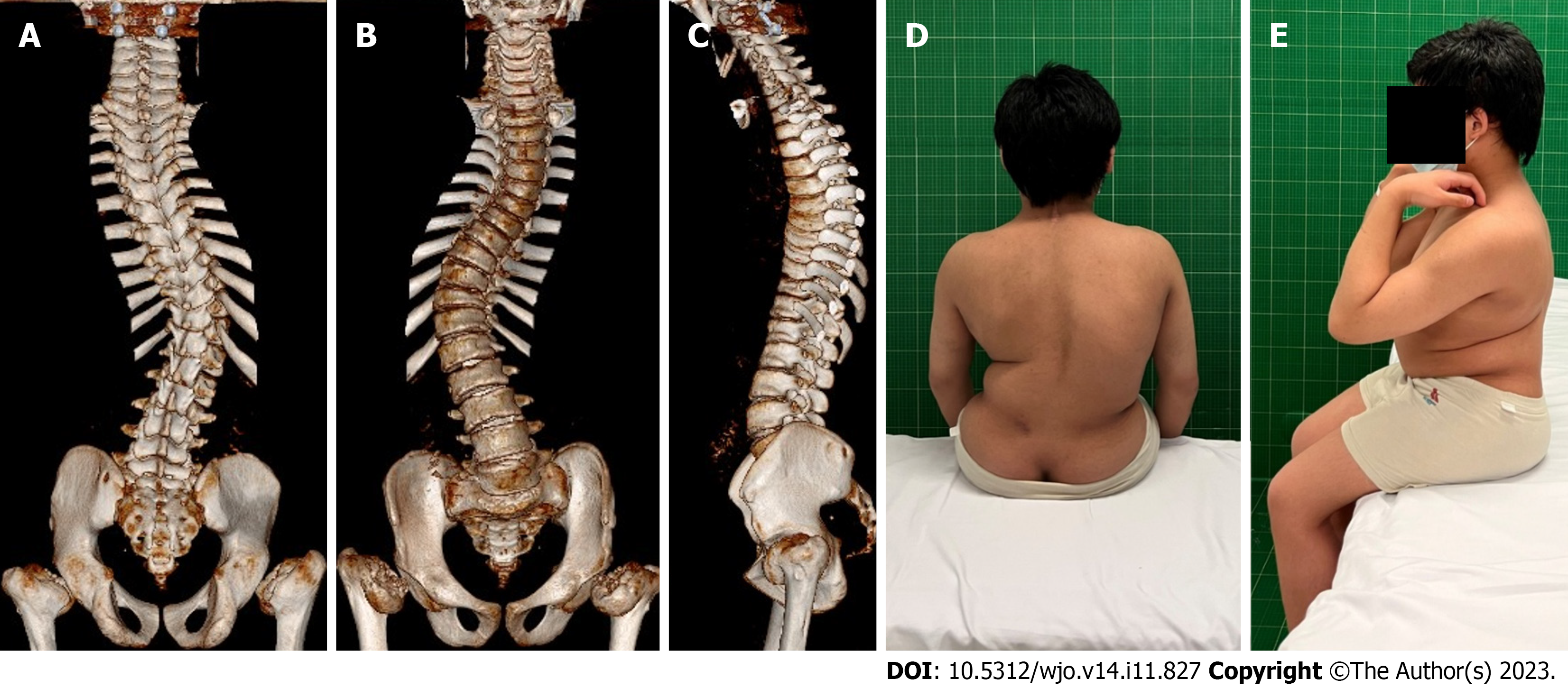
Figure 2 Preoperative computed tomography three-dimensional reconstruction of the spine and preoperative appearance.
A-C: Computed tomography three-dimensional of the spine shows postoperative changes of atlantoaxial vertebrae, scoliosis, flattening of the vertebral bodies, and dysplasia of the femoral head; D: Views from the back show unevenness of the back and right deviation of the trunk; E: Lateral views before the operation.
