Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2020; 26(3): 366-374
Published online Jan 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i3.366
Published online Jan 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i3.366
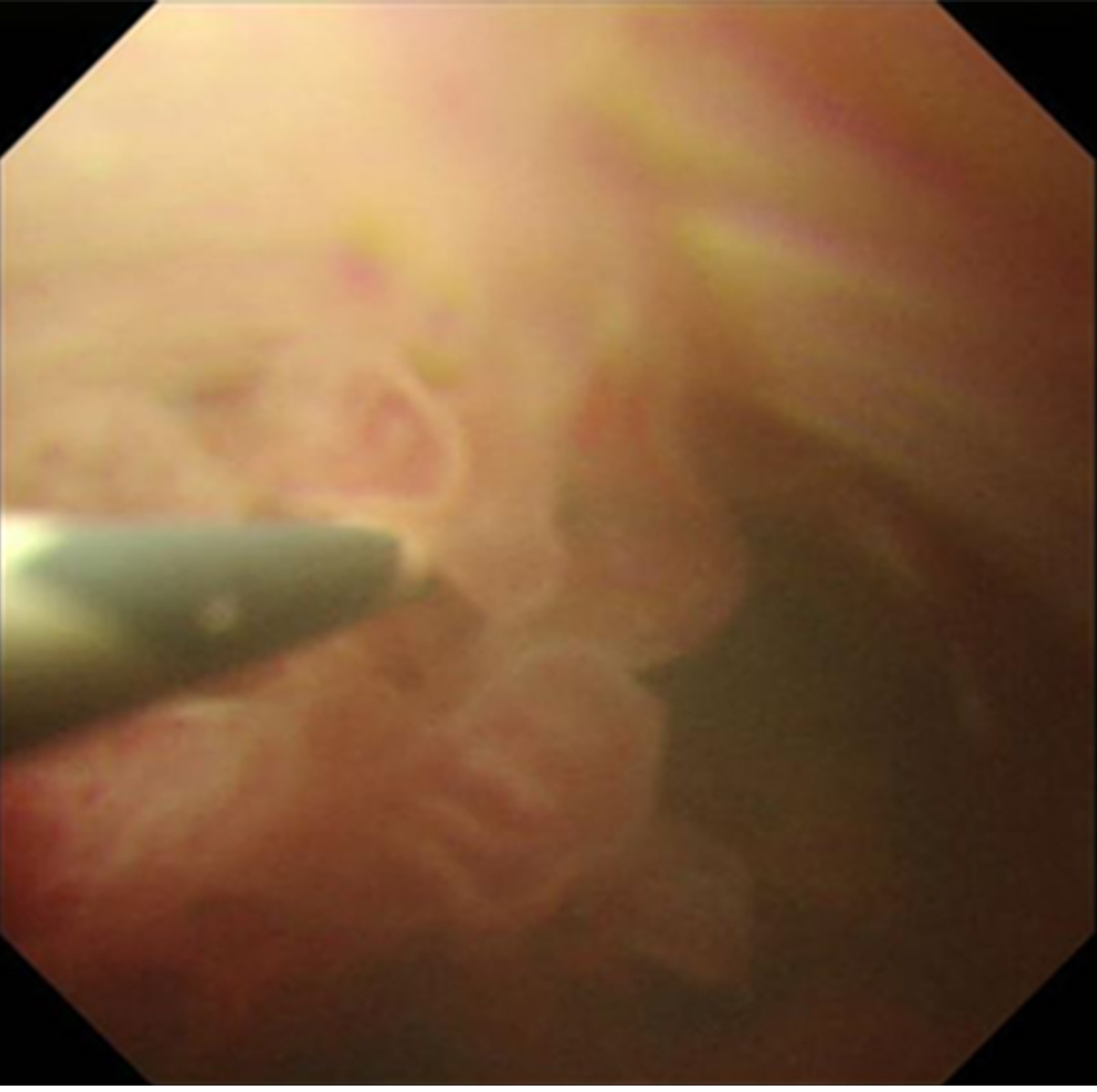
Figure 1 Peroral cholangioscopy findings: Biliary papillomatosis in the common bile duct.
