Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2005; 11(43): 6765-6769
Published online Nov 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i43.6765
Published online Nov 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i43.6765
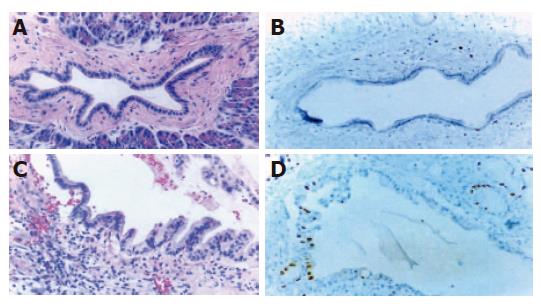
Figure 1 H&E and immunohistochemical staining of normal pancreatic and ductal hyperplasia tissues.
A: Normal interlobular duct surrounded by fibrous tissue is illustrated. Small cuboidal cells with basally located nuclei having intact nuclear polarity are seen in the inset. H&E stain, ×100; B: Ki-67 monoclonal Ab does not show reaction to almost epithelial cells. DAB and hematoxylin counter stain, ×100; C: Pancreatic duct hyperplasia with uniformly large columnar epithelial cells, which are more than twice as long as cytoplasm of normal cells and have mucinous metaplasia of the cytoplasm. The nuclei are small and basally located without atypia. H&E stain, ×100; D: Ki-67 monoclonal Ab shows a few proliferating nuclei of hyperplastic ductal epithelium. DAB and hematoxylin counter stain, ×100.
-
Citation: Jeong S, Lee DH, Lee JI, Lee JW, Kwon KS, Kim PS, Kim HG, Shin YW, Kim YS, Kim YB. Expression of Ki-67, p53, and K-
ras in chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(43): 6765-6769 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i43/6765.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i43.6765