Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2022; 28(35): 5141-5153
Published online Sep 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i35.5141
Published online Sep 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i35.5141
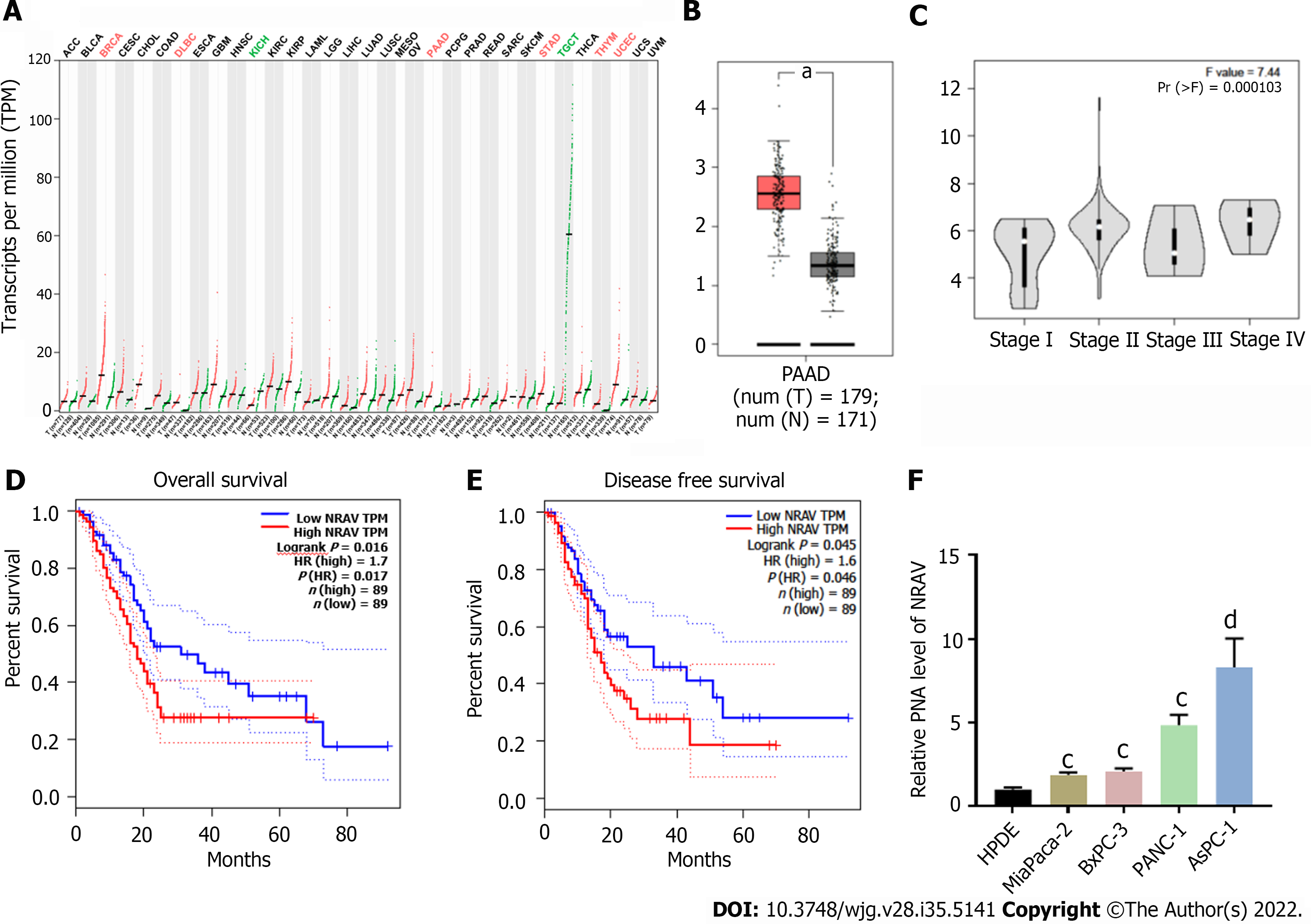
Figure 1 Relative expression of negative regulator of antiviral response in pancreatic cancer tissues and cells and its clinical significance.
