Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2023; 29(2): 332-342
Published online Jan 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i2.332
Published online Jan 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i2.332
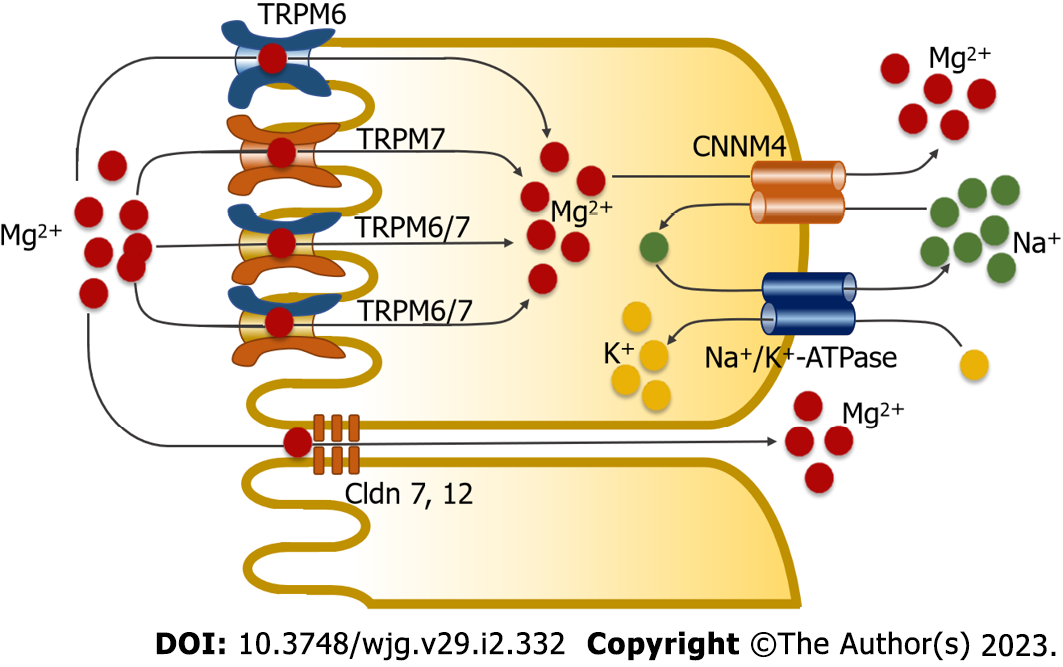
Figure 1 Magnesium absorption in the small intestine through two absorption pathways.
The transcellular transport mechanism involves magnesium (Mg2+) influx into enterocytes through the transient receptor potential melastatin 6 homodimer channel (TRPM6), transient receptor potential melastatin 7 homodimer channel (TRPM7), and transient receptor potential melastatin 6/7 heterodimer channel (TRPM6/7). Cystathionine β-synthase domain divalent metal cation transport mediator 4 (CNNM4) mediates basolateral Mg2+ extrusion by means of secondary active transport. In the paracellular mechanism, Mg2+ moves through tight-associated paracellular pores of Claudin 7 (Cldn 7) and Claudin 12 (Cldn 12).
- Citation: Chamniansawat S, Suksridechacin N, Thongon N. Current opinion on the regulation of small intestinal magnesium absorption. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(2): 332-342
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i2/332.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i2.332