Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2020; 26(40): 6111-6140
Published online Oct 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i40.6111
Published online Oct 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i40.6111
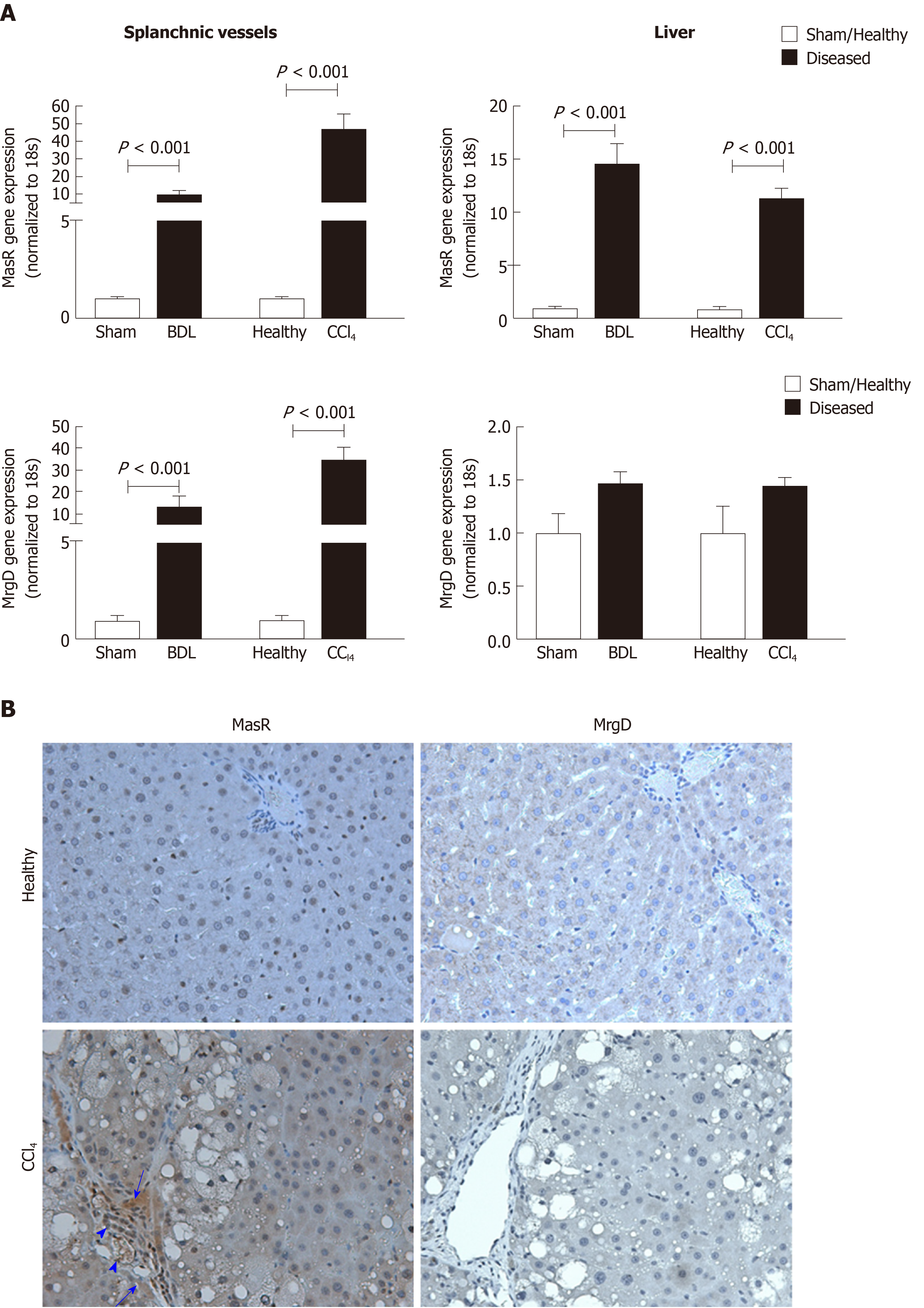
Figure 6 Expression of the receptors of the alternate renin angiotensin system in the splanchnic and hepatic vasculatures in cirrhosis.
A: Gene expression of Mas receptor (MasR) and Mas-related G protein-coupled receptor type-D (MrgD) in cirrhotic mesenteric arterial vessels and livers of carbon tetrachloride-injected (CCl4) and bile duct ligated rats compared with sham-operated and healthy controls. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM profile from 6-7 rats per group. Gene expression of both MasR and MrgD are upregulated in the splanchnic vascular bed of both cirrhotic models, suggesting that both receptors are likely involved in angiotensin-(1-7)-mediated splanchnic vasodilatation in cirrhosis. In marked contrast, MasR, but not MrgD, is upregulated in the cirrhotic livers, suggesting that MasR, but not MrgD of the alternate renin angiotensin system, likely contributes to the regulation of hepatic vascular resistance in cirrhosis; B: Shows immunohistochemical localization of MasR and MrgD in the livers of CCl4 rats and healthy controls. Consistent with gene expression analysis, strong positive staining for MasR is shown in liver sinusoids (arrow), bile duct epithelial cells (arrowhead-large) and hepatic arterioles (arrowhead-small) of the cirrhotic liver. Consistent with gene expression analysis, there was no positive staining for MrgD in the cirrhotic liver. Adapted from reference[23]. MasR: Mas receptor; MrgD: Mas-related G protein-coupled receptor-type D; CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride-injected; BDL: Bile duct ligated.
- Citation: Gunarathne LS, Rajapaksha H, Shackel N, Angus PW, Herath CB. Cirrhotic portal hypertension: From pathophysiology to novel therapeutics. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(40): 6111-6140
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i40/6111.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i40.6111