Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2016; 22(34): 7767-7777
Published online Sep 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i34.7767
Published online Sep 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i34.7767
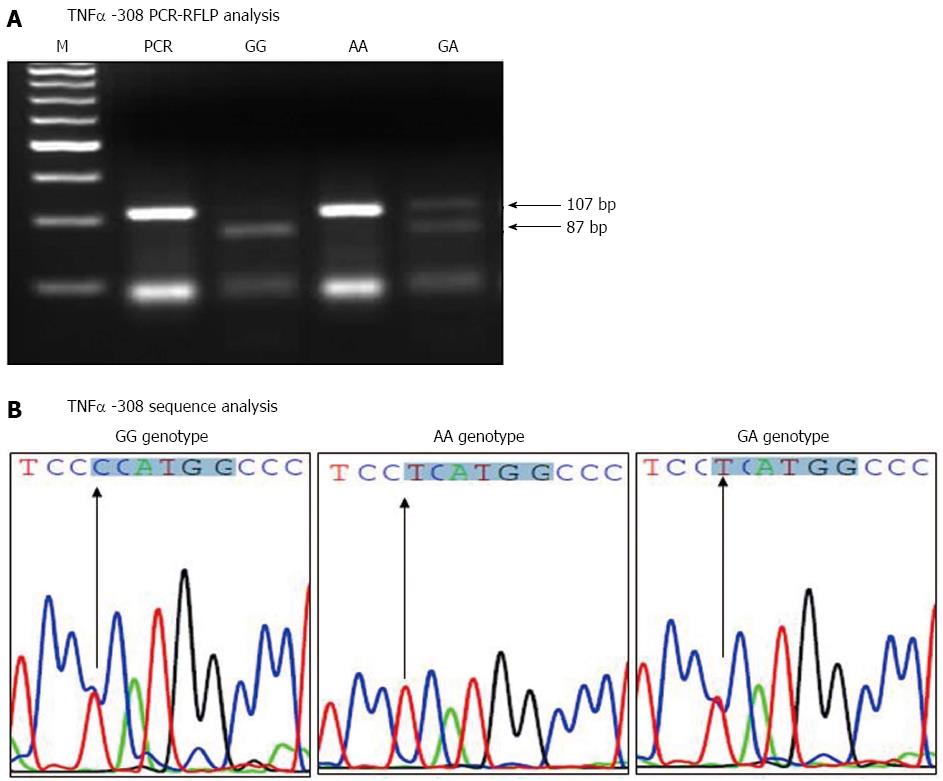
Figure 1 Tumor necrosis factor α -G308A polymorphism analysis.
A: TNFα -308 PCR-RFLP analysis, genomic DNA was extracted, amplified by PCR, digested with NcoI restriction enzyme and run on a 4% agarose gel. Lanes 1, 2, 3 and 4 correspond to PCR products before digestion, GG homozygote (87 bp), AA homozygote (107 bp) and GA heterozygote (107 and 87 bp) respectively. B: TNFα -308 PCR sequence analysis, the PCR products of different TNFα -308 genotypes were purified and sequenced using the reverse primer. The NcoI restriction site is highlighted and the arrow points to the single nucleotide polymorphism. TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; RFLP: Restriction fragment length polymorphism.
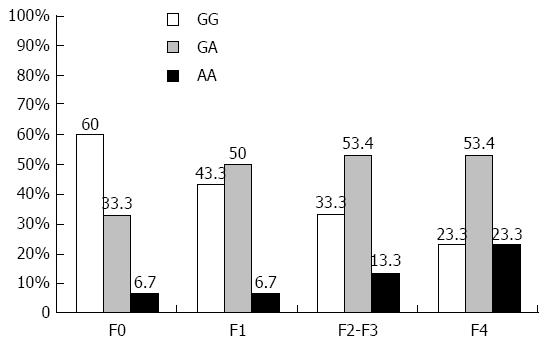
Figure 2 Distribution of tumor necrosis factor α -G308A polymorphism in hepatitis C virus infected patients with different fibrosis grade (F0-F4).
