Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2015; 21(30): 9021-9037
Published online Aug 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9021
Published online Aug 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9021
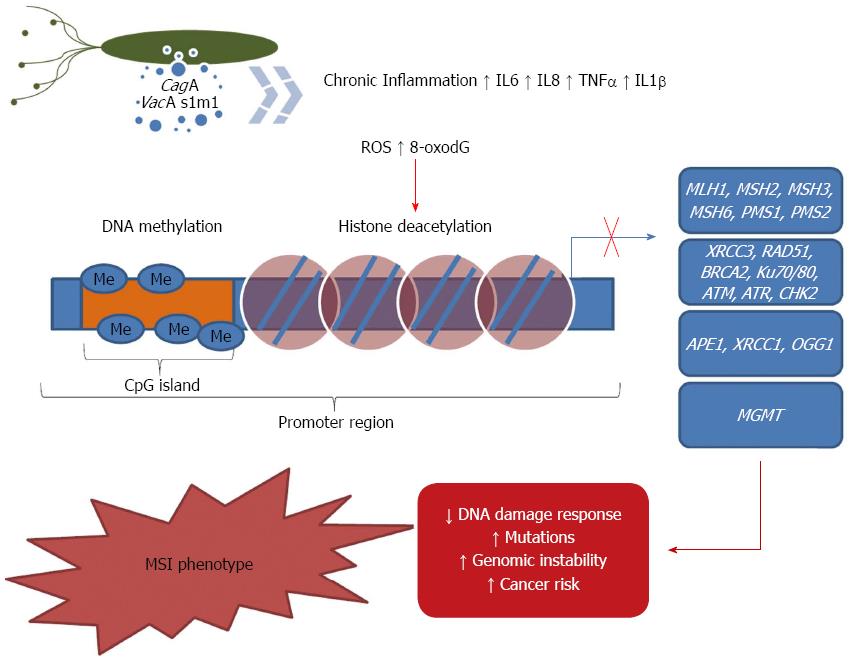
Figure 1 Proposed mechanism by which Helicobacter pylori induced epigenetic alteration affecting DNA repair.
The more virulent Helicobacter pylori strains (cagA and vacA s1m1) increase the inflammatory response, 8-oxodG and ROS production on epithelial cells. This landscape may cause the hypermethylation of CpG islands and/or the histone hypoacetylation, which results the in the DNA repair gene silencing. It might increase the mutation rate which may contribute to the genomic instability and gastric cancer development.
-
Citation: Santos JC, Ribeiro ML. Epigenetic regulation of DNA repair machinery in
Helicobacter pylori -induced gastric carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(30): 9021-9037 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i30/9021.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9021