Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2021; 13(6): 542-567
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i6.542
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i6.542
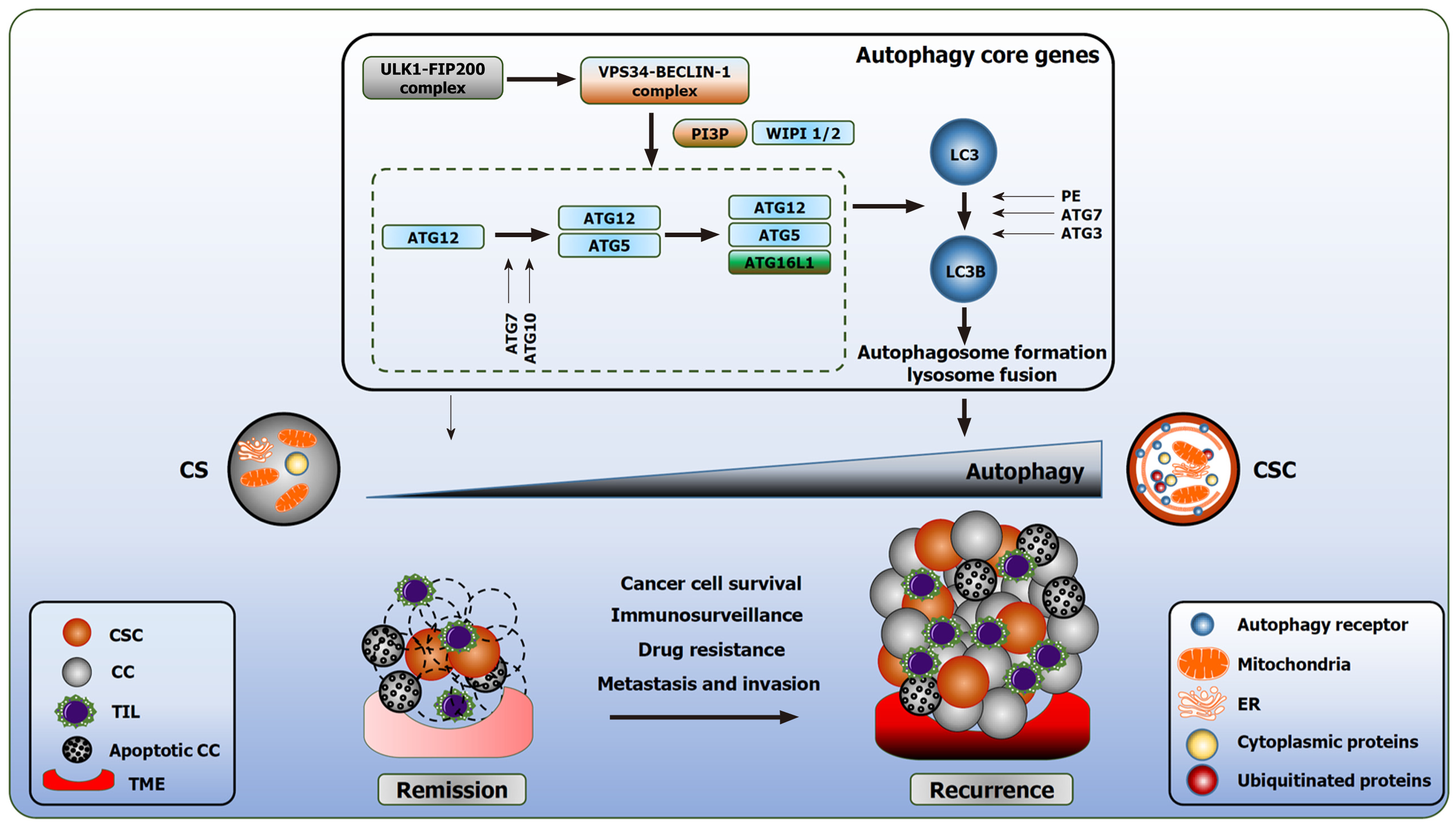
Figure 1 Role of autophagy in cancer cells and cancer stem cells.