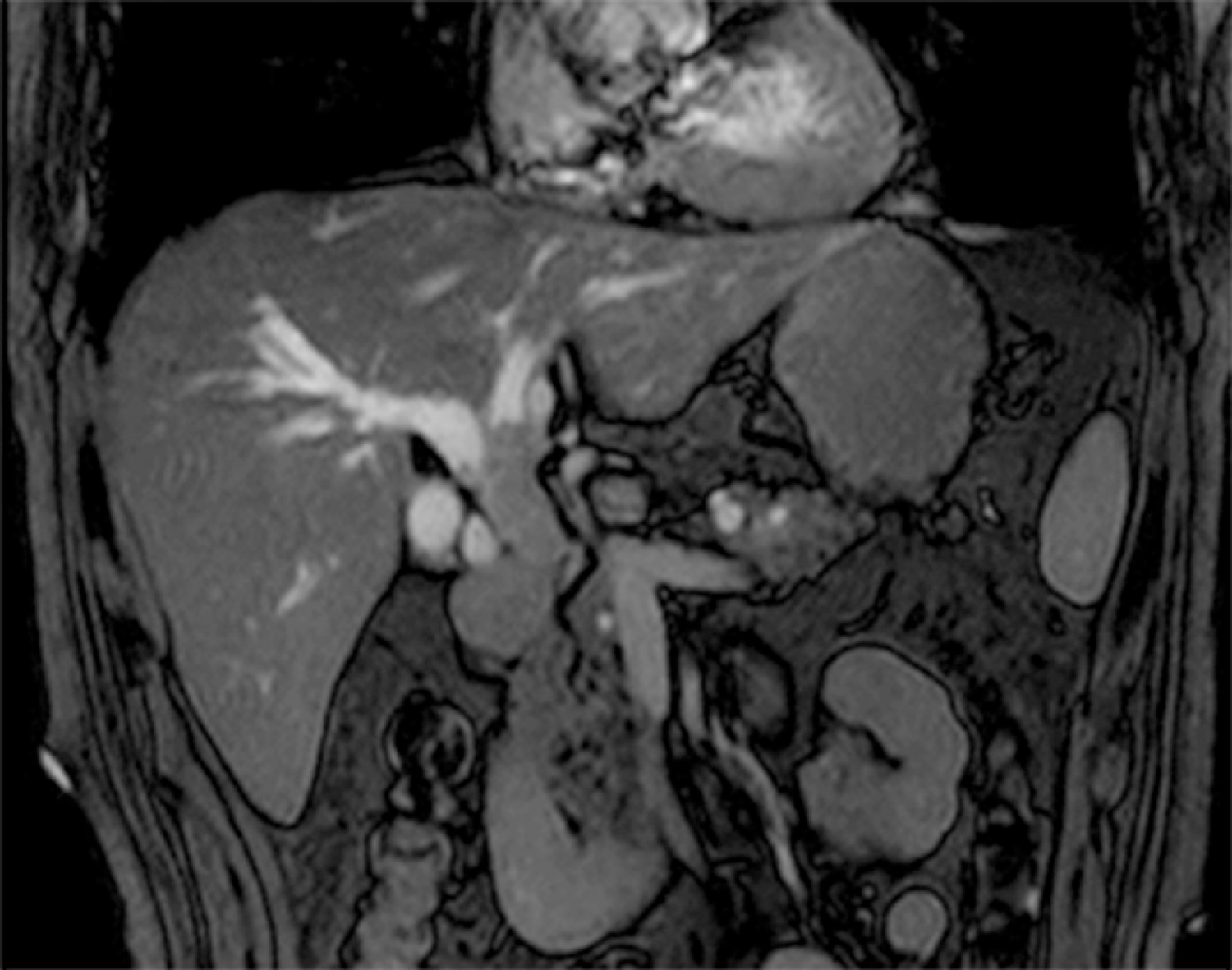
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging revealed extensively dilated bile ducts due to an intraluminal lesion located in the common bile duct.
