Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2022; 28(34): 4993-5006
Published online Sep 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i34.4993
Published online Sep 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i34.4993
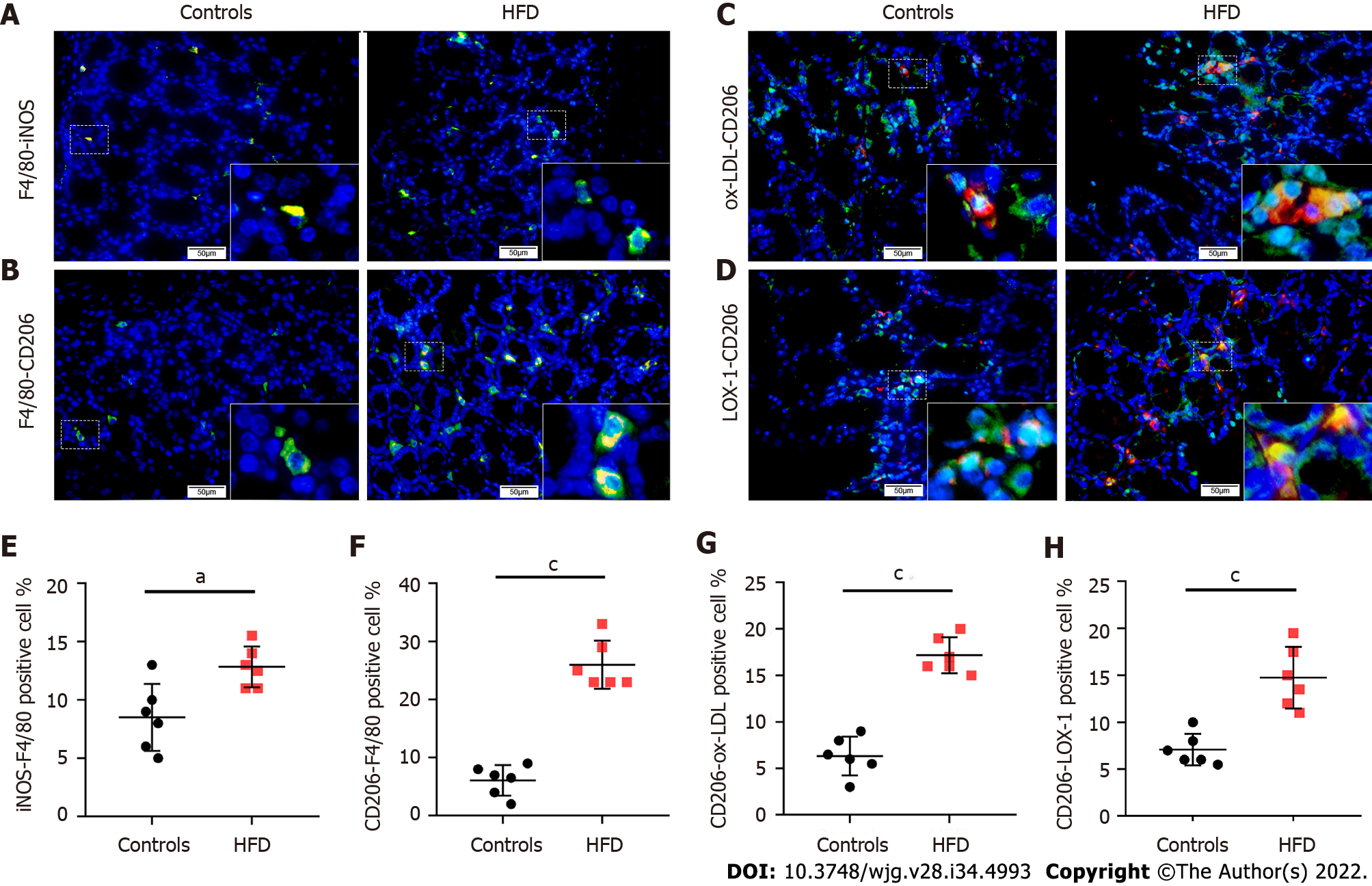
Figure 3 High-fat diet leads to increased expression of oxidized low-density lipoprotein and an increase of CD206 positive macrophages in mouse colorectal stroma.
A: Double immunofluorescence (IF) images of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)-F4/80 expression in colorectal tissues of controls and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice (scale bars represent 50 μm); B: Double IF images of inducible nitric oxide synthase CD206-F4/80 expression in colorectal tissues of controls and HFD-fed mice (scale bars represent 50 μm); C: Double IF images of CD206-oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) expression in colorectal tissues of controls and HFD-fed mice (scale bars represent 50 μm); D: Double IF images of CD206-LOX-1 expression in colorectal tissues of controls and HFD-fed mice (scale bars represent 50 μm); E: Quantification of iNOS positive macrophages in colorectal tissues based on IF results in Figure 3A; F: Quantification of CD206 positive macrophages in colorectal tissues based on IF results in Figure 3B; G: Quantification of CD206 and ox-LDL positive cells in colorectal tissues based on IF results in Figure 3C; H: Quantification of CD206 and LOX-1 positive cells in colorectal tissues based on IF results in Figure 3D. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. Statistical analyses were conducted using an unpaired t test. The boxed area is enlarged in the bottom right corner. aP < 0.05, cP < 0.001. ox-LDL: Oxidized low-density lipoprotein; HFD: High-fat diet; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase.
- Citation: Zheng SM, Chen H, Sha WH, Chen XF, Yin JB, Zhu XB, Zheng ZW, Ma J. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein stimulates CD206 positive macrophages upregulating CD44 and CD133 expression in colorectal cancer with high-fat diet. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(34): 4993-5006
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i34/4993.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i34.4993