Autophagy is a multifaceted pro-survival mechanism that supports the proliferation, growth, and stemness of cancer stem cells (CSCs). Autophagy facilitates CSCs plasticity by promoting immunosuppression, therapy resistance, metastasis, and invasion of CSCs. Several autophagy-related genes (ATGs) aid in the development, maturation and closure of the autophagosome (the ATG related signaling has been exhaustively discussed in our previous review; this figure has been adapted accordingly)[8,12]. CC: Cancer cell; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; PE: Phosphatidylethanolamine; PI3P: Phosphatidyl-inositol-3-phosphate; TIL: Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes; TME: Tumor microenvironment; WIPI: WD-repeat domain phosphoinositide-interacting protein.
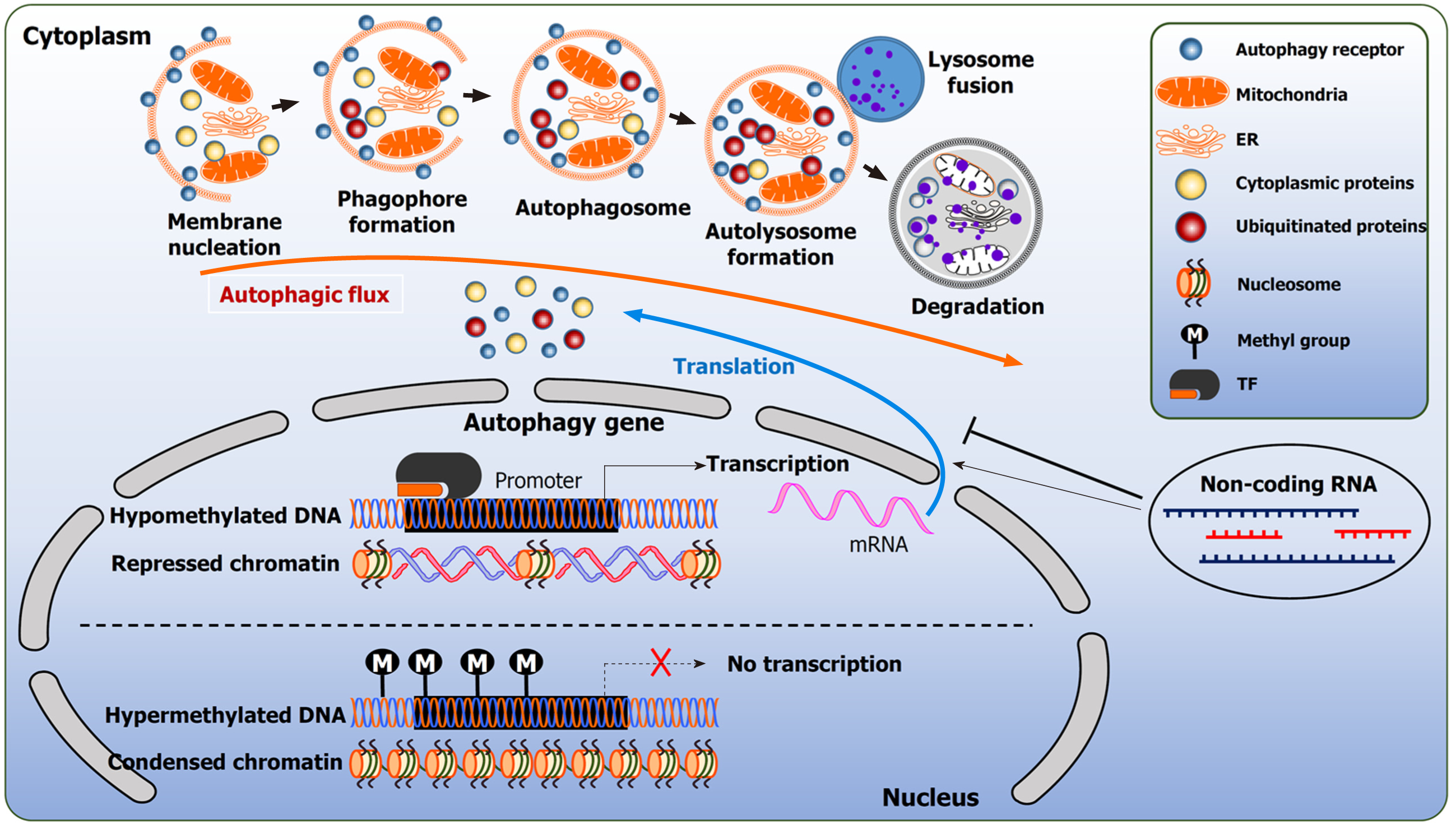
Figure 2 Epigenetic regulation of autophagy in cancer cells and cancer stem cells.