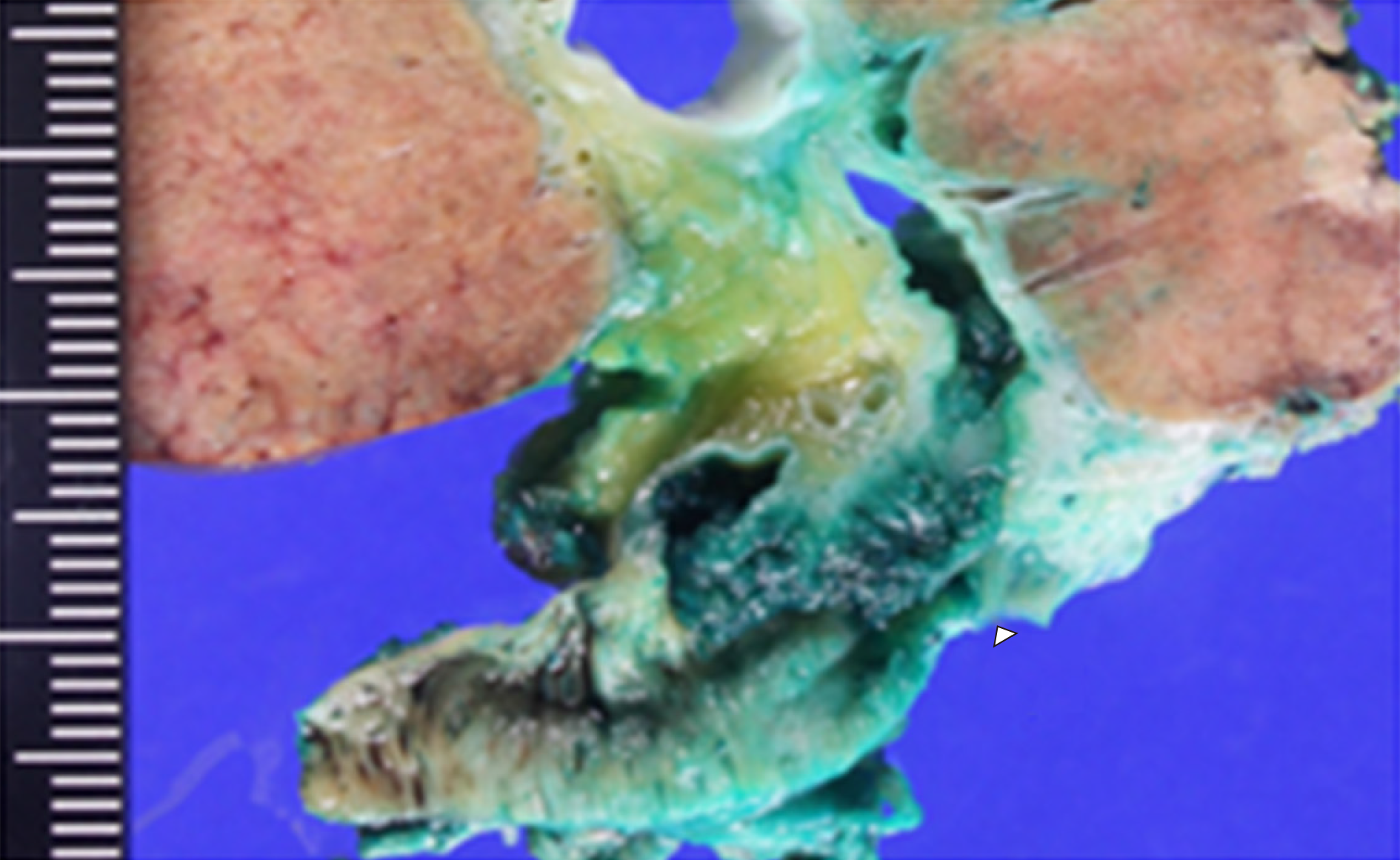
Figure 3 Macroscopic findings showed a papillary tumor of the bile duct (arrowhead).