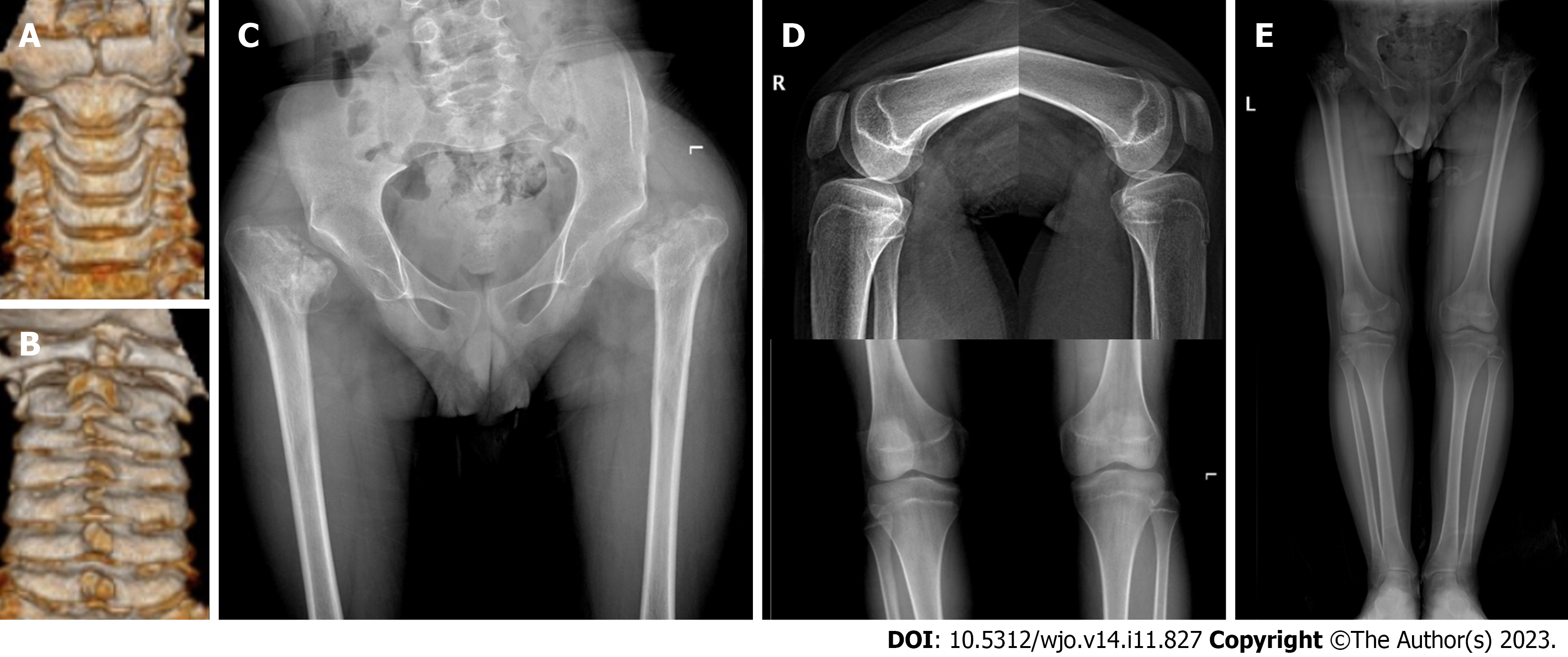
Figure 3 Computed tomography three-dimensional reconstruction of the cervical spine and X-ray of the hip.
A: The view from the front shows dysplasia of the anterior arch of the atlas and the odontoid process of axis; B: The view from the back shows dysplasia of the posterior arch of the atlas; C: A slight right inclination of the pelvis, dysplasia of bilateral hip joints, and severe damage to femoral heads are observed; D: No obvious abnormality is found in the X-ray of bilateral knee joints; E: X-ray of both lower limbs indicate that both lower limbs are equal in length.
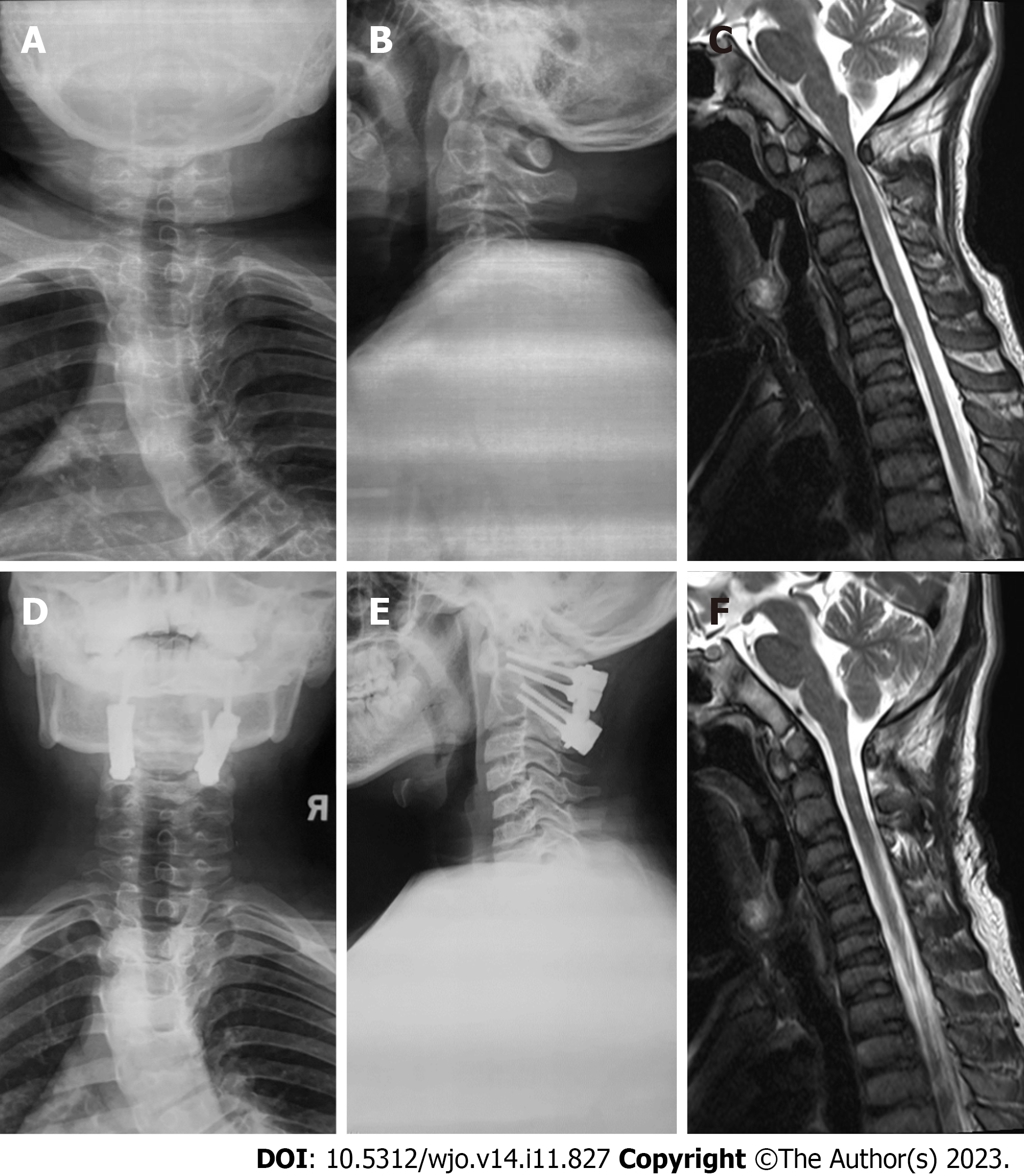
Figure 4 Imaging data of atlantoaxial dysplasia before and after surgical treatment.