Autophagy in cancer cells and cancer stem cells is tightly regulated by the dynamic interplay of different epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation, histone remodeling and non-coding RNAs. Pathological epigenetic changes in cancer can directly regulate autophagy by targeting the core genes or indirectly through the regulatory elements. ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; M: Methyl group; TF: Transcription factor.
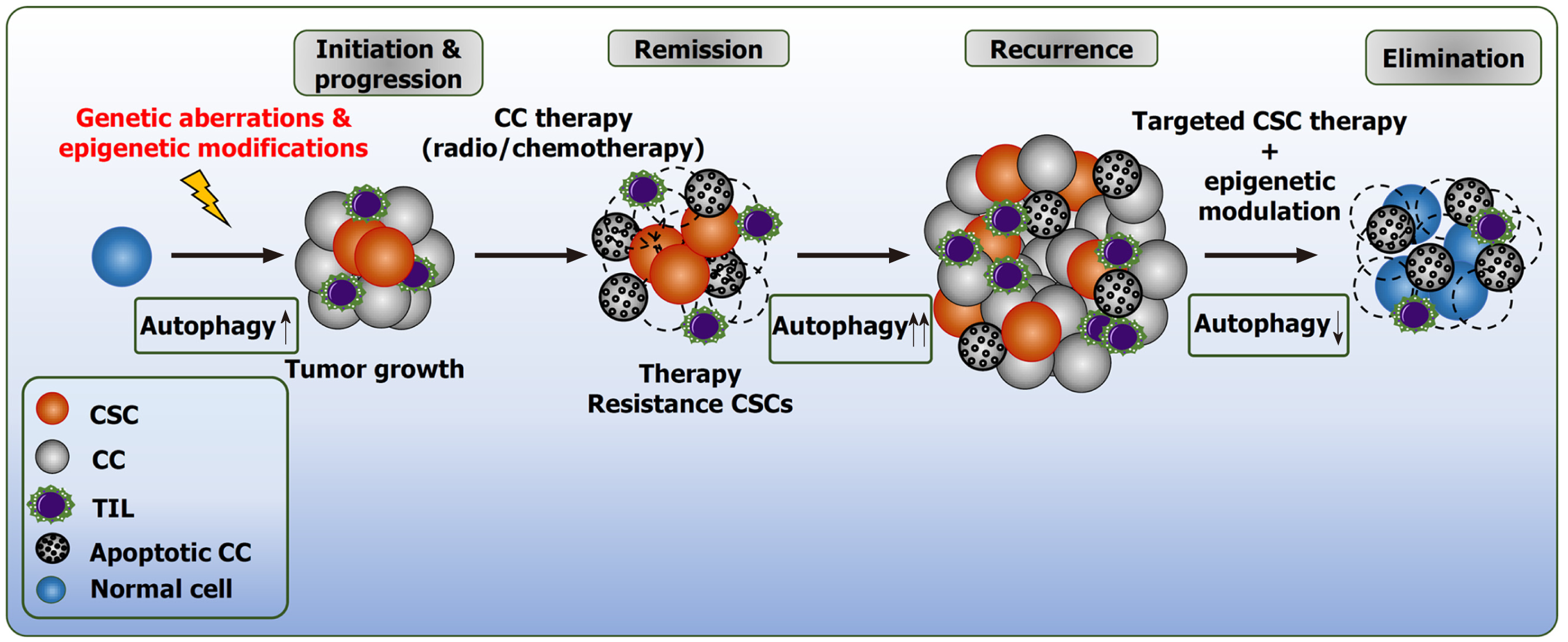
Figure 3 Epigenetic modulation of autophagy in resistance cancer cells and cancer stem cells.
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a heterogenous collection of different cells that acquire genetic aberrations and epigenetic modifications during carcinogenesis. The protective role of autophagy in CSCs facilitates radio/chemotherapeutic resistance. Targeting specific epigenetic alterations could potentially repress autophagy and sensitize the CSCs population to cell death. CC: Cancer cell; TIL: Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.
- Citation: Mandhair HK, Novak U, Radpour R. Epigenetic regulation of autophagy: A key modification in cancer cells and cancer stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(6): 542-567
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i6/542.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i6.542