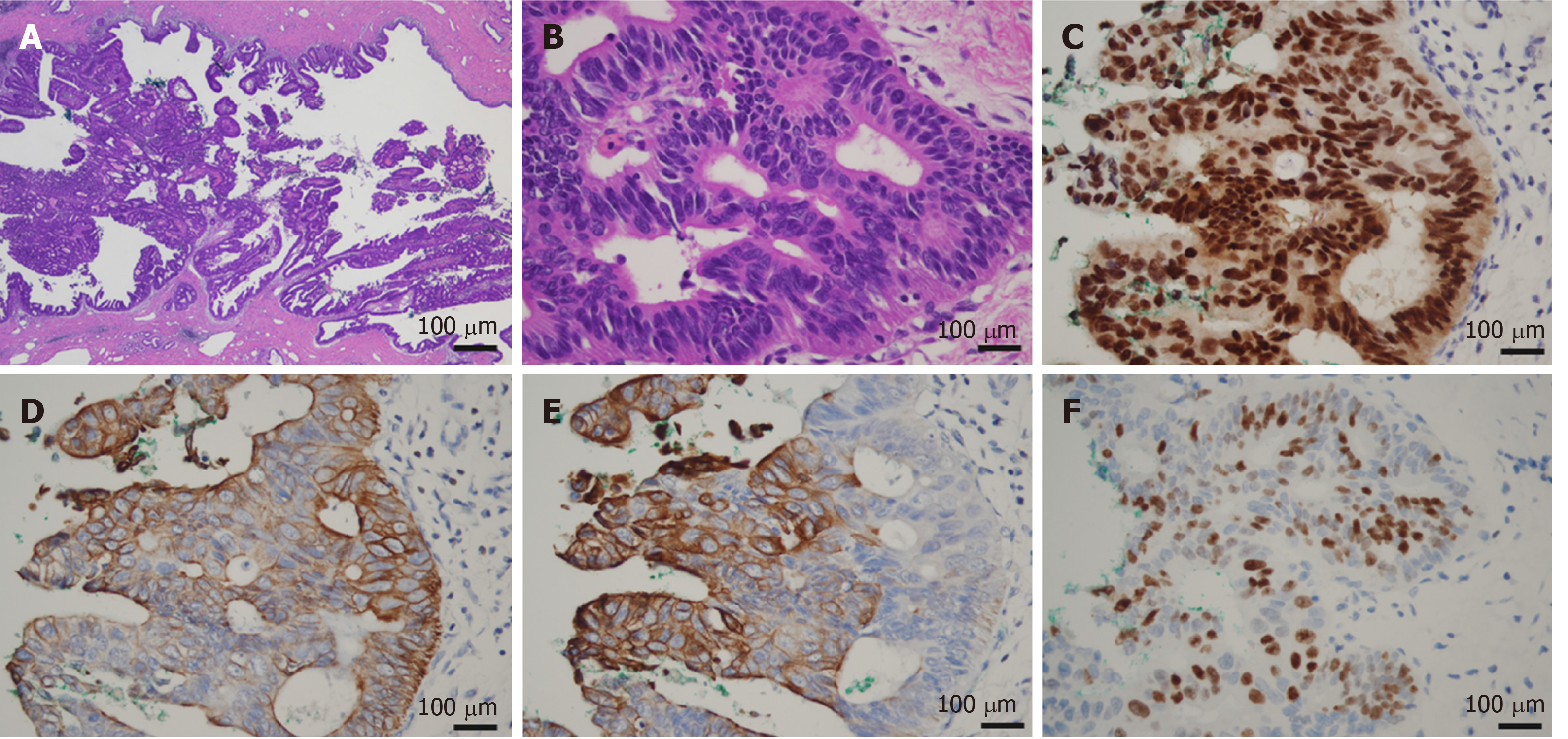
Figure 4 Microscopic findings of the bile duct tumor.
A: The tumor showed the intraductal papillary proliferation of columnar cells with a high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio; B: These neoplastic cells were entirely confined within the duct, and no invasion was identified (A: magnification × 20, B: magnification × 400); C-F: Immunohistological staining showed that the tumor cells were positive for CDX2, CK7, CK20, and Ki67.
