Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2025; 31(21): 107395
Published online Jun 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i21.107395
Published online Jun 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i21.107395
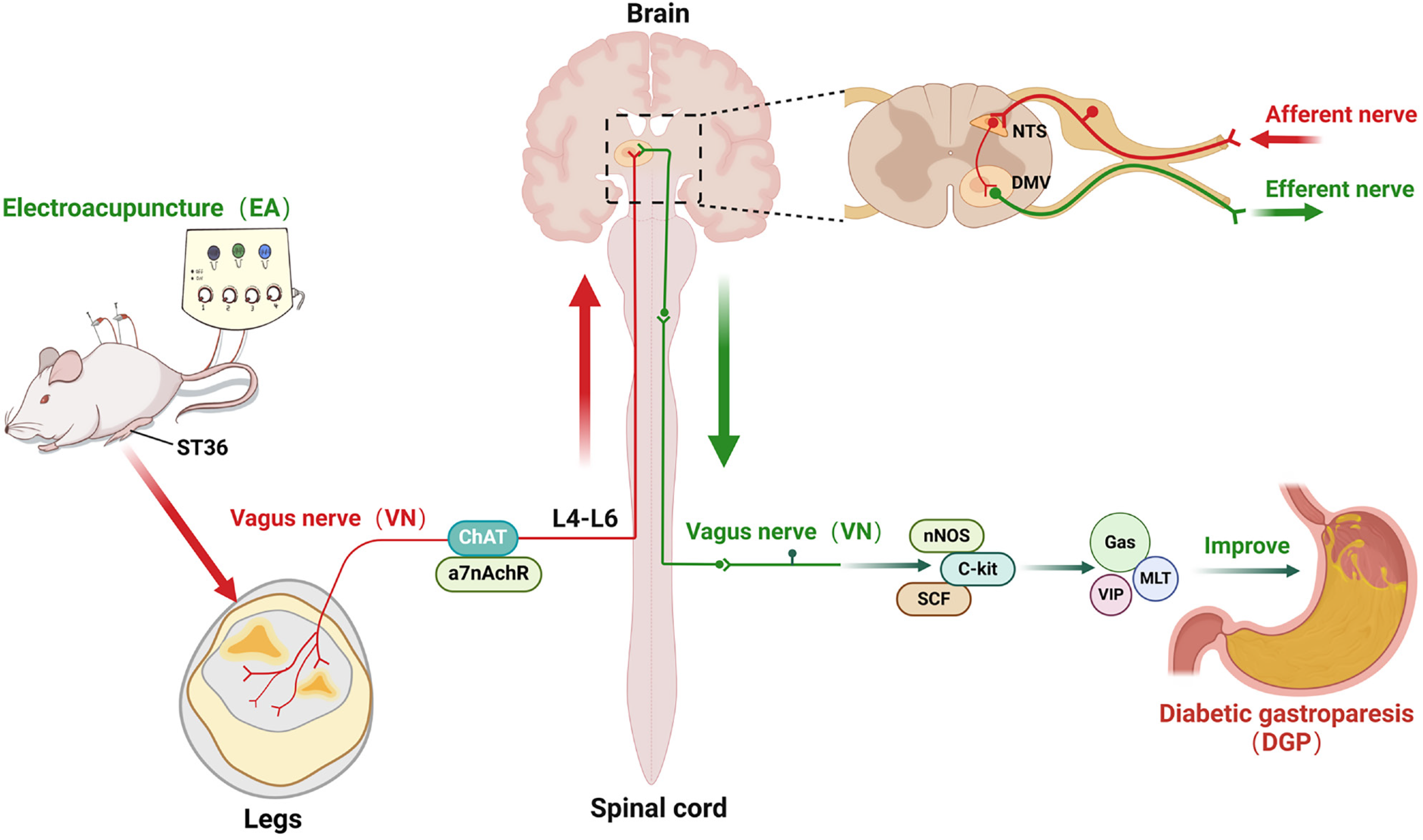
Figure 9 This schematic diagram illustrates the vagus nerve pathway through which electroacupuncture at ST36 enhances diabetic gastroparesis.
Electroacupuncture activates the choline acetyltransferase target of the vagus nerve by intervening in the ST36 acupoint area, which is transmitted up the spinal cord from L4-L6 to the intracranial nucleus tractus solitarius. This, in turn, regulates the gastric smooth muscle-related factors neuronal nitric oxide synthase, cluster of differentiation 117 and stem cell factor, as well as gastrointestinal peptides, through the subdiaphragmatic vagus nerve. This, in turn, improves the gastric motility disorder of diabetic gastroparesis. ChAT: Choline acetyltransferase; α7nAchR: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; nNOS: Neuronal nitric oxide synthase; C-kit: Cluster of differentiation 117; SCF: Stem cell factor; Gas: Gastrin; MLT: Motilin; VIP: Vasoactive intestinal peptide; NTS: Nucleus tractus solitarius; DMV: Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus.
- Citation: Zhang Y, Tang YW, Zhou J, Wei YR, Peng YT, Yan Z, Yue ZH. Electroacupuncture at ST36 ameliorates gastric dysmotility in rats with diabetic gastroparesis via the nucleus tractus solitarius-vagal axis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(21): 107395
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i21/107395.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i21.107395