Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2017; 8(4): 154-164
Published online Apr 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i4.154
Published online Apr 15, 2017. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i4.154
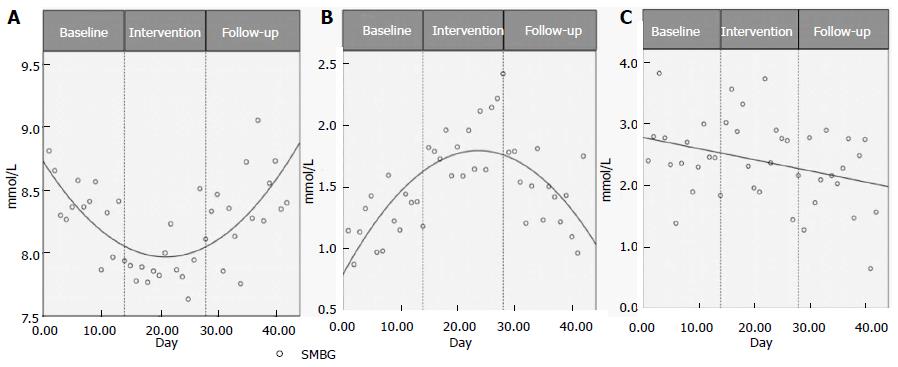
Figure 2 Intermittent Fasting improves morning fasted glucose levels and decreases postprandial variability.
The daily means for fasting morning glucose levels (from personal glucometers) on days 1 through 42 are shown in Figure 2A, with the three phases indicated. Means were calculated from pooled SMBG data from the nine individuals that provided complete log sets. Figure 2B represents the daily variance from the mean for fasting morning SMBG, days 1-42, using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test. Figure 2C shows the daily variance from the mean for evening postprandial SMBG values on days 1-42. Inflection points of quadratic equations were calculated using the formula [f 1 (y) of C + Ax + B × 2 = 0] rounded down to the nearest full integer. A: Mean morning fasted SMBG; B: Morning fasted SMBG variability; C: Evening random SMBG variability. SMBG: Self-monitored blood glucose.
- Citation: Arnason TG, Bowen MW, Mansell KD. Effects of intermittent fasting on health markers in those with type 2 diabetes: A pilot study. World J Diabetes 2017; 8(4): 154-164
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v8/i4/154.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v8.i4.154