Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2006; 12(45): 7380-7387
Published online Dec 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i45.7380
Published online Dec 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i45.7380
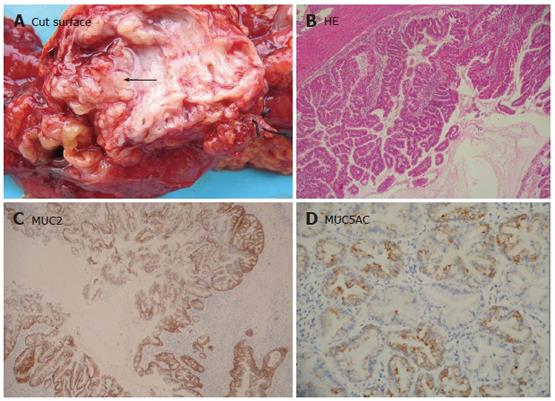
Figure 1 Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasia.
A: Sectioning of the pancreas revealing papillary tumors (arrow) with sticky mucin in dilated main panceatic ducts; B: Epithelial proliferative lesions that involve the main or secondary pancreatic duct showing a papillary architecture (HE × 40); C: MUC2 diffuse expression in papillary epithelial cells of intestinal type (Envison × 40); D: Focally stained MUC5AC in cytoplasm of gastric subtype tumor cells (Envison × 100).
- Citation: Ji Y, Lou WH, Jin DY, Kuang TT, Zeng MS, Tan YS, Zeng HY, Sujie A, Zhu XZ. A series of 64 cases of pancreatic cystic neoplasia from an institutional study of China. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(45): 7380-7387
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i45/7380.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i45.7380