Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2019; 25(45): 6607-6618
Published online Dec 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i45.6607
Published online Dec 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i45.6607
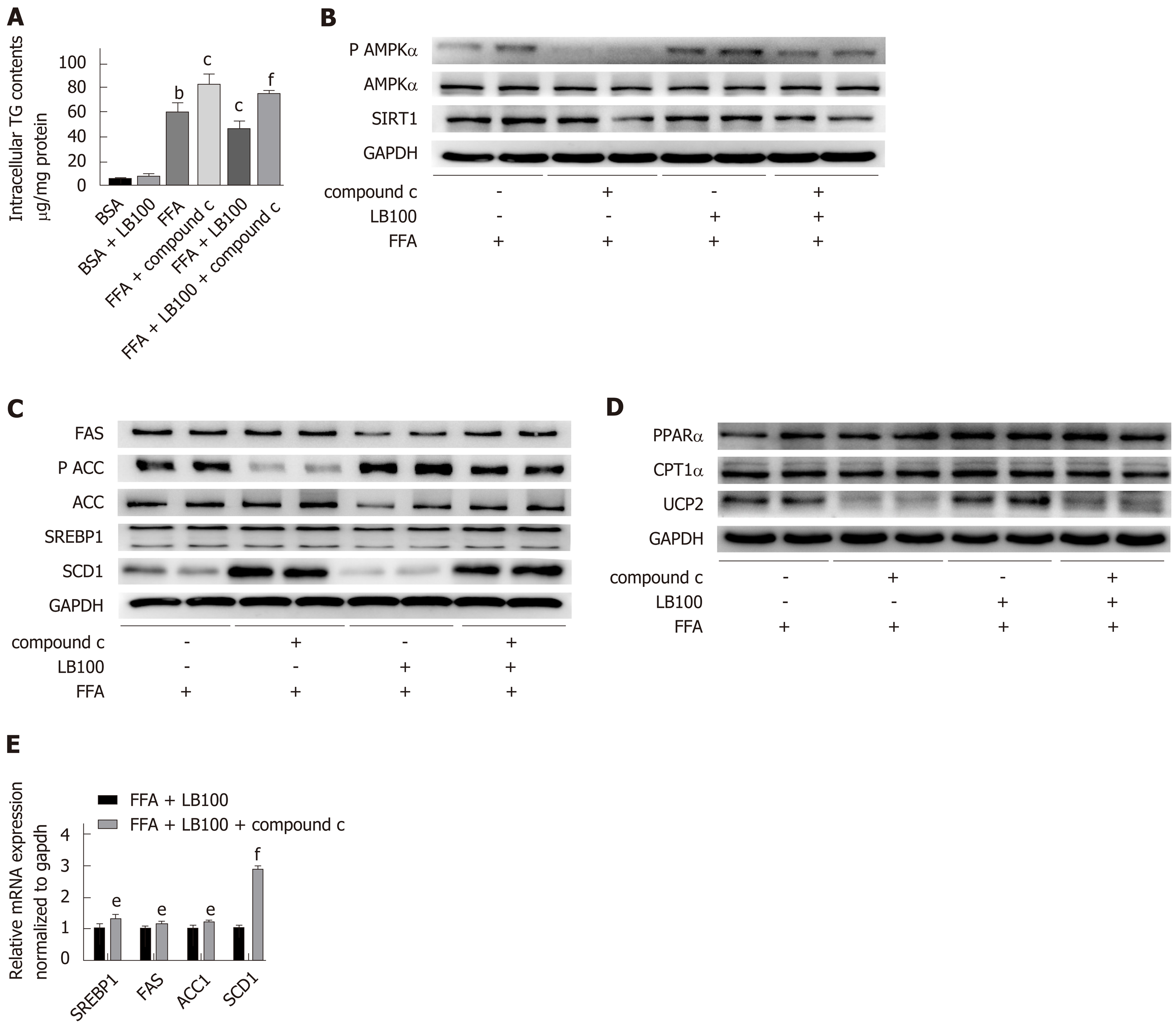
Figure 5 Inhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase α abolishes the effects of LB100 on the alleviation of hepatic steatosis in L02 cells.
After pretreatment with the AMP-activated protein kinase α (AMPK α) inhibitor, compound C for 2 h, L02 cells were incubated in normal medium or medium containing free fatty acid (FFA) with or without LB100 for 24 h. A: Intracellular triglyceride (TG) content in L02 cells; B: phosphorylated AMPK α (P-AMPKα), AMPKα, and Sirtuin 1 protein expression was detected by western blot analysis; C: Western blot analysis of proteins involved in lipid synthesis, such as fatty acid synthase (FAS), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1), and stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1); D: proteins involved in fatty acid β-oxidation, such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1α, and uncoupling protein 2; E: Gene expression levels of SREBP1, FAS, ACC1, and SCD1 were determined using real-time PCR. Three independent experiments were analyzed, and the data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs bovine serum albumin group; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs FFA group; eP < 0.05, fP < 0.01 vs FFA+LB100 group. P AMPK α: Phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase α; Sirt1: Sirtuin 1; TG: Triglyceride; FFA: Free fatty acid; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; SREBP1: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; SCD1: Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; CPT1α: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1α; UCP2: Uncoupling protein 2; BSA: Bovine serum albumin.
- Citation: Chen XY, Cai CZ, Yu ML, Feng ZM, Zhang YW, Liu PH, Zeng H, Yu CH. LB100 ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via the AMPK/Sirt1 pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(45): 6607-6618
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i45/6607.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i45.6607