Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2022; 28(30): 4221-4226
Published online Aug 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4221
Published online Aug 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4221
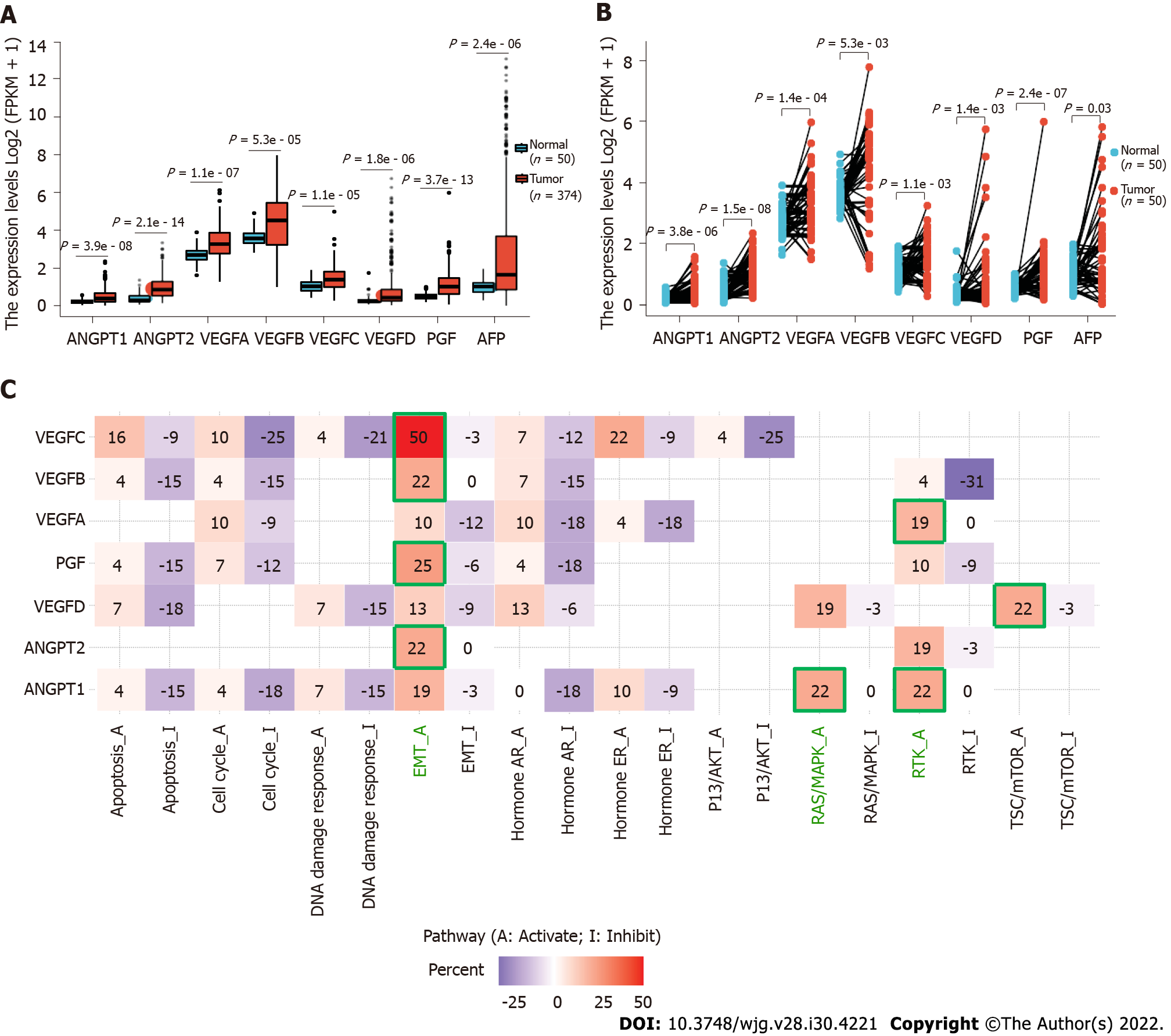
Figure 1 Roles of angiopoietins 1 and 2, vascular endothelial growth factors A-D, and placental growth factor in development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Data source: UCSC XENA (https://xenabrowser.net/datapages/) mRNA-Seq data of TPM format for GTEx and TCGA processed uniformly via the Toil process[11]. Liver hepatocellular carcinoma tissue data from TCGA and corresponding normal tissue data from GTEx were used. A: Differential expression of angiopoietin (ANGPT) 1, ANGPT2, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) A, VEGFB, VEGFC, VEGFD, and placental growth factor (PGF) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and normal tissue samples; B: Differential expression of ANGPT1, ANGPT2, VEGFA, VEGFB, VEGFC, VEGFD, and PGF in paired HCC and normal samples. The expression in cancer tissues is represented in orange, and that in normal tissues is displayed in blue; C: Pathway analysis for ANGPT1, ANGPT2, VEGFA, VEGFB, VEGFC, VEGFD, and PGF in HCC. ANGPT: Angiopoietin; PGF: Placental growth factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; AR: Androgen receptor; ER: Estrogen receptor; P13K/AKT: Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/AKT; RAS/MAPK: RAS/mitogen-activated protein kinase; RTK: Receptor tyrosine kinase; TSC/mTOR: TSC/mammalian target of rapamycin.
- Citation: Miao YD, Tang XL, Wang JT, Mi DH. Prognostic role of expression of angiogenesis markers in hepatocellular carcinoma: A bioinformatics analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(30): 4221-4226
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i30/4221.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4221