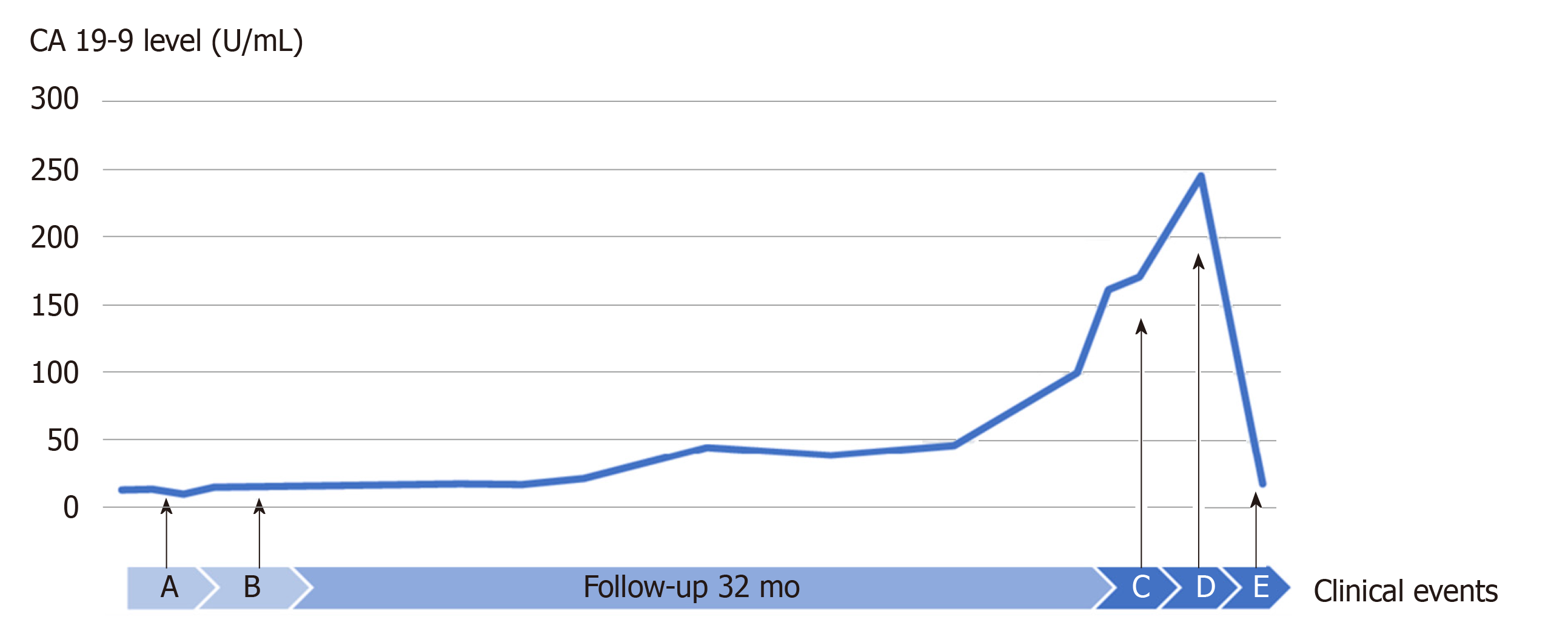
Figure 5 Variation in the CA 19-9 level in correlation with clinical events.
Time A (2015 December): Diagnosis of intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct T1N0M0; Time B (2016 January): Good prognosis with satisfactory postoperative pathological findings, such as high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia pattern without an invasive component, R0 resection, no extended metastasis, lymph node (-) and ascites cytology (-); Time C (2018 September): Detection of suspected metastatic adenocarcinoma of bile duct origin with a 26 mm lung tumor, a 12 mm brain tumor and a 4-fold higher level of CA 19-9; Time D (2018 November): VATS lobectomy and SRT for brain tumor; and Time E (2019 January): Stable condition with normal level of CA 19-9.
