Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2025; 31(21): 107395
Published online Jun 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i21.107395
Published online Jun 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i21.107395
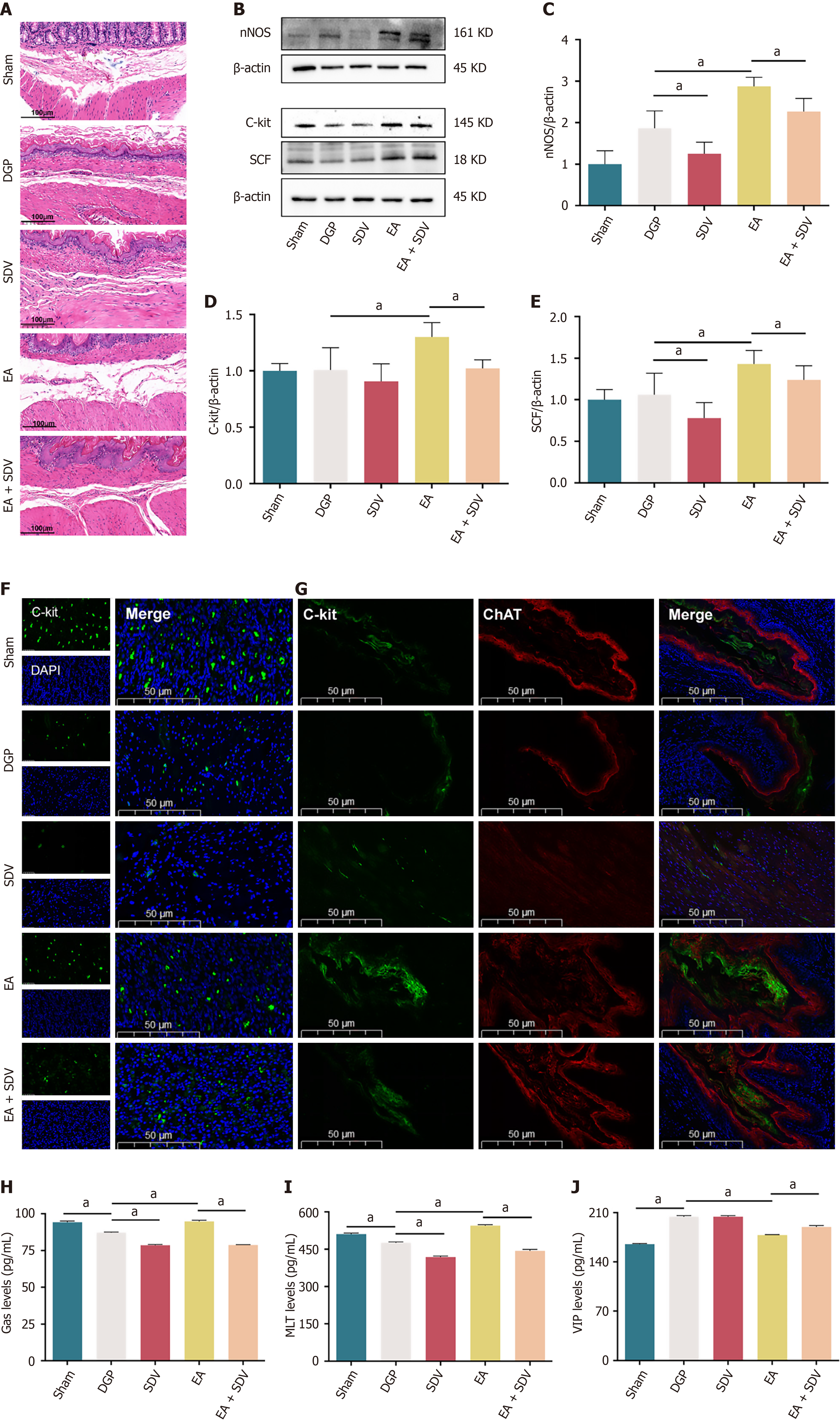
Figure 8 The effect of electroacupuncture on the function of smooth muscle after subdiaphragmatic vagotomy.
A: Representative images of hematoxylin-eosin in the stomach. Scale bar: 100 μm; B-E: Western blotting analysis and quantification of neuronal nitric oxide synthase, cluster of differentiation 117 (C-kit) and stem cell factor protein levels in stomach tissue (n = 5); F: Representative immunofluorescence images of C-kit. Scale bar: 50 μm; G: Expression of C-kit +/choline acetyltransferase + in the stomach in each group. Scale bar: 50 μm; H-J: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect the concentration of gastrin, motilin and vasoactive intestinal peptide in supernatant (n = 5). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. DGP: Diabetic gastroparesis; EA: Electroacupuncture; SDV: Subdiaphragmatic vagotomy; nNOS: Neuronal nitric oxide synthase; C-kit: Cluster of differentiation 117; SCF: Stem cell factor; ChAT: Choline acetyltransferase; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; Gas: Gastrin; MLT: Motilin; VIP: Vasoactive intestinal peptide.
- Citation: Zhang Y, Tang YW, Zhou J, Wei YR, Peng YT, Yan Z, Yue ZH. Electroacupuncture at ST36 ameliorates gastric dysmotility in rats with diabetic gastroparesis via the nucleus tractus solitarius-vagal axis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(21): 107395
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i21/107395.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i21.107395