A: The negative regulator of antiviral response (NRAV) expression profile across all tumor samples and paired normal tissues; B: The NRAV expression of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in tissues was significantly higher than that in normal pancreas tissues; C: Expression of NRAV in patients divided by cancer stages using expression data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database; D: Overall survival analyzed by GEPIA based on the TCGA database; E: Disease-free survival analyzed by GEPIA based on the TCGA database; F: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis measured NRAV expression level in four pancreatic cancer and normal cell lines. cP < 0.001; dP < 0.0001. PAAD: Pancreatic adenocarcinoma; TPM: Transcripts per million; NRAV: Negative regulator of antiviral response; HR: Hazard ratio.
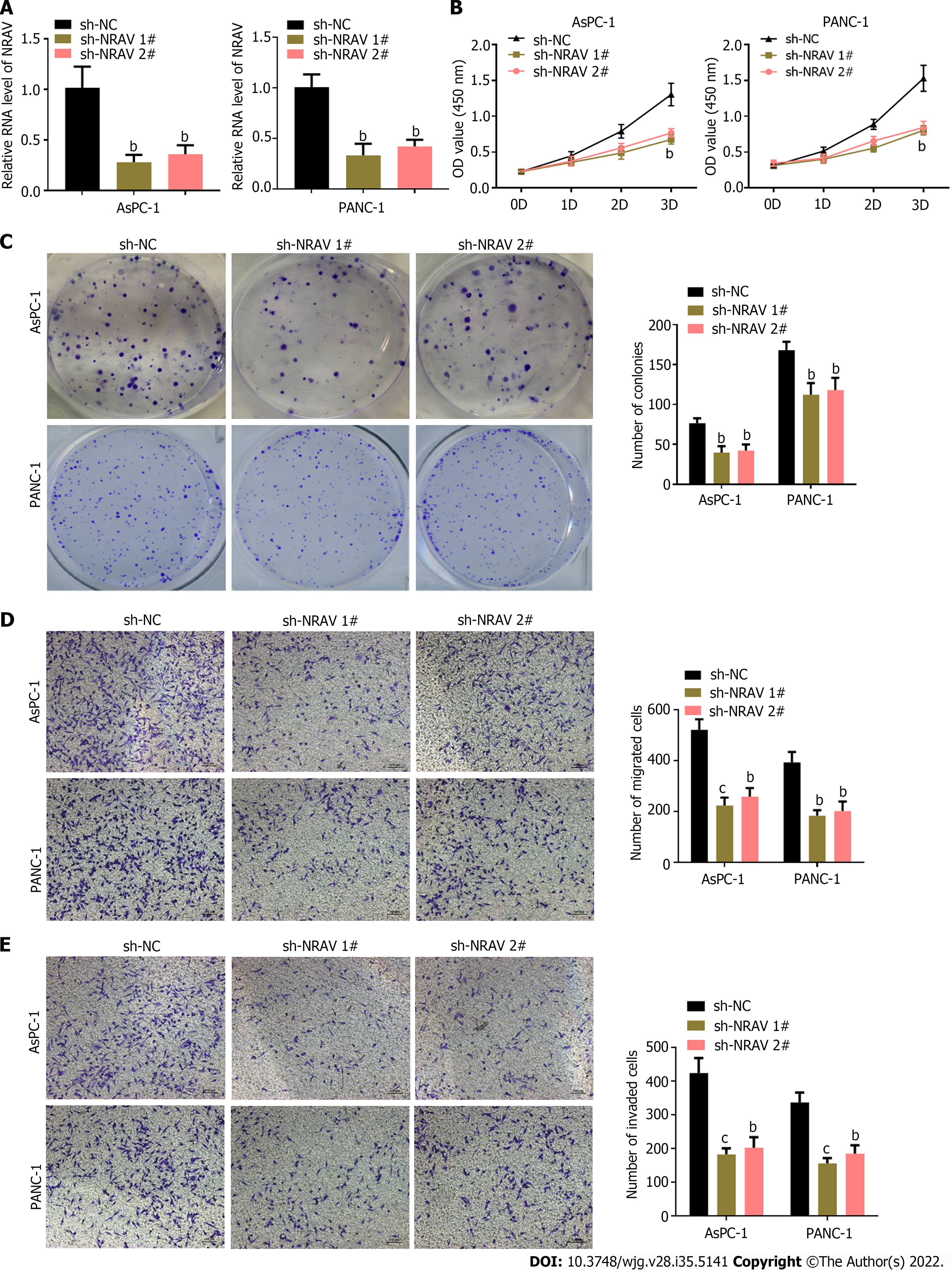
Figure 2 Knockdown of negative regulator of antiviral response inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells.
