Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2007; 13(2): 244-249
Published online Jan 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.244
Published online Jan 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.244
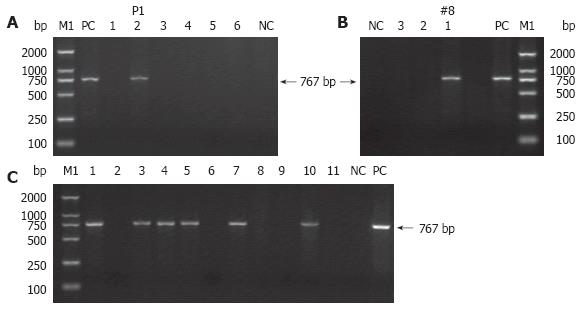
Figure 3 PCR detection of TyBS gene from genomic DNA of the potential transgenic founders (A and B) and subsequent generation(s) (C).
Lane M1: DL 2000 DNA Marker (TaKaRa); lane PC: positive control (TyBS as template); lane NC: negative control using genomic DNA from normal Kunming mice as template. The arrows indicate the positions of PCR products amplified by the primers shown in Figure 1. (A) Littermates (F0, six mice) were verified for the transgene presence by PCR analysis. Lanes 1-6: genomic DNA from the potential founder(s) of 6 littermates; Lane 2: 767-bp band amplified from genomic DNA of P1 with pigmentation in the eyes. (B) Littermates (F0, three mice) were confirmed for the transgene presence by PCR analysis. Lanes 1-3: genomic DNA from the potential founder(s) of three siblings. Lane 1: 767-bp band amplified from genomic DNA of #8 with pigmentation in the eyes. Other details are as in Figure 2G. (C) Littermates (F1, 11 mice) were examined for the transgene presence by PCR analysis. The founder P1 (♀) was crossed with normal Kunming mouse to produce 11 littermates (F1) with six mice with pigmented eyes. Lanes 1-11: genomic DNA from F1 offspring derived from P1; Lanes 1, 3-5, 7, 10: 767-bp specific band amplified from genomic DNA of F1 offspring exhibiting pigmented eyes.
- Citation: Xiao D, Yue Y, Deng XY, Huang B, Guo ZM, Ma Y, Lin YL, Hong X, Tang H, Xu K, Chen XG. Rescue of the albino phenotype by introducing a functional tyrosinase minigene into Kunming albino mice. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(2): 244-249
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i2/244.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.244