A and B: Preoperative X-ray shows the widening of space between the anterior arch and odontoid process and dysplasia of the odontoid process; C: Preoperative MRI shows atlas-level spinal canal stenosis, spinal cord compression, and mild degeneration; D and E: Postoperative X-ray shows atlantoaxial fixation and fusion; F: The compression of the atlantoaxial spinal cord is relieved after the operation.
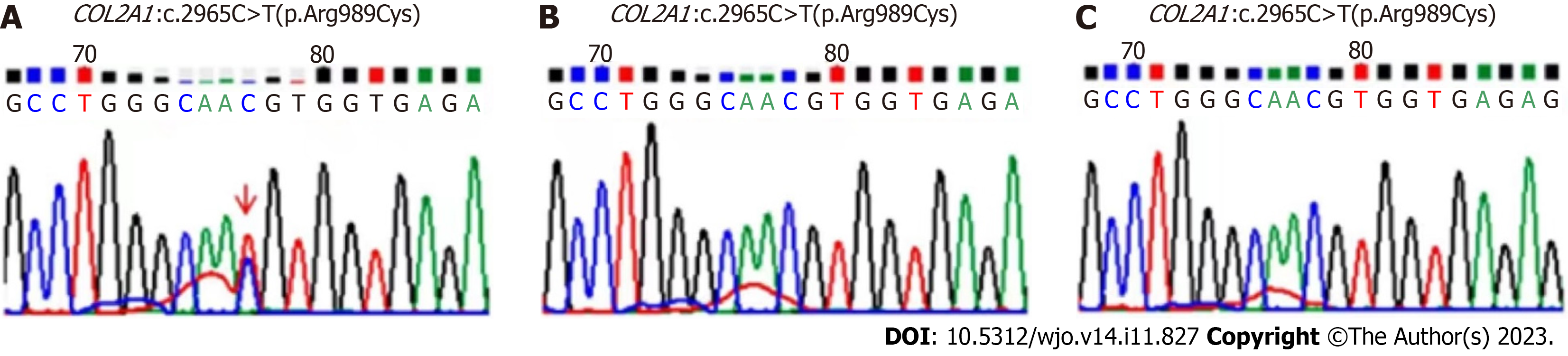
Figure 5 Gene detection and Sanger sequencing in patients' pedigrees.
A: The COL2A1 heterozygous mutation c.2965C>T(p.Arg989Cys) was found in the proband; B and C: The same pathogenic mutation was not found in the parents of the proband.
