Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2025; 31(33): 108653
Published online Sep 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i33.108653
Published online Sep 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i33.108653
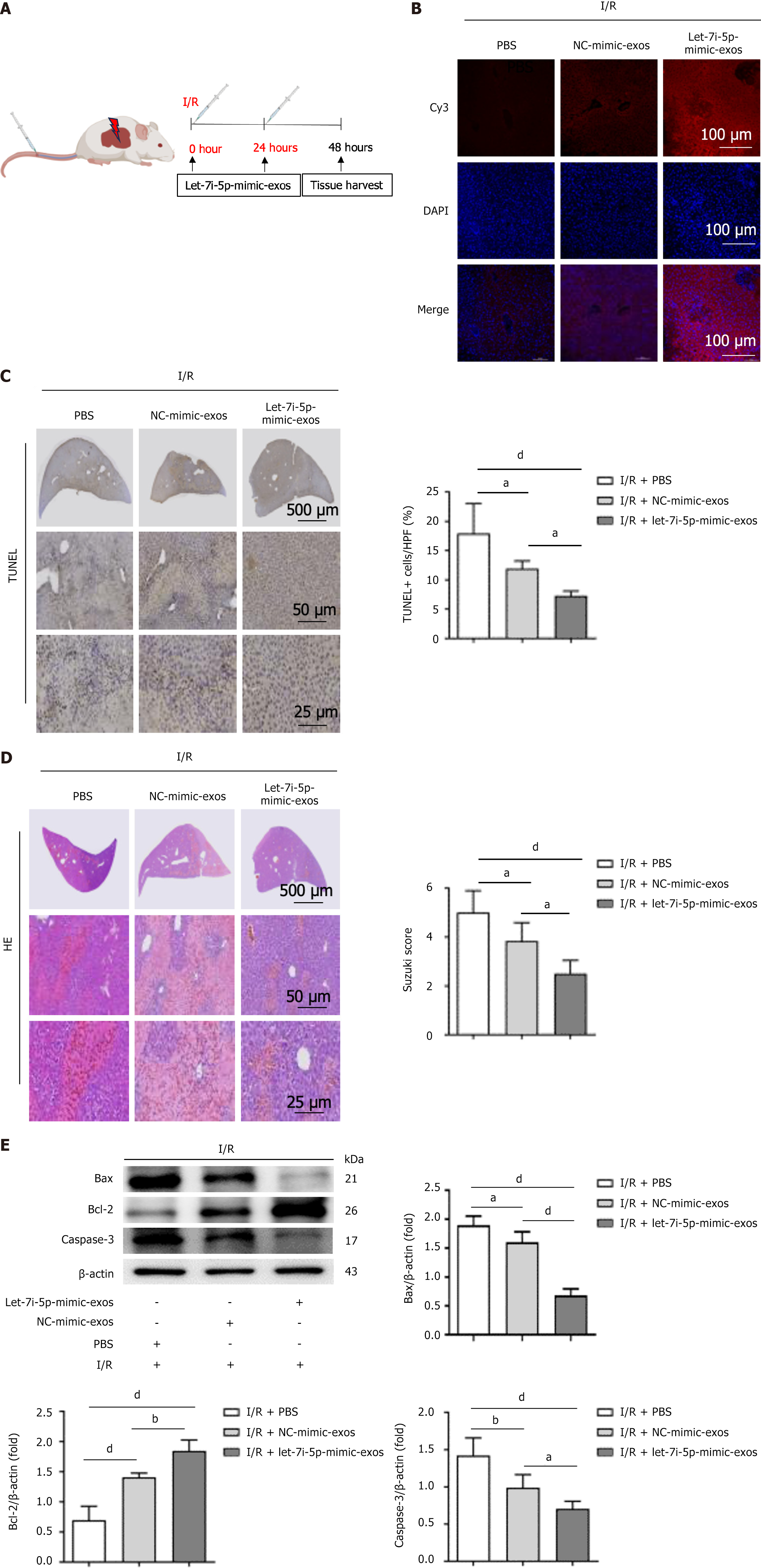
Figure 6 The let-7i-5p mimic enhances the protective effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury in mice.
A: A schematic of the experimental design of the hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury (HIRI) mouse model is shown. The mice were subjected to 1 hour of occlusion of hepatic blood flow in the left lateral lobe and left medial lobe followed by reperfusion. At the beginning of reperfusion, 100 μg of cyanine3 (Cy3)-let-7i-5p-mimic-exosomes (exos) or Cy3-negative control-mimic-exos was injected via the tail vein. For the HIRI control group, 100 μL of sterile phosphate-buffered saline was used. Liver tissue samples were collected 48 hours after HIRI induction; B: The uptake of Cy3-labelled human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exos in liver tissue is shown. Scale bars: 100 μm; C: TUNEL staining of liver tissues. Scale bars: 500 μm (top panel), 50 μm (middle panel), and 25 μm (bottom panel); D: Haematoxylin and eosin staining. Scale bars: 500 μm (top panel), 50 μm (middle panel), and 25 μm (bottom panel); E: Western blot analysis was used to detect the protein levels of apoptosis-related markers in liver tissue. I/R: Ischaemia/reperfusion; exos: Exosomes; Cy3: Cyanine3; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; PBS: Phosphate-buffered saline; NC: Negative control; TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labelling; HE: Haematoxylin and eosin; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma-2; Bax: B-cell lymphoma-2-associated X protein; Caspase-3: Cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase-3. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, and dP < 0.000.
- Citation: Gao Y, He M, Bian CW, Yu R, Luo JJ, Xiang YM, Yang YX, Huang HF, Zeng Z. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells attenuate hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury via the let-7i-5p/Faslg axis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(33): 108653
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i33/108653.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i33.108653