Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2020; 26(6): 562-597
Published online Feb 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.562
Published online Feb 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.562
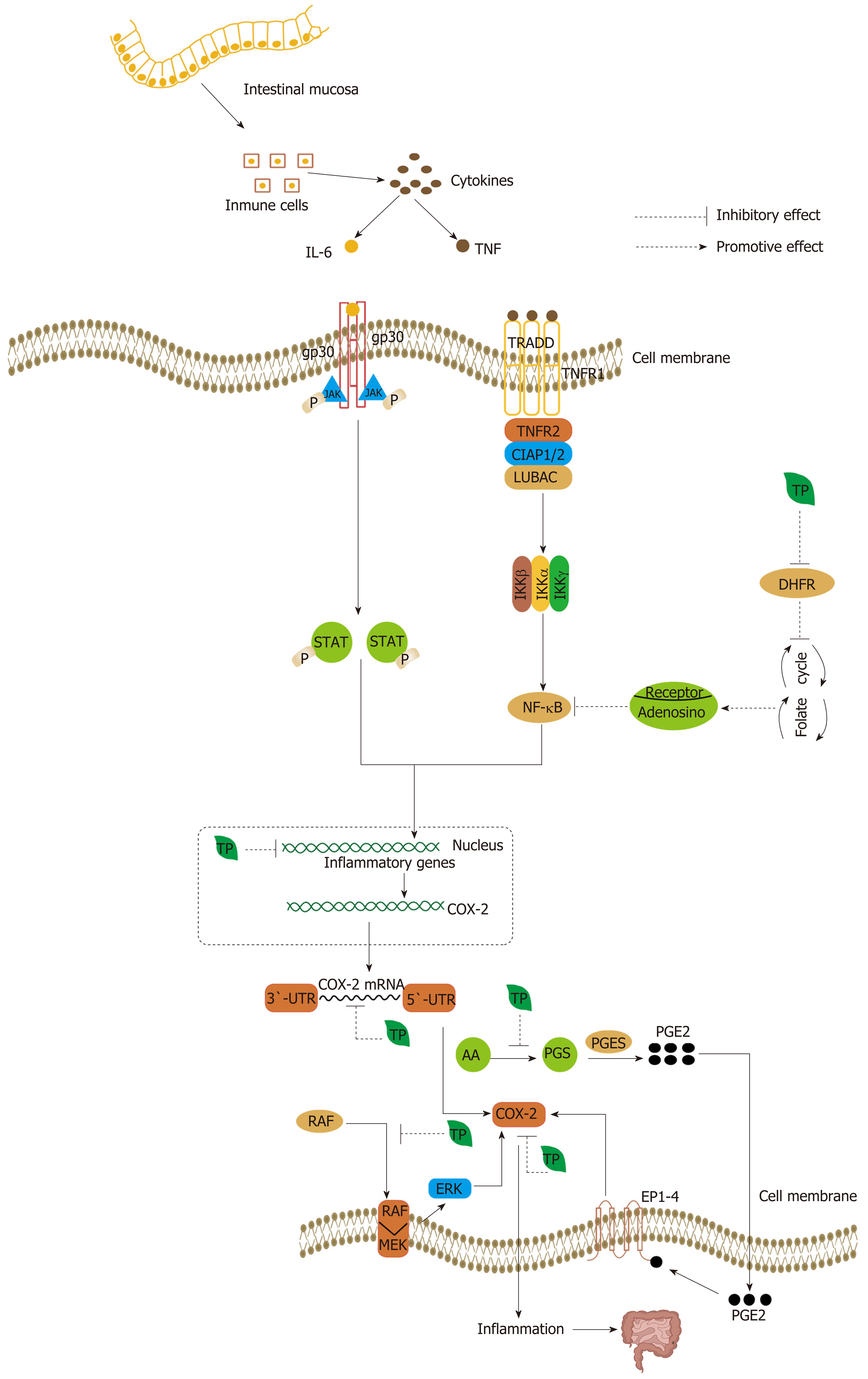
Figure 7 Tumor necrosis factor from immune cells can activate nuclear factor-kappa B, a central activator that induces the expression of inflammatory genes, such as COX-2, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and ICAM-1, and tumor cell survival, proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis are affected when tumor necrosis factor binds to tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and assembles with tumor necrosis factor receptor 1-associated death domain protein, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1 or 2, and linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex[219,230].
Similarly, another cytokine, interleukin (IL)-6, is also secreted in the tumor microenvironment. The binding of IL-6 to the IL-6 receptor activates STAT3, a major oncogenic transcription factor[229]. After binding to the IL-6 receptor at the cell surface, gp130 dimerization and activation and the transphosphorylation of JAKs are achieved and then contribute to the phosphorylation of STAT3, causing its translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, where it modulates the expression of a variety of genes[229]. Tea polyphenols (TPs) can inhibit inflammatory gene expression caused by cytokines secreted by immune cells in colorectal cancer, with the suppression of COX-2 being particularly important. TPs can inhibit COX-2 in a multilevel process, majorly at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional level. In addition, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) can suppress the expression of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) through interruption of folate cycle. EGCG can inhibit dihydrofolate reductase and thereby interfere with the folate cycle, causing the release of adenosine. Adenosine binding to specific receptors inhibits the activation of NF-κB. In addition, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) can also activate COX-2 by stimulating EP receptor (EP1-4) signaling, with the subsequent induction of colorectal cancer onset. Moreover, TPs can inhibit the synthesis of PGE2 and thereby suppress the expression of COX-2. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TRADD: TNFR1-associated death domain protein; TRAF2: TNFR-associated factor 2; LUBAC: Linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex; IL-6: Interleukin 6; TP: Tea polyphenol.
- Citation: Wang ST, Cui WQ, Pan D, Jiang M, Chang B, Sang LX. Tea polyphenols and their chemopreventive and therapeutic effects on colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(6): 562-597
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i6/562.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.562