A: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis assessed expression of NRAV in PANC-1 and AsPC-1 cells transfected with shNC, shRNA #1 and shRNA #2 targeting negative regulator of antiviral response; B: Cell Counting Kit-8 analysis showed that compared with the NC group, NRAV gene knockout significantly reduced the proliferation of PANC-1 and AsPC-1 cells; C: The colony formation test showed that NRAV ablation inhibited the colony numbers of PANC-1 and AsPC-1 cells; D: Transwell assays were performed to measure migration of PANC-1 and AsPC-1 cells; E: Transwell assays were performed to measure invasion of PANC-1 and AsPC-1 cells. bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. NRAV: Negative regulator of antiviral response; sh: Short hairpin; NC: Negative control.
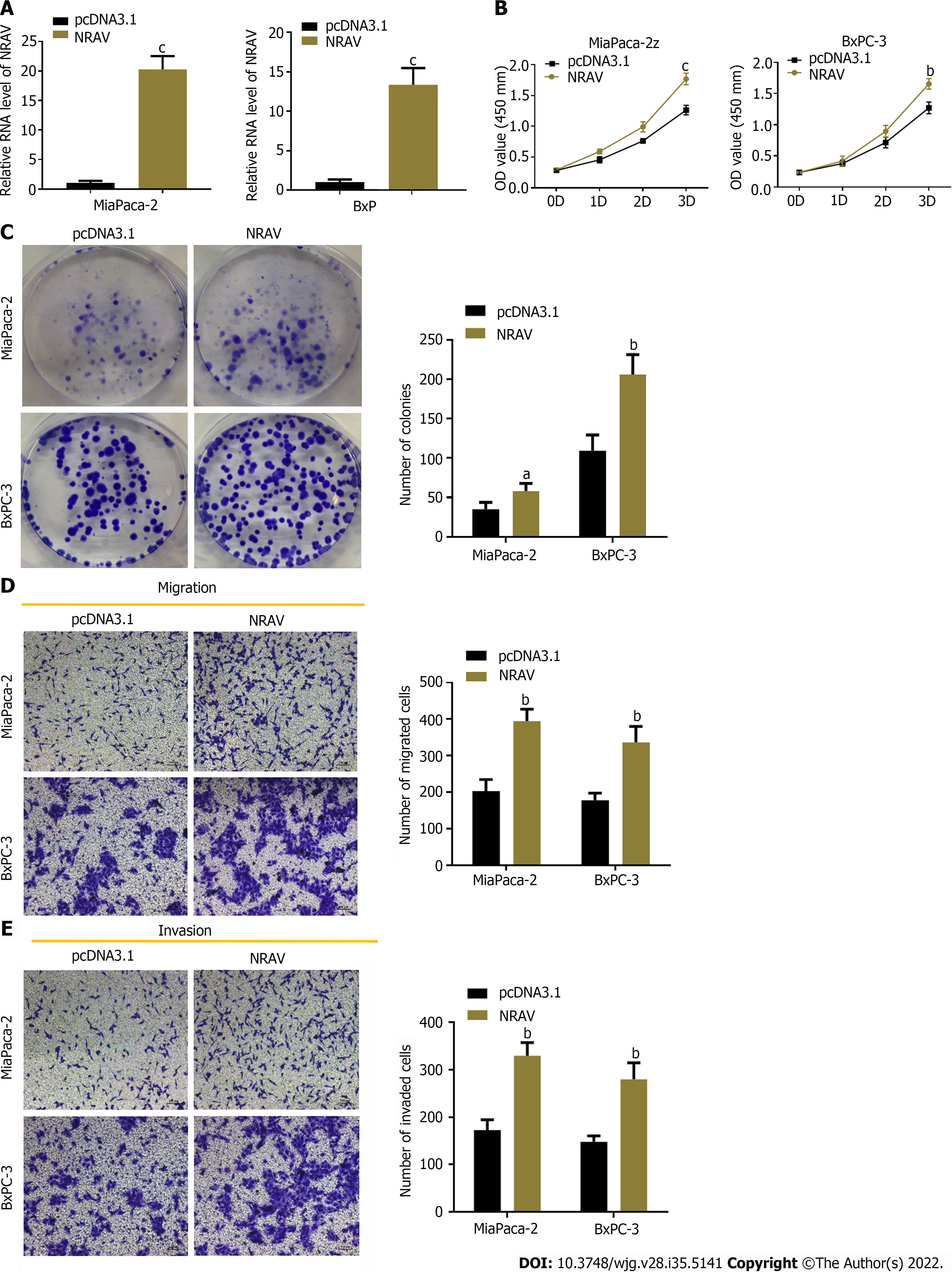