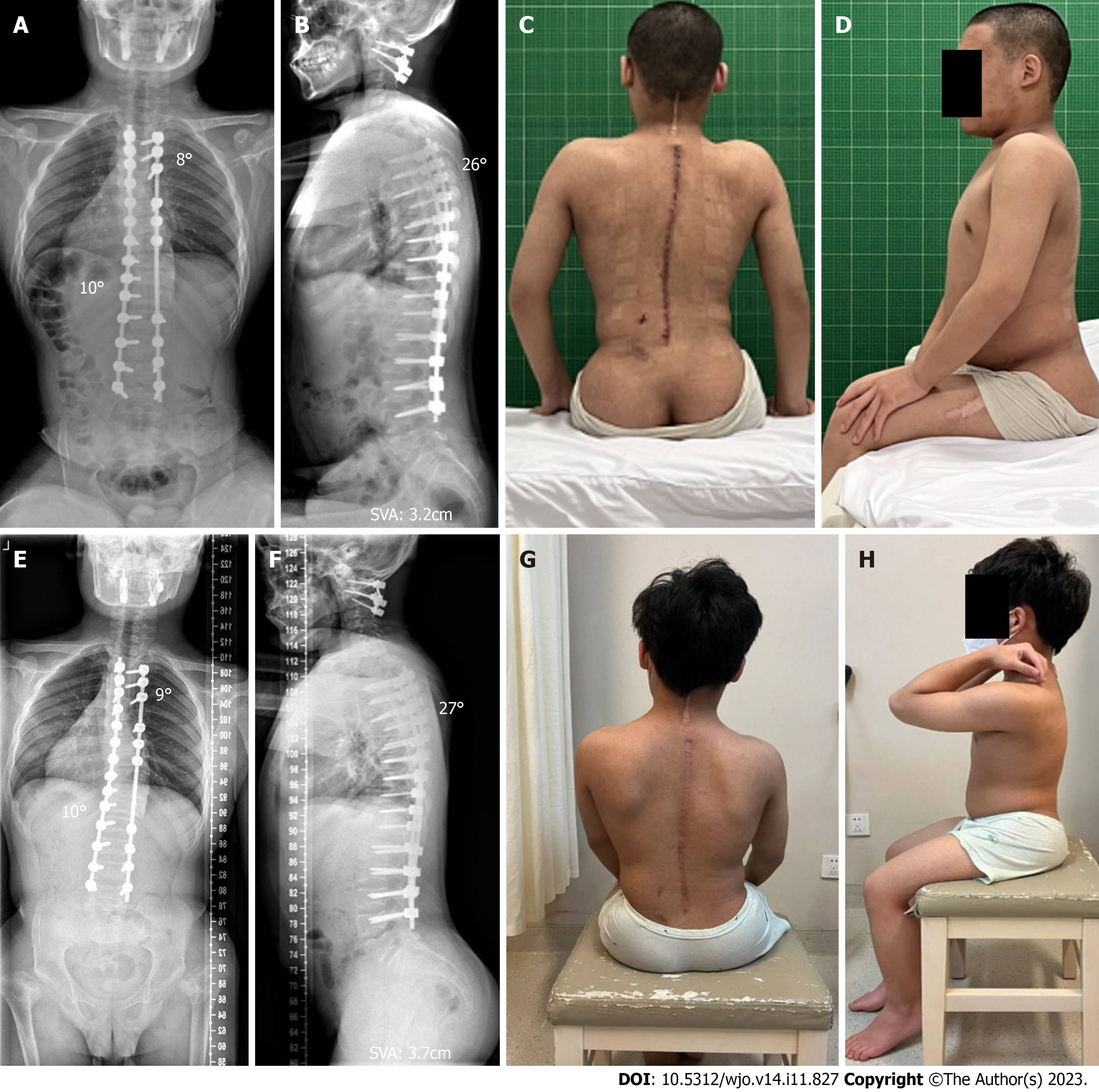
Figure 6 Images and appearance at one week and two years after the operation.
A: Spinal X-ray one week after operation showed that the Cobb angles of the proximal thoracic curve and main thoracic curve were 8° and 10°, respectively; B: The thoracic kyphosis was 26°, and the sagittal vertical axis (SVA) was 3.2 cm; C: Postoperative appearance from the back showed improvements in the unevenness of the back and balance of the trunk; D: Postoperative lateral appearance; E: Spinal X-ray two years after operation showed that the correction of scoliosis remained stable, with the Cobb angles of the proximal and main thoracic curves of 9° and 10°, respectively; F: The sagittal plane remained balanced with a SVA of 3.7 cm, and the thoracic kyphosis was 27°; G and H: The appearance of the back remained good.
- Citation: Jiao Y, Zhao JD, Huang XA, Cai HY, Shen JX. Surgical treatment of atlantoaxial dysplasia and scoliosis in spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita: A case report. World J Orthop 2023; 14(11): 827-835
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v14/i11/827.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v14.i11.827