Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2007; 13(19): 2649-2654
Published online May 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i19.2649
Published online May 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i19.2649
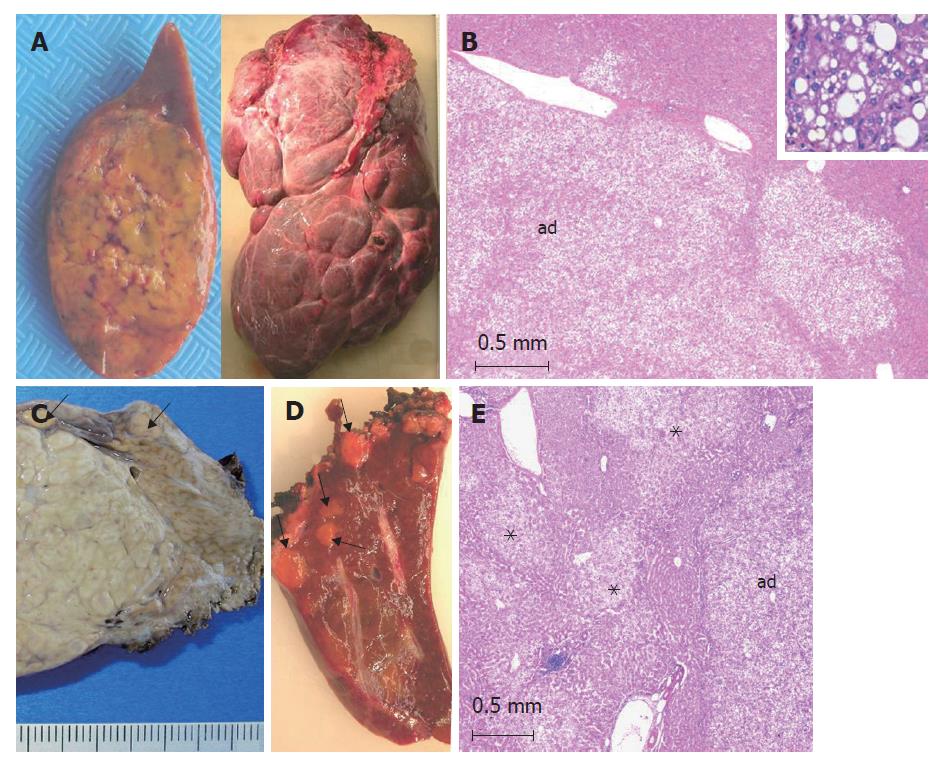
Figure 1 HNF1α-mutated adenomas (from different cases).
A: left: single, yellowish HCA; right: a massive form involving the whole right lobe made of several numerous adjacent nodules of different sizes; B: typical aspect of a steatotic HCA (ad) with a lobulated contour. Inset: HCA at a higher magnification showing macro and microvesicular steatosis (HE); C: left: part of a large focal nodular hyperplasia (indication of surgery), nearby small adenomas (arrows) discovered by chance on the surface of the liver (corresponding to a somatic HNF1α-mutated adenomatosis). D: several yellow microadenomas in a somatic HNF1α-mutated adenomatosis; E: multiple not well limited steatotic microadenomas (asterix) nearby a larger adenoma (ad) in a patient with a constitutional HNF1α-mutated adenomatosis.
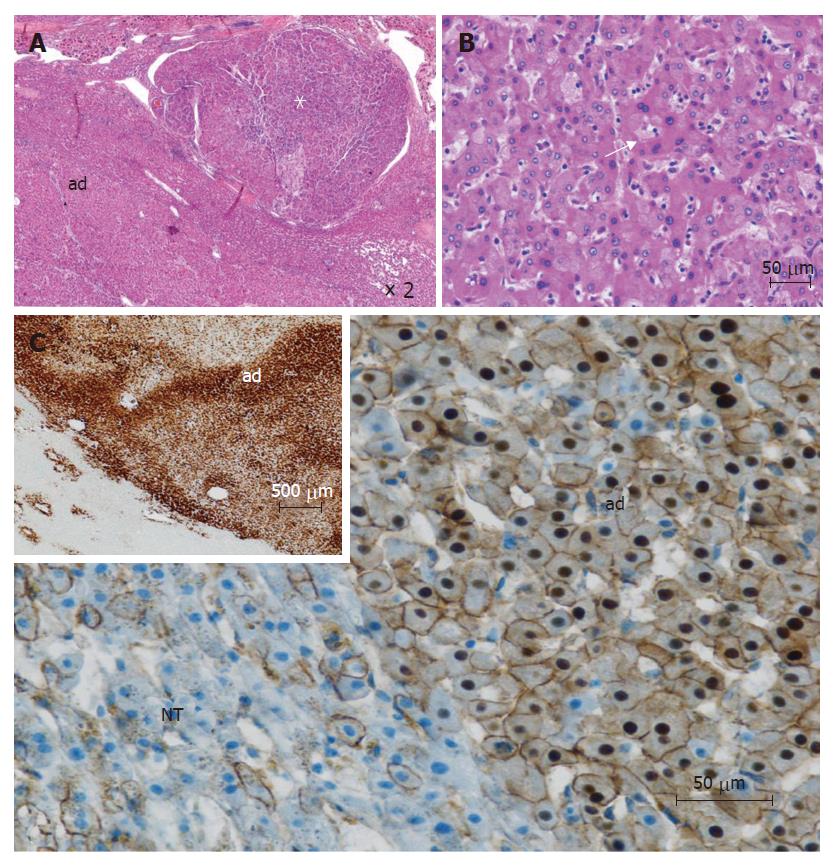
Figure 2 β-catenin mutated adenomas (from different cases).