Figure 3 Overexpression of negative regulator of antiviral response promoted pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion.
A: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction measured negative regulator of antiviral response (NRAV) expression in Mia Paca-2 and BxPC-3 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1 empty vector or pcDNA3.1-NRAV; B: Cell Counting Kit-8 was performed to detect proliferation of Mia Paca-2 and BxPC-3 cells; C: Colony formation test showed that NRAV overexpression increased the number of clones of Mia-Paca-2 and BXPC-3 cells; D: Transwell assays were performed to measure migration of Mia Paca-2 and BxPC-3 cells; E: Transwell assays were performed to measure invasion of Mia Paca-2 and BxPC-3 cells. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. NRAV: Negative regulator of antiviral response.
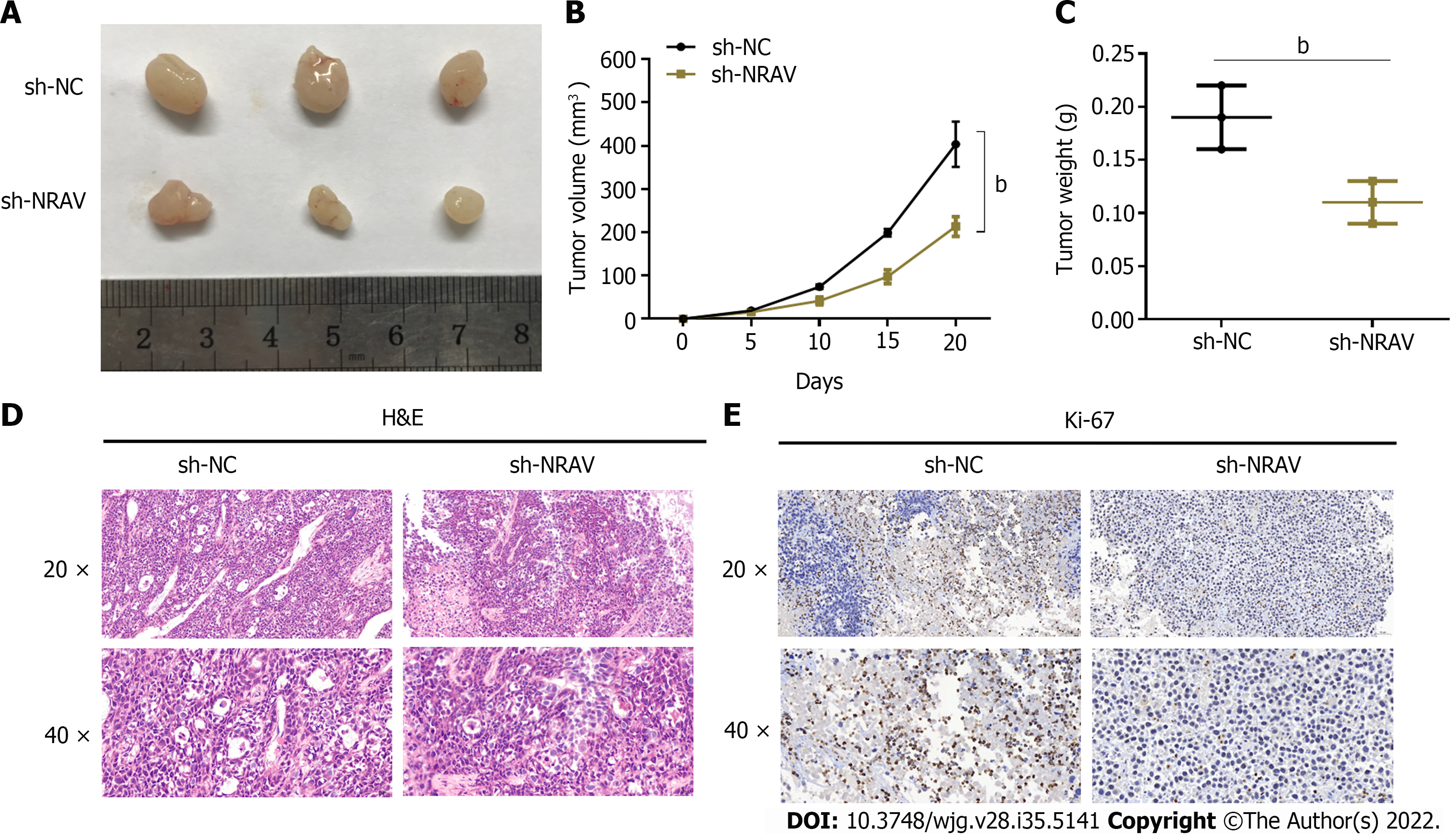
Figure 4 Negative regulator of antiviral response ablation inhibited tumor growth in a mouse xenograft models.
A: Representative images of xenograft tumors after transfection with short hairpin NC or sh-negative regulator of antiviral response (NRAV); B: Tumor volume was measured; C: Tumor weight was measured; D: Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin staining for xenograft tumor tissue samples; E: Expression pattern of Ki-67 in the harvested tumor tissues was detected by immunohistochemical staining. bP < 0.01. sh: Short hairpin; NRAV: Negative regulator of antiviral response; NC: Negative control.
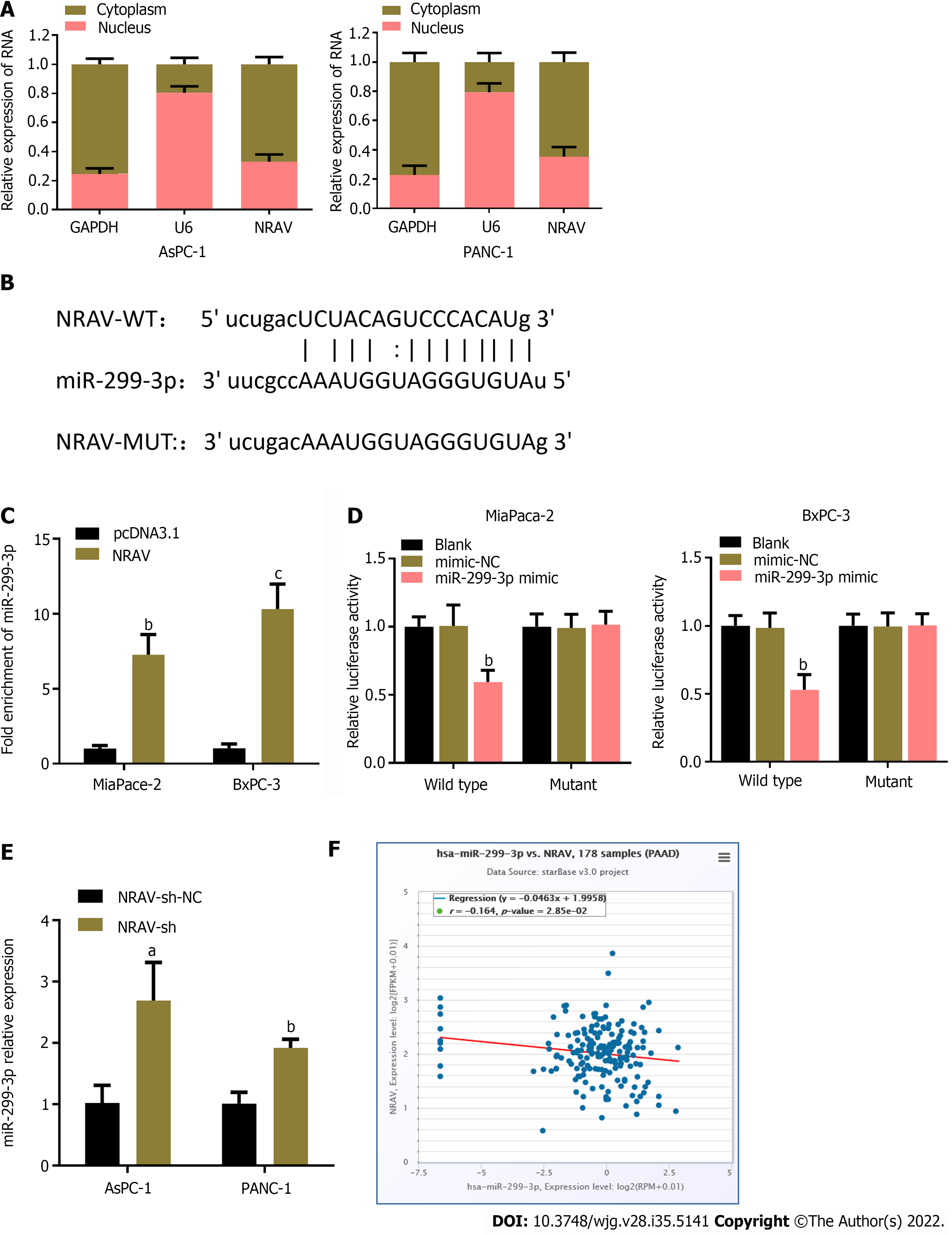
Figure 5 Negative regulator of antiviral response acted as a molecular sponge for miR-299-3p.
A: Subcellular fractionation assay was used to determine the subcellular localization of NRAV; B: A complementary binding site of NRAV in miR-299-3p was predicted via starBase v3.0 online database; C: RNA immunoprecipitation assays were performed to validate whether NRAV could interact with miR-299-3p in MiaPaca-2 and BxPC-3 cells; D: Luciferase reporter assays were carried out to verify the direct binding of NRAV and miR-299-3p in MiaPaca-2 and BxPC-3 cells; E: Relative expression of miR-299-3p in AsPC-1 and PANC-1 cells following knockdown of NRAV; F: Spearman’s correlation analysis between NRAV and miR-299-3p expression in PAAD by the starBase v3.0 project. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. NRAV: Negative regulator of antiviral response; MUT: Mutant; NC: Negative control; WT: Wild-type.
