Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2013; 19(38): 6408-6415
Published online Oct 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i38.6408
Published online Oct 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i38.6408
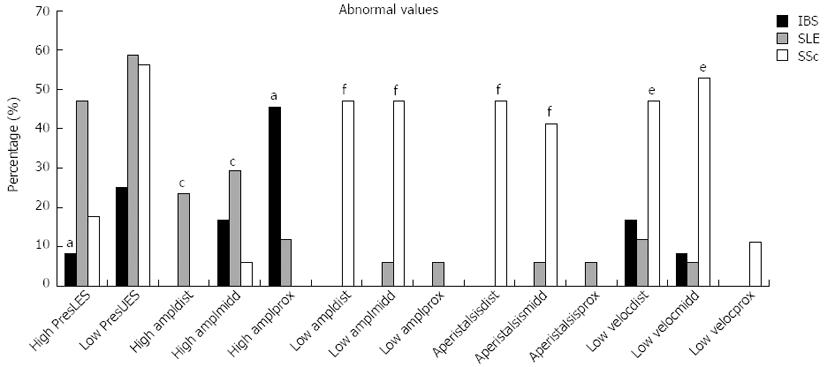
Figure 3 Comparative analysis of pathological manometric parameters in patients with irritable bowel syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis.
47.1% of SLE patients showed pressure of lower esophagus sphincter > 30 mmHg. 58.8% of SLE patients and 56.35% of SSc patients showed resting pressure of the upper esophagus sphincter < 40 mmHg. 23.5% of patients with SLE showed distal amplitudes > 160 mmHg and 29.4% middle amplitudes > 100 mmHg, whereas in the proximal part 45.5% of IBS patients had amplitudes > 60 mmHg. The majority of SSc patients showed as expected reduced peristaltic activity in the lower two thirds of esophagus. aP < 0.05 vs SLE and SSc; cP < 0.05 vs IBS and SSc; eP < 0.05, fP < 0.01 vs IBS and SLE. High PresLES: Pressure lower esophageal sphincter (LES) > 30 mmHg; Low PresUES: Pressure upper esophageal sphincter (UES) < 40 mmHg; High ampldist: Distal amplitude > 160 mmHg; High amplmidd: Middle amplitude > 100 mmHg; High amplprox: Proximal amplitude > 60 mmHg; Low ampldist: Distal amplitude < 50 mmHg; Low amplmidd: Middle amplitude < 40 mmHg; Low amplprox: Proximal amplitude < 30 mmHg; Low velocdist: Distal velocoty < 2 cm/s; Low velocmidd: Middle velocity < 2 cm/s; Low velocprox: Proximal velocity < 2 cm/s. IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome; SLE: Systemic lupus erythematosus; SSc: Systemic sclerosis.
- Citation: Thomaidis T, Goetz M, Gregor SP, Hoffman A, Kouroumalis E, Moehler M, Galle PR, Schwarting A, Kiesslich R. Irritable bowel syndrome and organic diseases: A comparative analysis of esophageal motility. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(38): 6408-6415
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i38/6408.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i38.6408