Genotyping of TNFα -G308A was conducted for 120 chronic HCV patients (F0-F4) using PCR-RFLP analysis. The different TNFα -G308A genotypes were represented as percentages and compared among HCV patients with different fibrosis grades: F0 (n = 30), F1 (n = 30), F2-F3 (n = 30), F4 (n = 30). TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; RFLP: Restriction fragment length polymorphism.
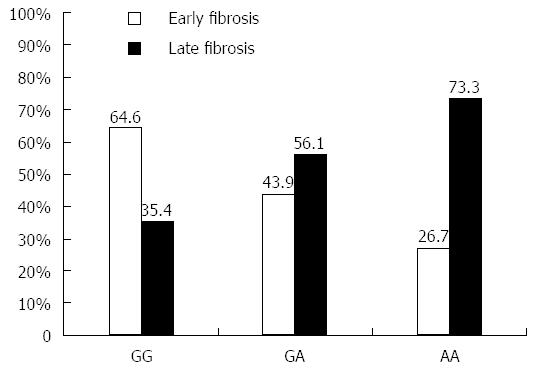
Figure 3 Frequency of each tumor necrosis factor α -308 genotype in early and late hepatitis C virus fibrosis patients.
Genotyping of TNFα -G308A was conducted in 120 chronic HCV patients (F0-F4) using PCR-RFLP analysis. The frequency of each genotype (GG, GA, AA) was calculated as percentage and compared in early (F0-F2, n = 60) and late (F2-F4, n = 60) HCV fibrosis patients. TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; RFLP: Restriction fragment length polymorphism.
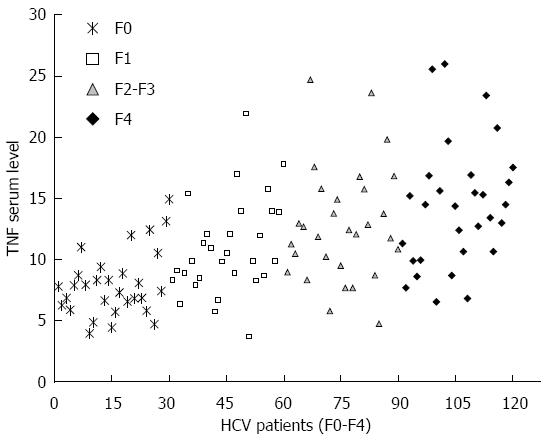
Figure 4 Tumor necrosis factor α serum level in 120 chronic hepatitis C virus patients (F0-F4).
The circulating TNFα level was determined using ELISA in 120 chronic HCV patients with different fibrosis grades: F0 (n = 30), F1 (n = 30), F2-F3 (n = 30), F4 (n = 30). TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; ELISA: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
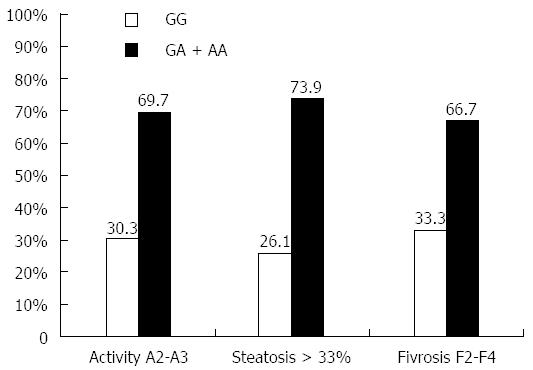
Figure 5 Effect of different tumor necrosis factor α genotypes on liver pathological parameters (inflammation, steatosis and fibrosis).
The effect of high expressing TNFα genotypes (GA + AA) were statistically compared with the low expressing TNFα genotype (GG), and the results showed strong effect of (GA + AA) genotypes on liver inflammation (P = 0.007), steatosis (P = 0.005) and fibrosis (P = 0.032). P≤ 0.05 is considered significant while P≤ 0.01 is highly significant. TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
- Citation: Bader El Din NG, Farouk S, El-Shenawy R, Ibrahim MK, Dawood RM, Elhady MM, Salem AM, Zayed N, Khairy A, El Awady MK. Tumor necrosis factor-α -G308A polymorphism is associated with liver pathological changes in hepatitis C virus patients. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(34): 7767-7777
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i34/7767.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i34.7767