Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2025; 31(33): 108653
Published online Sep 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i33.108653
Published online Sep 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i33.108653
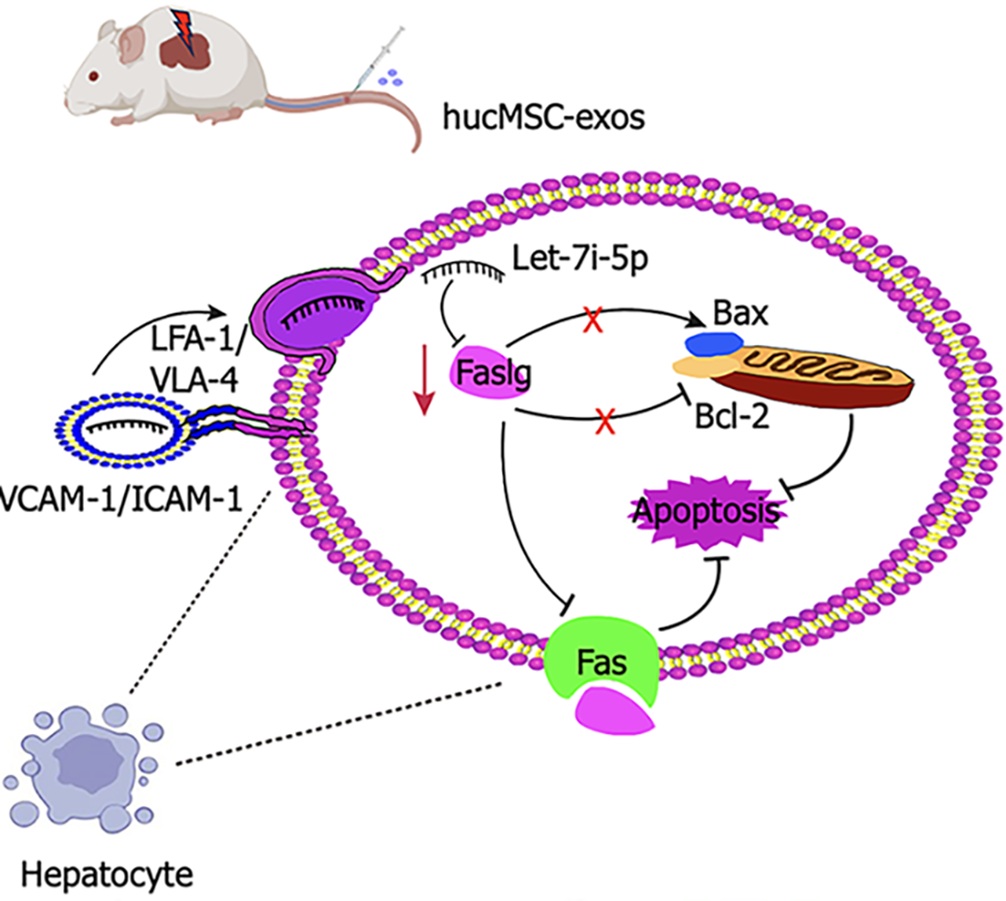
Figure 7 Schematic illustration of the therapeutic mechanism of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury.
Hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury induces hepatocyte damage and triggers apoptosis. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes target the injured liver via very late antigen-4/Lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1-mediated adhesion interactions. The therapeutic effects of these exosomes primarily involve the inhibition of the death receptor-mediated extrinsic apoptotic pathway through the downregulation of factor-related apoptosis ligand expression; and the inhibition of the mitochondrial-mediated intrinsic apoptotic pathway by modulating the B-cell lymphoma-2/B-cell lymphoma-2-associated X protein expression ratio. This process synergistically suppresses hepatocyte apoptosis. HucMSC-exos: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes; VLA-4: Very late antigen-4; LFA-1: Lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma-2; Bax: B-cell lymphoma-2-associated X protein; Fas: Factor-related apoptosis; Faslg: Factor-related apoptosis ligand; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; ICAM-1: Intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1.
- Citation: Gao Y, He M, Bian CW, Yu R, Luo JJ, Xiang YM, Yang YX, Huang HF, Zeng Z. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells attenuate hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury via the let-7i-5p/Faslg axis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(33): 108653
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i33/108653.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i33.108653