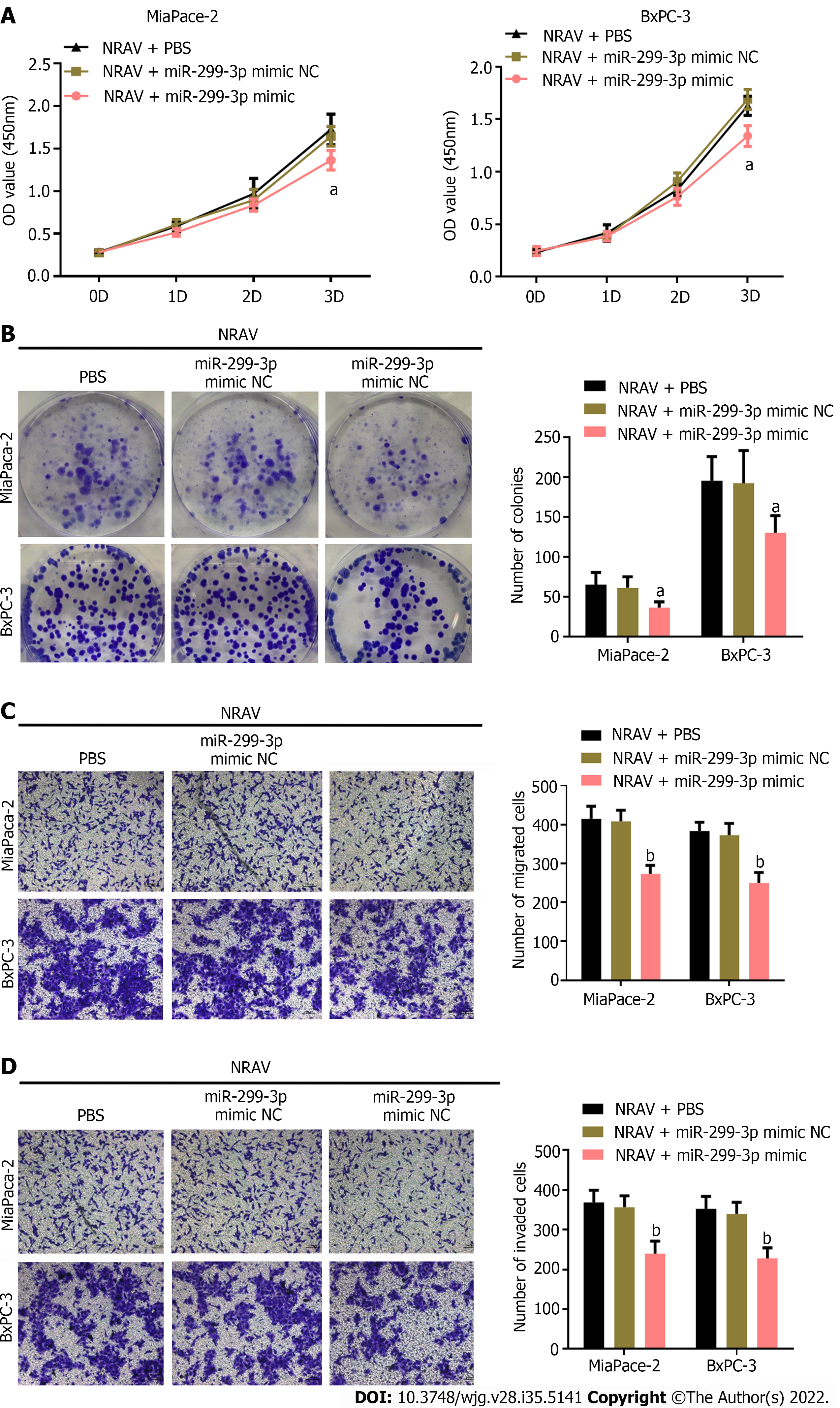
Figure 6 miR-299-3p reversed the effect of negative regulator of antiviral response on pancreatic cancer cells.
A: Viability of MiaPaca-2 and BxPC-3 cells was determined following transfection with pcDNA3.1-NRAV and miR-299-3p mimic by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay; B: Proliferation of MiaPaca-2 and BxPC-3 cells was detected by colony formation assay; C: Transwell assays of cell migration was performed in MiaPaca-2 and BxPC-3 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1-NRAV and miR-299-3p mimic; D: Transwell assays of cell invasion were performed in MiaPaca-2 and BxPC-3 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1-NRAV and miR-299-3p mimic. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. NRAV: Negative regulator of antiviral response; NC: Negative control; PBS: Phosphate-buffered saline.
