Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2022; 28(31): 4310-4327
Published online Aug 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4310
Published online Aug 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4310
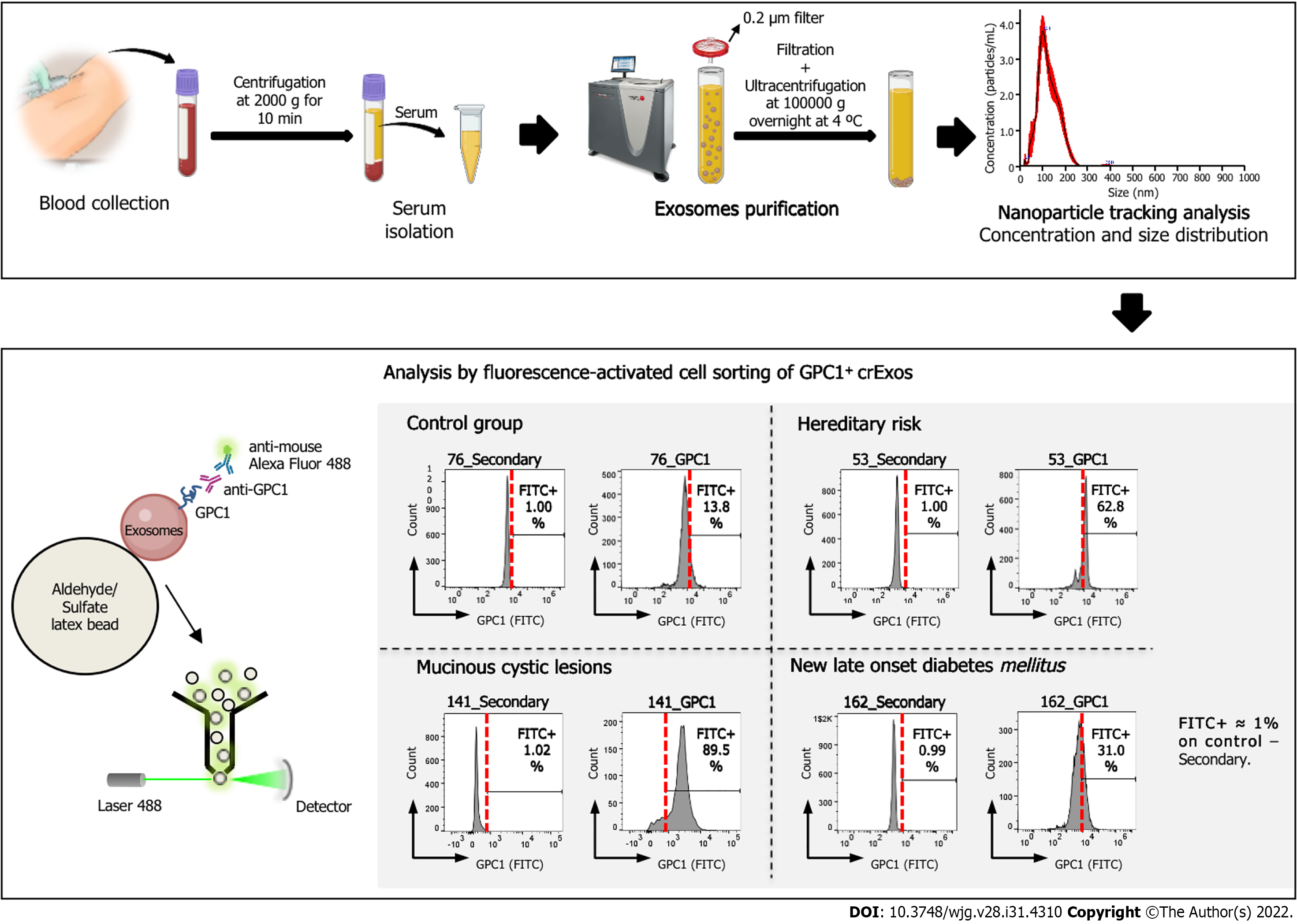
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the workflow for the analysis of circulating exosomes from control group, mucinous cystic lesions, hereditary risk and new-late onset diabetes mellitus patients for the expression of glypican-1.
Scheme illustrating the workflow of our study of the expression of glypican-1 (GPC1) on exosomes retrieved from patients’ blood samples, from blood collection to the analysis by flow cytometry of GPC1+ circulating exosomes (crExos). A representative histogram of the percentage of beads bound to GPC1-positive crExos (GPC1+ crExos) that were isolated from the serum of a control group, composed by individuals submitted to endoscopic ultrasound for other reasons than pancreatic pathology, as well as the following pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma risk groups: Mucinous cystic lesions, hereditary risk, and new-late onset diabetes mellitus. Red dashed lines in each histogram depict the start of the fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-positive gate (anti-immunoglobulin G) Alexa Fluor 488), which was determined for each patient separately by considering FITC+ approximately 1% on control–secondary–but maintained between control and GPC1 samples. GPC1: Glypican-1; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; crExos: Circulating exosomes.
- Citation: Moutinho-Ribeiro P, Batista IA, Quintas ST, Adem B, Silva M, Morais R, Peixoto A, Coelho R, Costa-Moreira P, Medas R, Lopes S, Vilas-Boas F, Baptista M, Dias-Silva D, Esteves AL, Martins F, Lopes J, Barroca H, Carneiro F, Macedo G, Melo SA. Exosomal glypican-1 is elevated in pancreatic cancer precursors and can signal genetic predisposition in the absence of endoscopic ultrasound abnormalities. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(31): 4310-4327
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i31/4310.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4310