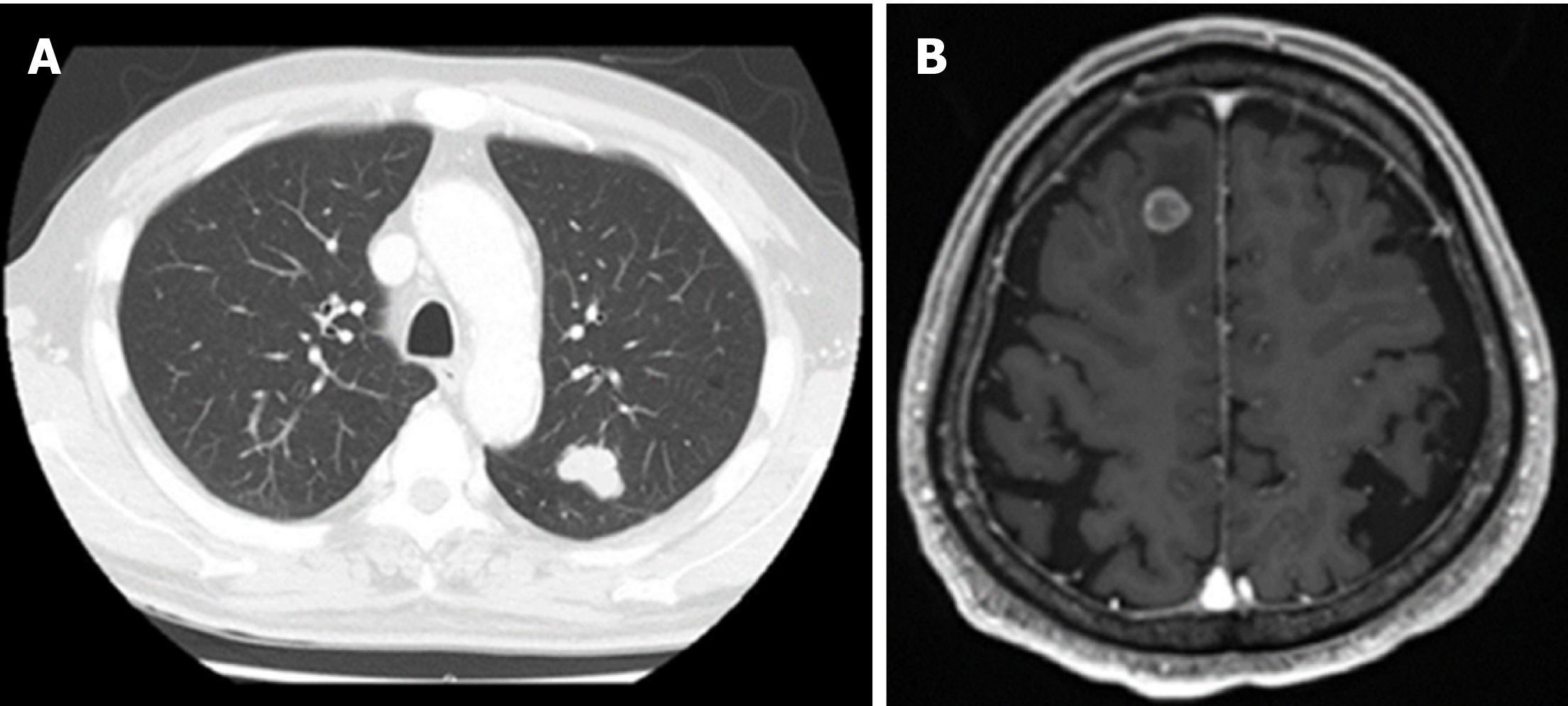
Figure 6 Magnetic resonance imaging of a metastatic lung tumor in the left upper lobe (A) and suspected metastatic brain tumor on the right frontal lobe (B).