A: This tumor is composed of 2 parts: an adenoma (ad) and a hepatocellular carcinoma (white asterix) (HE); B: In this adenoma, some irregular nuclei and acinar arrangements are seen (white arrow) (HE); C: immunohistochemistry: cytoplasmic and nuclear overexpression of β-catenin in adenoma (ad), contrasting with normal membranous staining in adjacent non tumoral liver (NT); Inset (upper left): homogeneous immunostaining with glutamine synthetase in adenoma (ad), contrasting with normal staining of pericentral hepatocytes (lower left).
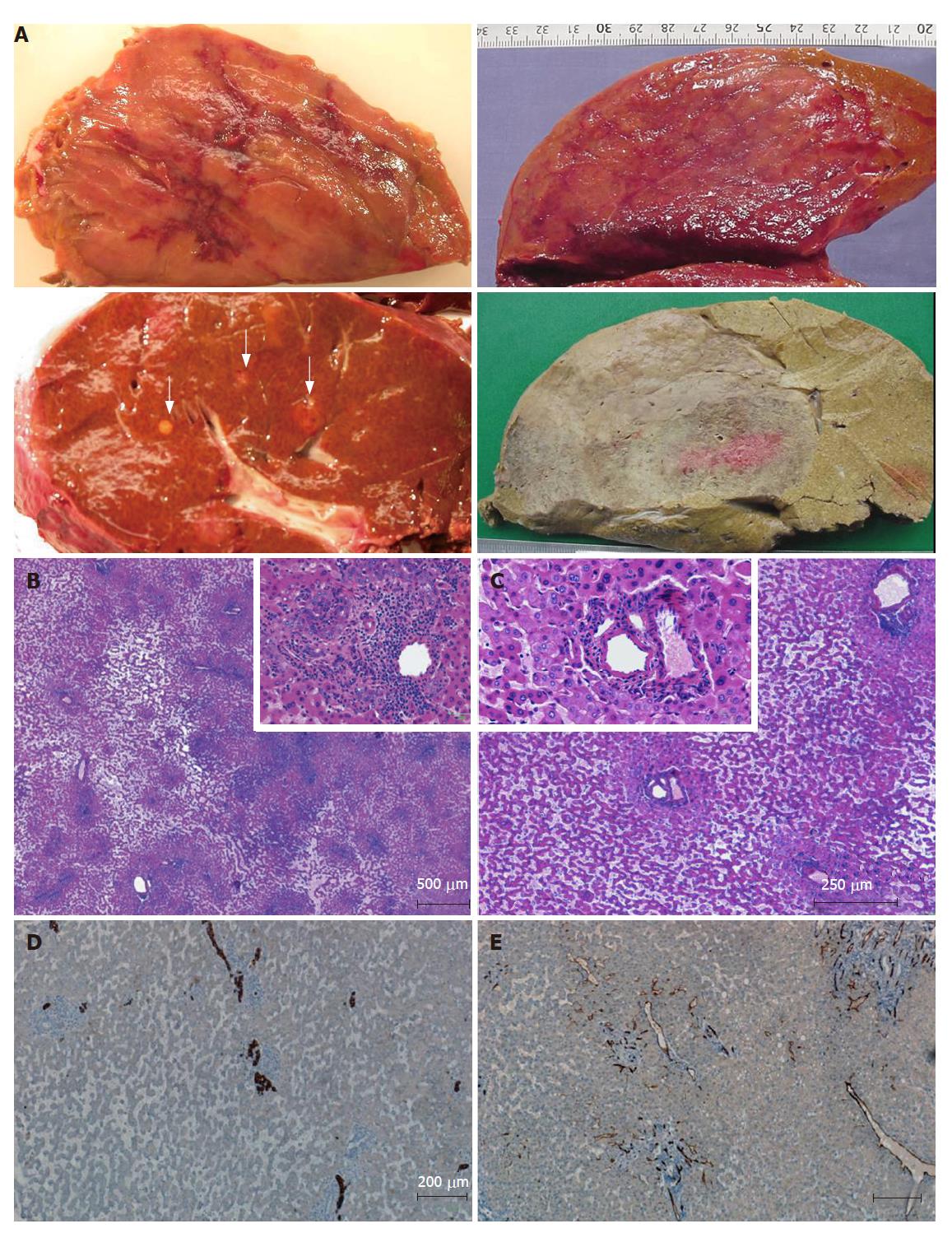
Figure 3 Inflammatory/telangiectatic adenomas (from different cases).
A: several sections of adenomas showing different aspects. Upper left: hemorrhagic areas in the center of the tumor; lower left: several micronodules (white arrows) in a patient with a large inflammatory/telangiectatic adenoma (not shown); upper right: this massive adenoma is difficult to identify on fresh tissue; the same is more easily identified after fixation (lower right); B, C and insets: typical aspects with obvious telangiectasia and inflammatory infiltrates (B) around thick arteries (C) (HE); D: some ductular reaction is visible on cytokeratin 7 immunostaining; E: CD34 immunostaining highlights capillarized sinusoids around arteries.
- Citation: Bioulac-Sage P, Blanc JF, Rebouissou S, Balabaud C, Zucman-Rossi J. Genotype phenotype classification of hepatocellular adenoma. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(19): 2649-2654
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i19/2649.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i19.2649