Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2021; 27(41): 7014-7024
Published online Nov 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i41.7014
Published online Nov 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i41.7014
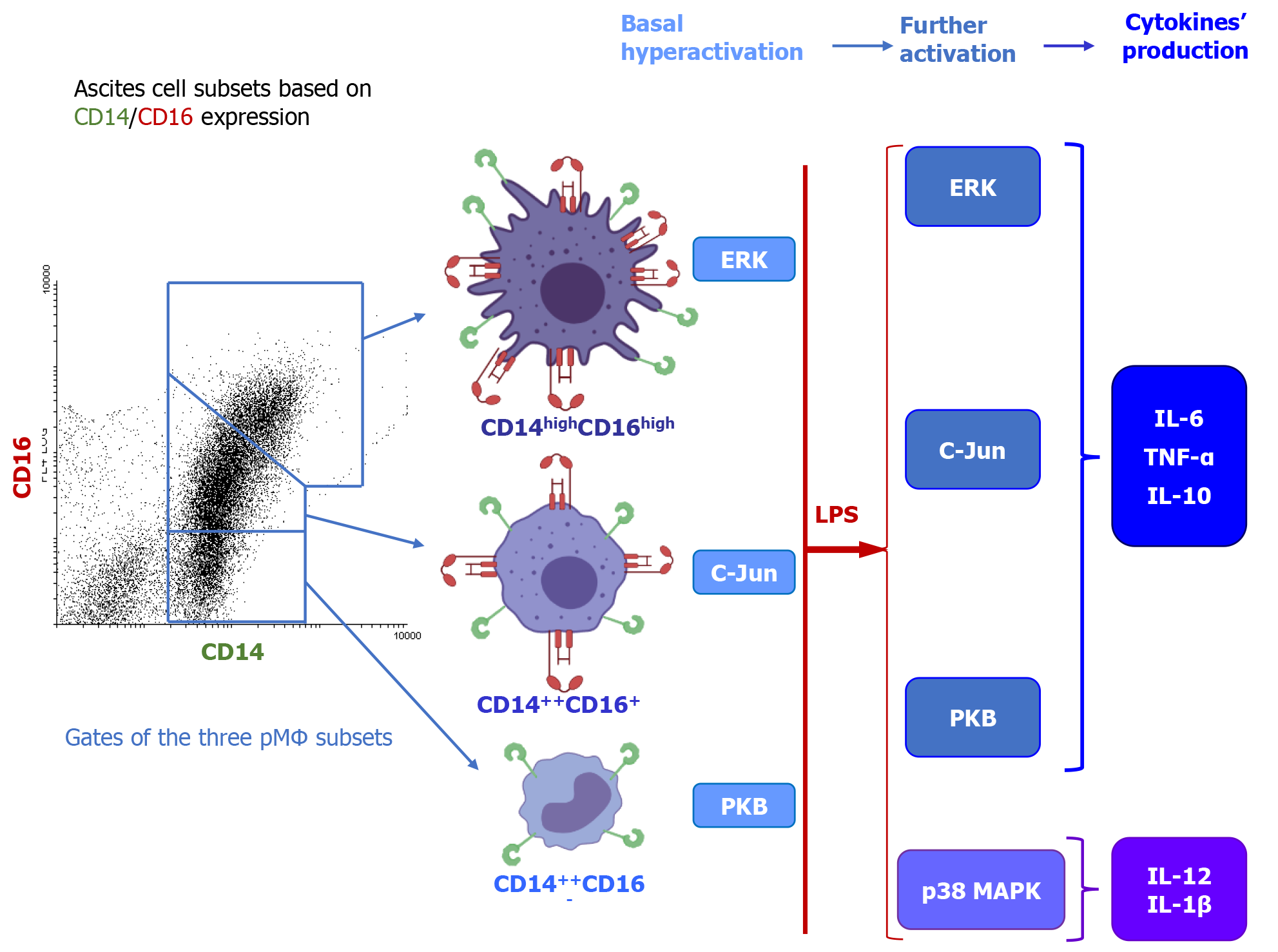
Figure 3 Peritoneal macrophage subsets from cirrhotic patients.
The ascitic fluid of cirrhotic patients presents three different subpopulations of peritoneal macrophages based on their cell morphology and CD14/CD16 expression. Baseline hyperactivation of ERK and JNK/c-Jun signaling routes detected in ascites peritoneal macrophage (pMϕ) correlates with CD14/CD16 high expressing subsets, whereas PI3K/PKB correlated with the CD16 low expressing cells. In vitro treatment with LPS drastically increases PKB/Akt, ERK1/2, and c-Jun activation, whereas the corresponding p38 MAPK is lowered in pMϕ from ascites cells compared to monocyte-derived macrophages (M-DM) from the control blood. In vitro LPS-activated macrophages from cirrhotic ascites also produce statistically higher levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10, as well as lower levels of IL-1β and IL-12 than the control blood M-DM. Adapted from Ruiz-Alcaraz et al[44] with permission from Elsevier. Citation: Ruiz-Alcaraz AJ, Tapia-Abellán A, Fernández-Fernández MD, Tristán-Manzano M, Hernández-Caselles T, Sánchez-Velasco E, Miras-López M, Martínez-Esparza M, García-Peñarrubia P. A novel CD14(high) CD16(high) subset of peritoneal macrophages from cirrhotic patients is associated to an increased response to LPS. Mol Immunol 2016; 72: 28-36. Copyright© Elsevier.
- Citation: García-Peñarrubia P, Ruiz-Alcaraz AJ, Ruiz-Ballester M, Ramírez-Pávez TN, Martínez-Esparza M. Recent insights into the characteristics and role of peritoneal macrophages from ascites of cirrhotic patients. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(41): 7014-7024
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i41/7014.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i41.7014