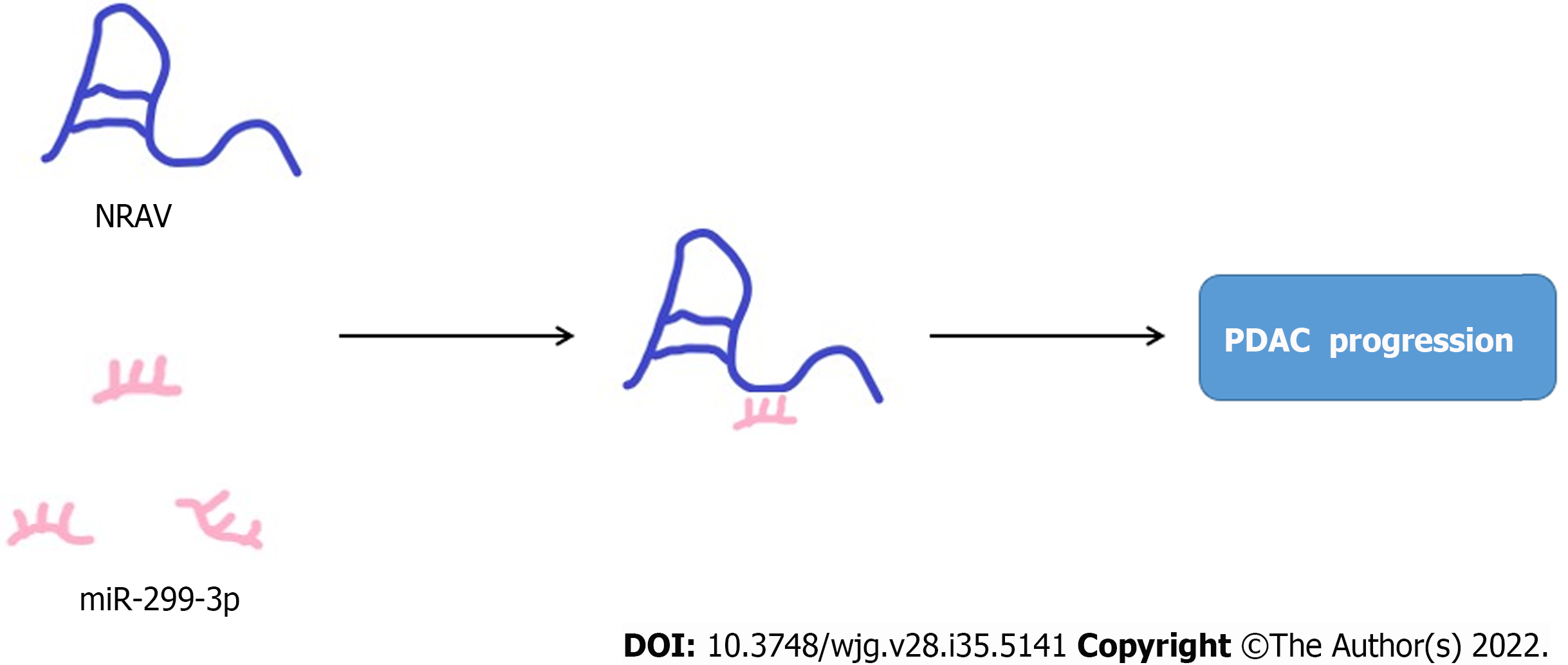
Figure 7 Negative regulator of antiviral response plays the role of miR-299-3p molecular sponge to promote the progress of pancreatic ductal cancer.
- Citation: Wang HQ, Qian CH, Guo ZY, Li PM, Qiu ZJ. Long noncoding RNA negative regulator of antiviral response contributes to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression via targeting miR-299-3p. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(35): 5141-5153
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i35/5141.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i35.5141