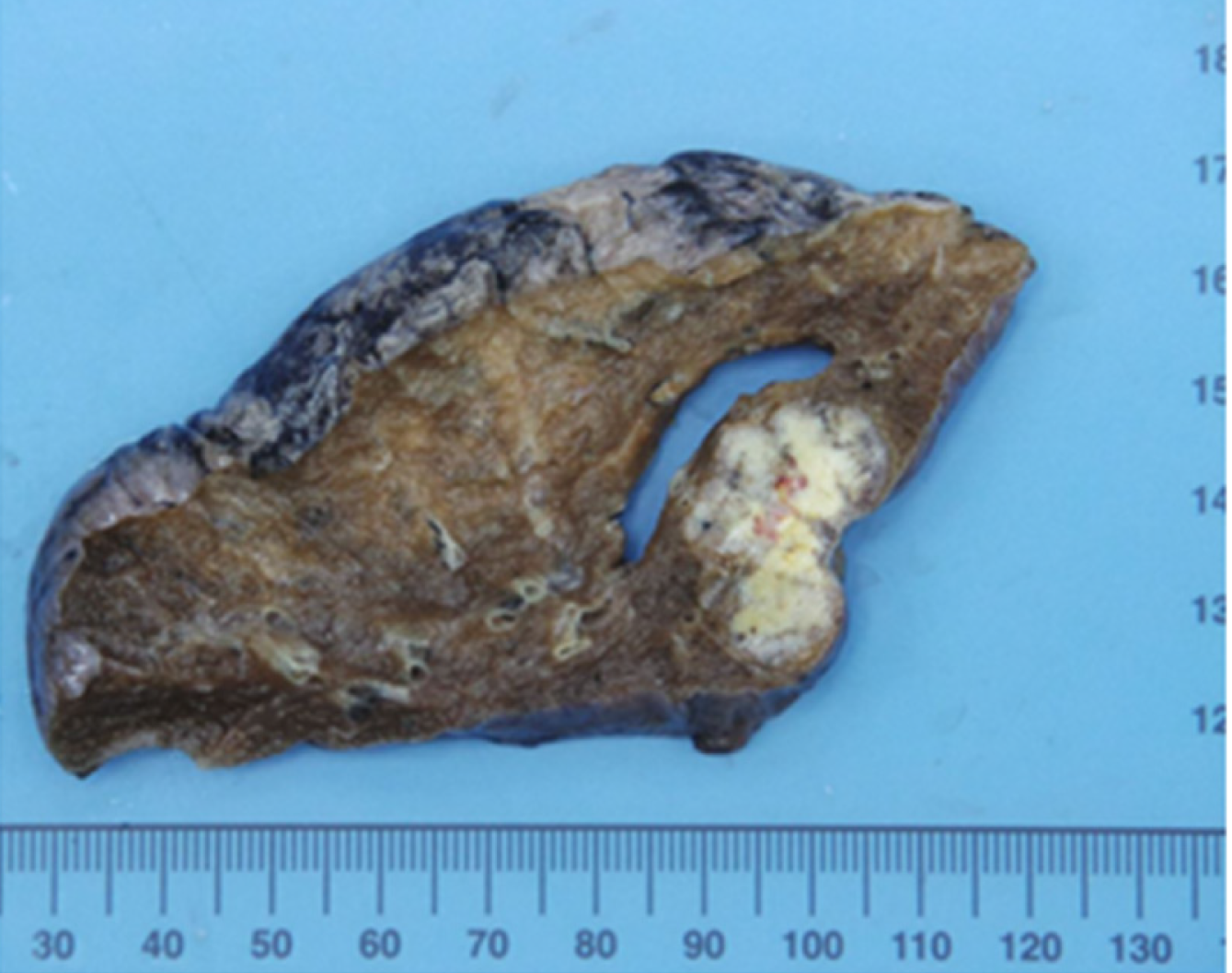
Figure 7 Macroscopic findings of lung-resected specimens.
