Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2025; 31(15): 104875
Published online Apr 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.104875
Published online Apr 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.104875
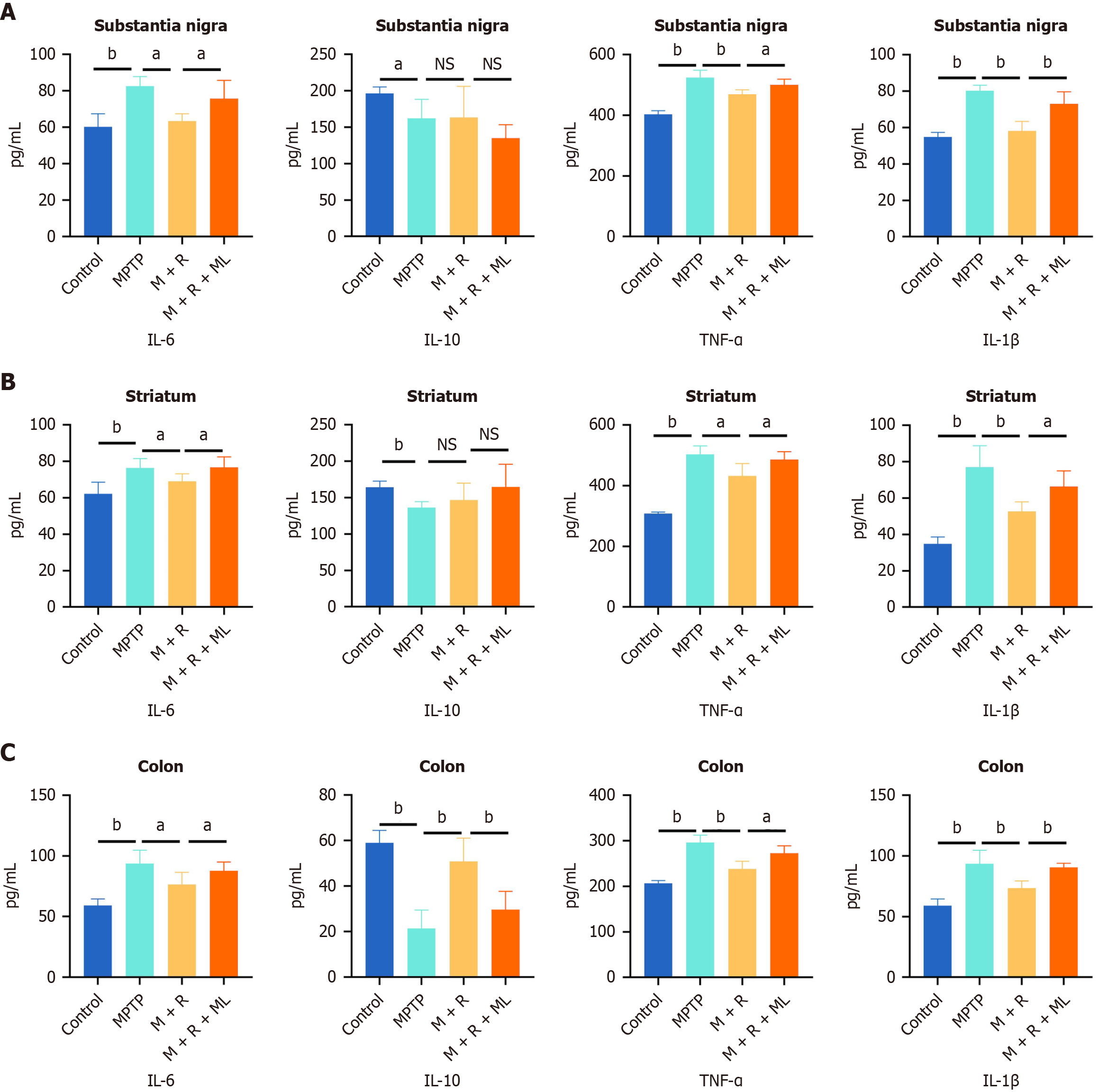
Figure 4 Rhapontin ameliorates inflammation of Parkinson's disease mice.
A: Quantification analysis of pro-inflammatory cytokines [Interleukin (IL)-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, and IL-1β] and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10) in the substantia nigra; B: Quantification analysis of pro-inflammatory cytokines and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the striatum; C: Quantification analysis of pro-inflammatory cytokines and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the colon; n = 10. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; NS: Not significant; MPTP: 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; M: MPTP; R: Rhapontin; ML: ML385.
- Citation: Wang XY, Liu F, Wang QT, Li SZ, Ye YZ, Chen T, Cai BC. Rhapontin activates nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 to ameliorate 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson's disease mice. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(15): 104875
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i15/104875.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i15.104875