Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2025; 31(30): 108680
Published online Aug 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i30.108680
Published online Aug 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i30.108680
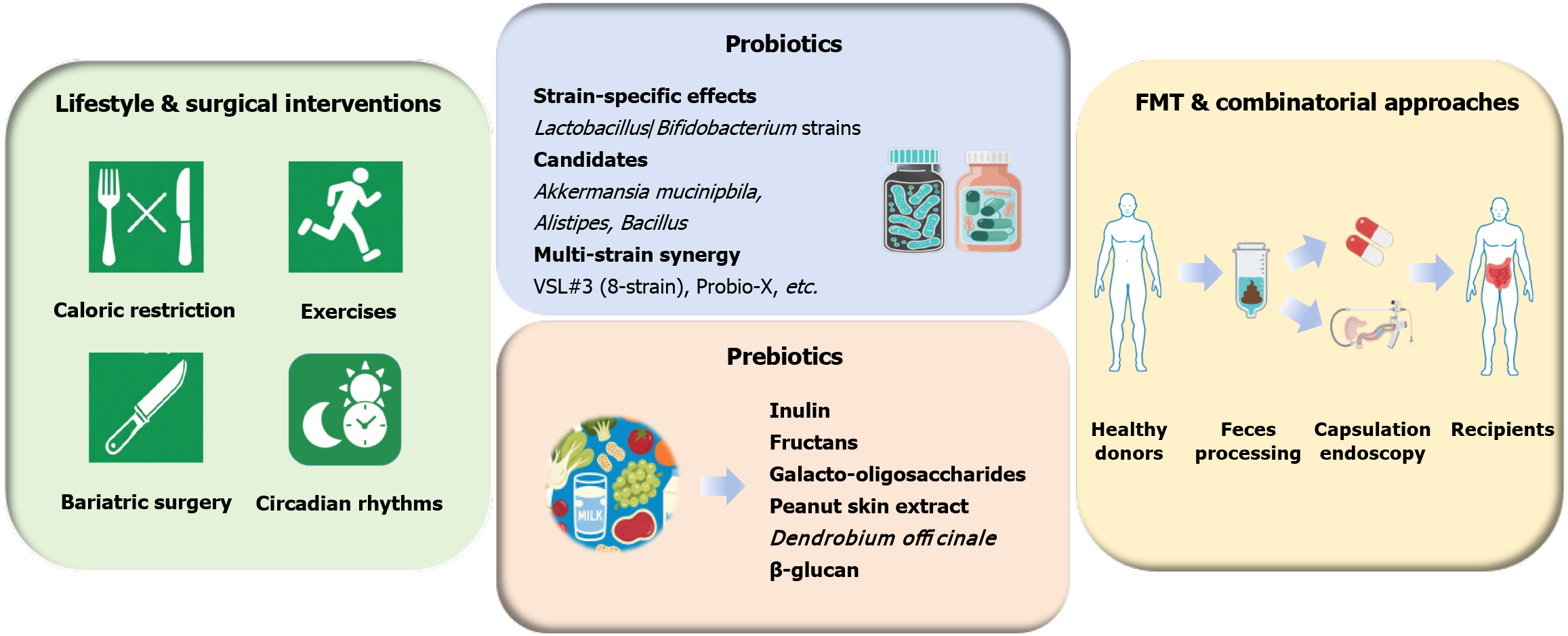
Figure 3 Therapeutic strategies targeting gut microbiota for dyslipidemia.
The gut microbiota (GM) has emerged as a therapeutic target in dyslipidemia management. Lifestyle modifications, including caloric restriction and aerobic exercise, induce beneficial GM shifts, which are strongly correlated with restored microbial gene richness and improved lipid profiles. Current GM-targeting strategies employ probiotics (e.g., Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains), prebiotics (e.g., inulin and resistant starches), and fecal microbiota transplantation. While, future synergistic design integrating probiotics, prebiotics or fecal microbiota transplantation with lifestyle intervention and pharmacotherapies may amplify strain-specific effects. FMT: Fecal microbiota transplantation.
- Citation: Lv J, Zhao HP, Yu Y, Wang JH, Zhang XJ, Guo ZQ, Jiang WY, Wang K, Guo L. From gut microbial ecology to lipid homeostasis: Decoding the role of gut microbiota in dyslipidemia pathogenesis and intervention. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(30): 108680
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i30/108680.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i30.108680