Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2015; 21(34): 9863-9886
Published online Sep 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9863
Published online Sep 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9863
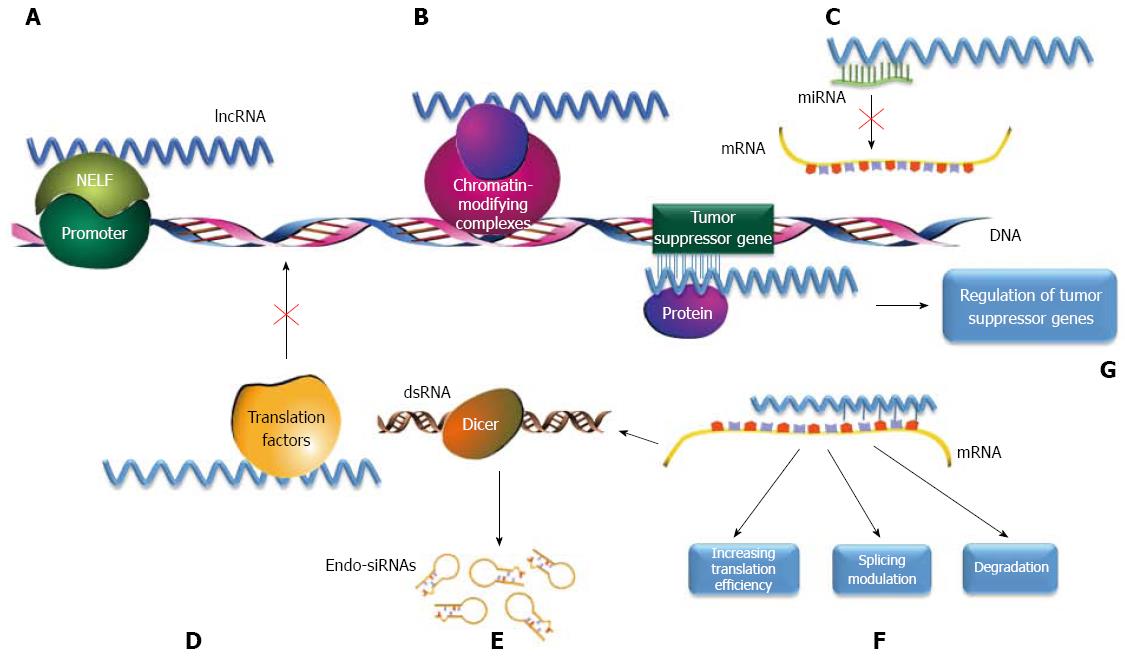
Figure 2 Mechanisms of long non-coding RNA function.
A: Serve as enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) to compete with nascent mRNA for negative elongation factor (NELF) complex binding at the target promoter for transcriptional regulation; B: Serve as a scaffolding base for the coordination of epigenetic or chromatin-modifying complexes; C: Serve as molecular sponges for microRNAs (miRNAs); D: Function as a decoy for miRNAs or translation factors to regulate gene expression; E: Hybridize with their corresponding spliced mRNAs to form dsRNAs, which are cleaved by Dicer to generate endogenous small interfering RNAs (endo-siRNAs) to modulate gene expression; F: Gene expression regulation by direct long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)-mRNA interactions; G: Directly modulate tumor suppressor signaling by either transcriptional regulation of tumor suppressor genes or mediation of tumor suppressor target gene activation.
- Citation: Huang YK, Yu JC. Circulating microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer diagnosis: An update and review. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(34): 9863-9886
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i34/9863.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9863