Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2007; 13(1): 48-64
Published online Jan 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.48
Published online Jan 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.48
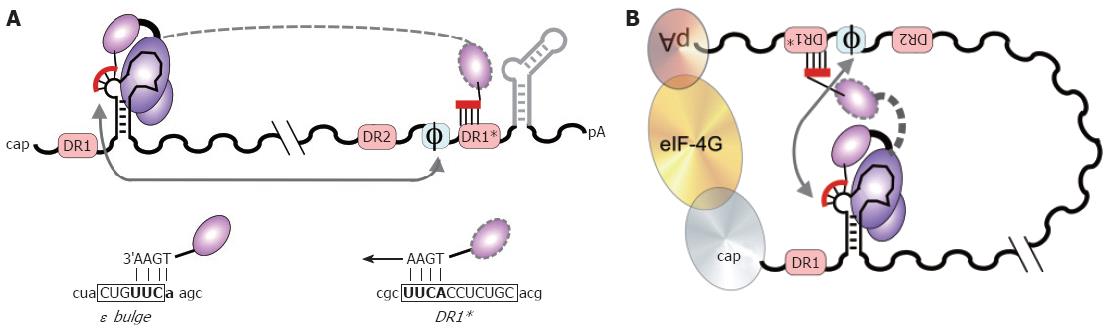
Figure 7 DNA primer translocation (first template switch).
P copies 3 to 4 nt from the 5´ ε bulge, yielding the TP-linked DNA oligonucleotide which is translocated to the complementary motif in the 3´ proximal DR1*. A: Linear representation. DR1* is nearly 3 kb apart from 5´ ε in primary sequence, and numerous other UUCA motifs are not used as acceptors. Φ denotes a newly identified cis-element with partial sequence complementarity to the 5´ half of ε. 3´ ε (light grey) is dispensable. The HBV specific sequences in the ε bulge, and in DR1* are shown below in capitals, flanking sequences in lower case; B: Models for juxtaposition of 5´ ε and DR1*. A general mechanism would be closed loop formation[80] of the pgRNA by cap-binding and poly-A binding factors (ovals), e.g. via elongation initiation factor 4G (eIF-4G; large oval). More specifically, ε might base-pair with Φ[146,147], as indicated by the grey arrows. In such an arrangement, a small movement, rather than a big jump, of TP with the bound DNA primer (dashed outline) would suffice for specific translocation to DR1*.
- Citation: Beck J, Nassal M. Hepatitis B virus replication. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(1): 48-64
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i1/48.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.48