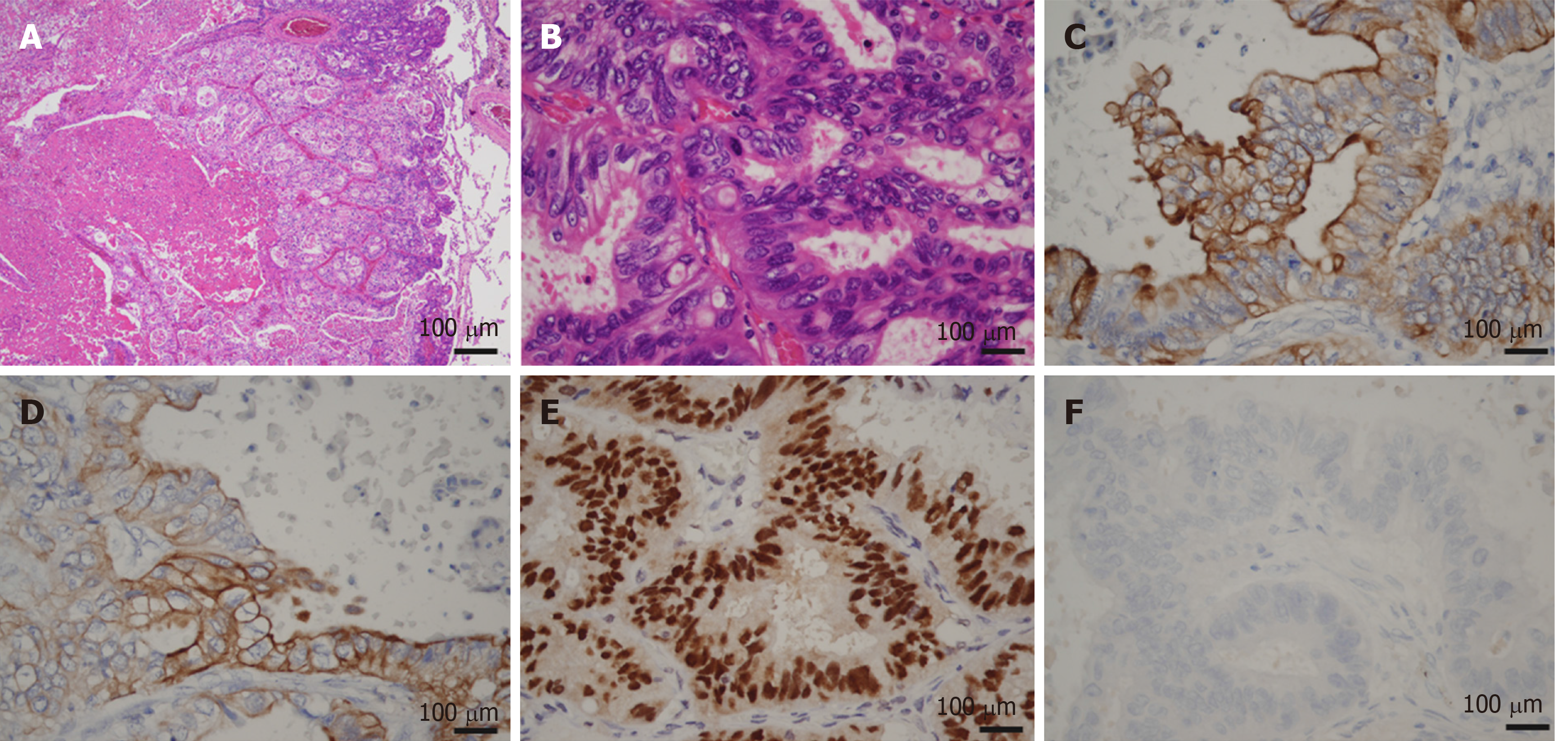
Figure 8 Microscopic images of lung metastasis.
A and B: Histologic appearance showed a well-demarcated nodule with marked necrosis in the center of the tumor (A: magnification × 20, B: magnification × 400). At high power magnification, there were eosinophilic, tall, columnar cells with nuclear pseudostratification. C-E: Immunohistological staining showed that the tumor cells were positive for CK7 (Panel C), CK20 (Panel D) and CDX2 (Panel E); F: Immunohistological staining showed that the tumor cells were negative for TTF-1.
- Citation: Nam NH, Taura K, Kanai M, Fukuyama K, Uza N, Maeda H, Yutaka Y, Chen-Yoshikawa TF, Muto M, Uemoto S. Unexpected metastasis of intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct without an invasive component to the brain and lungs: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(3): 366-374
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i3/366.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i3.366