Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2019; 25(36): 5515-5529
Published online Sep 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i36.5515
Published online Sep 28, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i36.5515
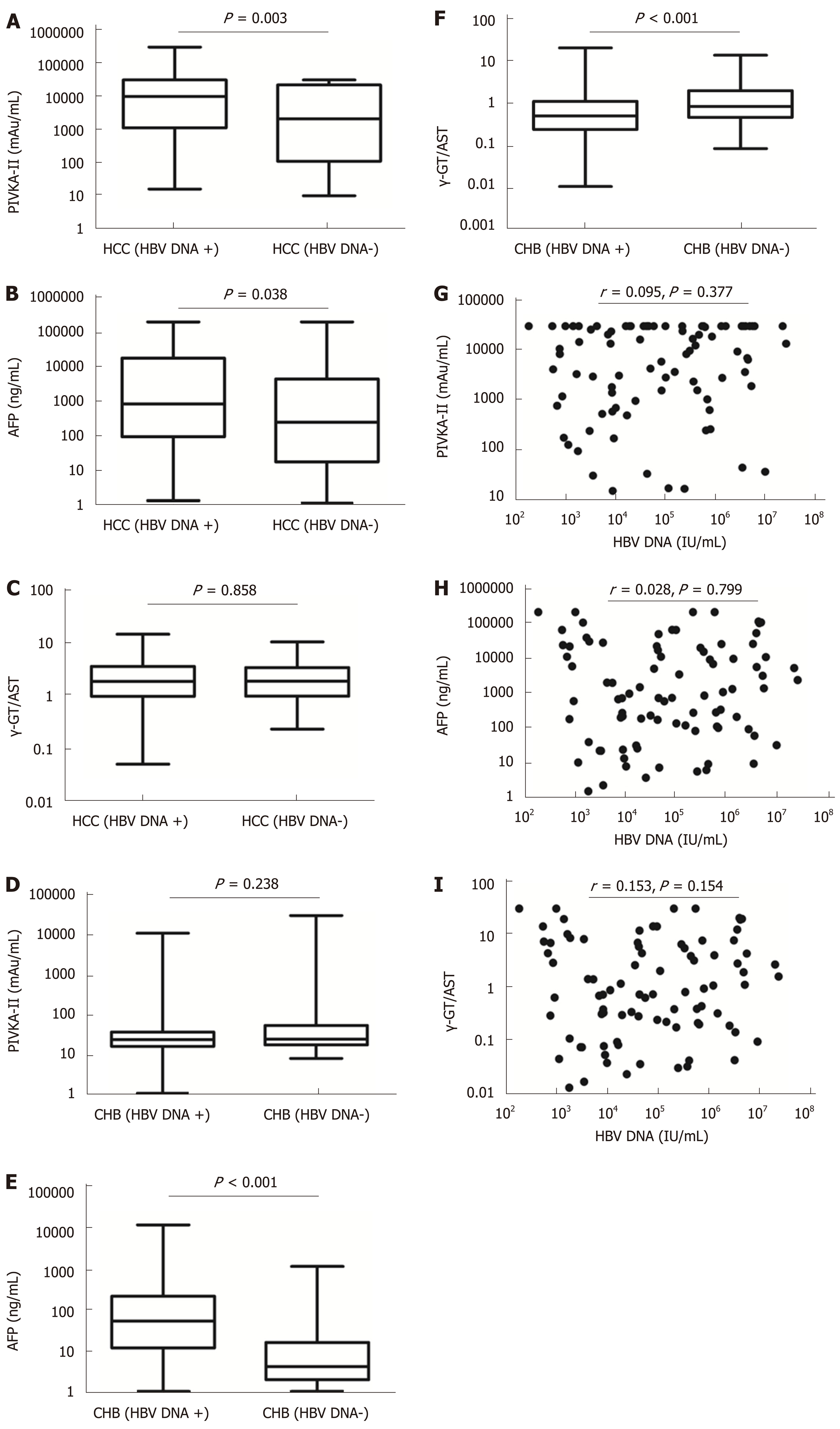
Figure 3 Correlations of serum levels of protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist II, alpha-fetoprotein, and the ratio of gamma-glutamyltransferase to aspartate aminotransferase with hepatitis B virus DNA.
A-C: Comparisons of serum levels of protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist II (PIVKA-II), alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), and the ratio of gamma-glutamyltransferase to aspartate aminotransferase (γ-GT/AST) between hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA+ and HBV DNA- hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients; D-F: Comparisons of serum levels of PIVKA-II, AFP, and γ-GT/AST between HBV DNA+ and HBV DNA- chronic hepatitis B patients. G-I: Correlations of PIVKA-II, AFP, and γ-GT/AST with serum levels of HBV DNA in HBV DNA+ HCC patients. PIVKA-II: Protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist II; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; γ-GT/AST: The ratio of gamma-glutamyltransferase to aspartate aminotransferase; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; CHB: Chronic hepatitis B.
- Citation: Wang Q, Chen Q, Zhang X, Lu XL, Du Q, Zhu T, Zhang GY, Wang DS, Fan QM. Diagnostic value of gamma-glutamyltransferase/aspartate aminotransferase ratio, protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist II, and alpha-fetoprotein in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(36): 5515-5529
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i36/5515.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i36.5515