Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Methodol. Dec 14, 2018; 8(4): 51-58
Published online Dec 14, 2018. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v8.i4.51
Published online Dec 14, 2018. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v8.i4.51
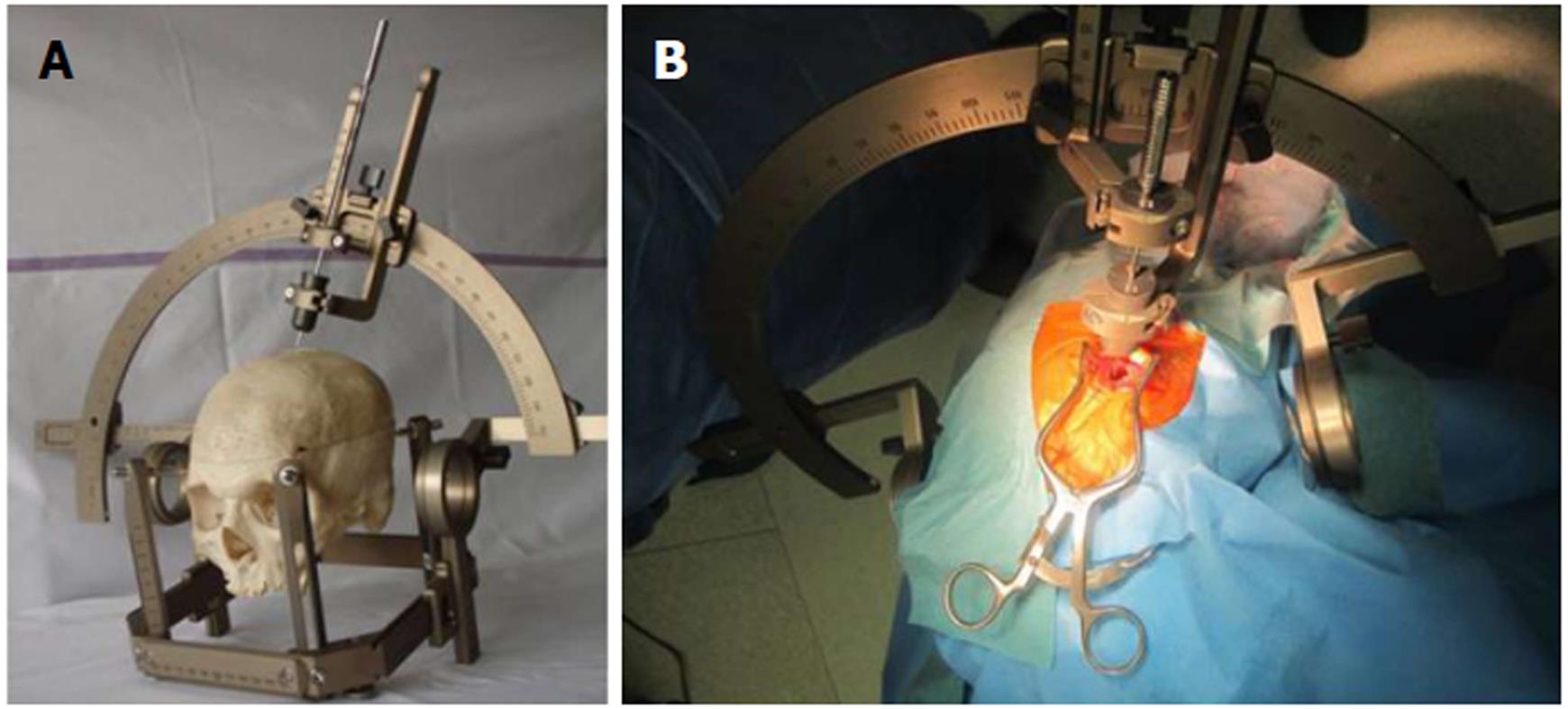
Figure 1 An illustration of the stereotactic biopsy procedure.
A: A stereotactic frame (Leksell, Sweden) is mounted on the skull, and a probe is inserted through a previously drilled burr hole into the brain parenchyma, the tip of the probe reaching the lesion of interest; B: A stereotactic procedure in surgical practice with the tip inserted.
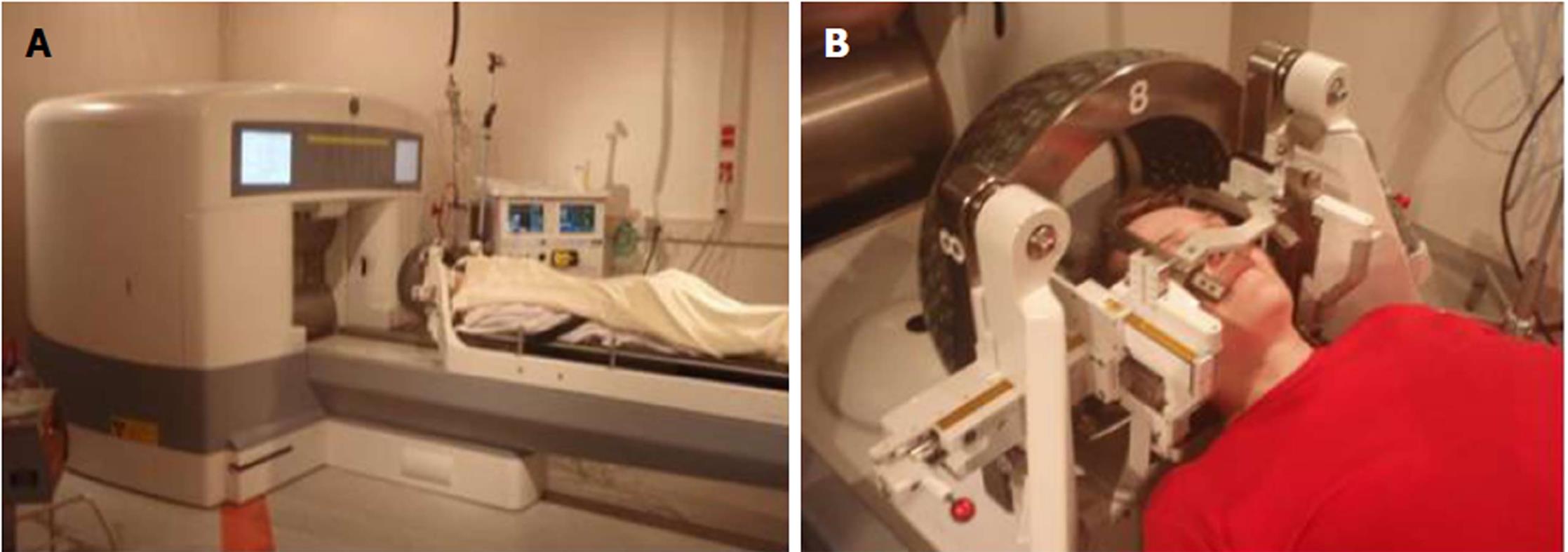
Figure 2 Positioning of the patient.
A: Gamma knife and the patient position before the treatment procedure; B: Sources of radioactive cobalt are hidden in the in the “helmet” of the gamma knife, which is located over the patient’s head.
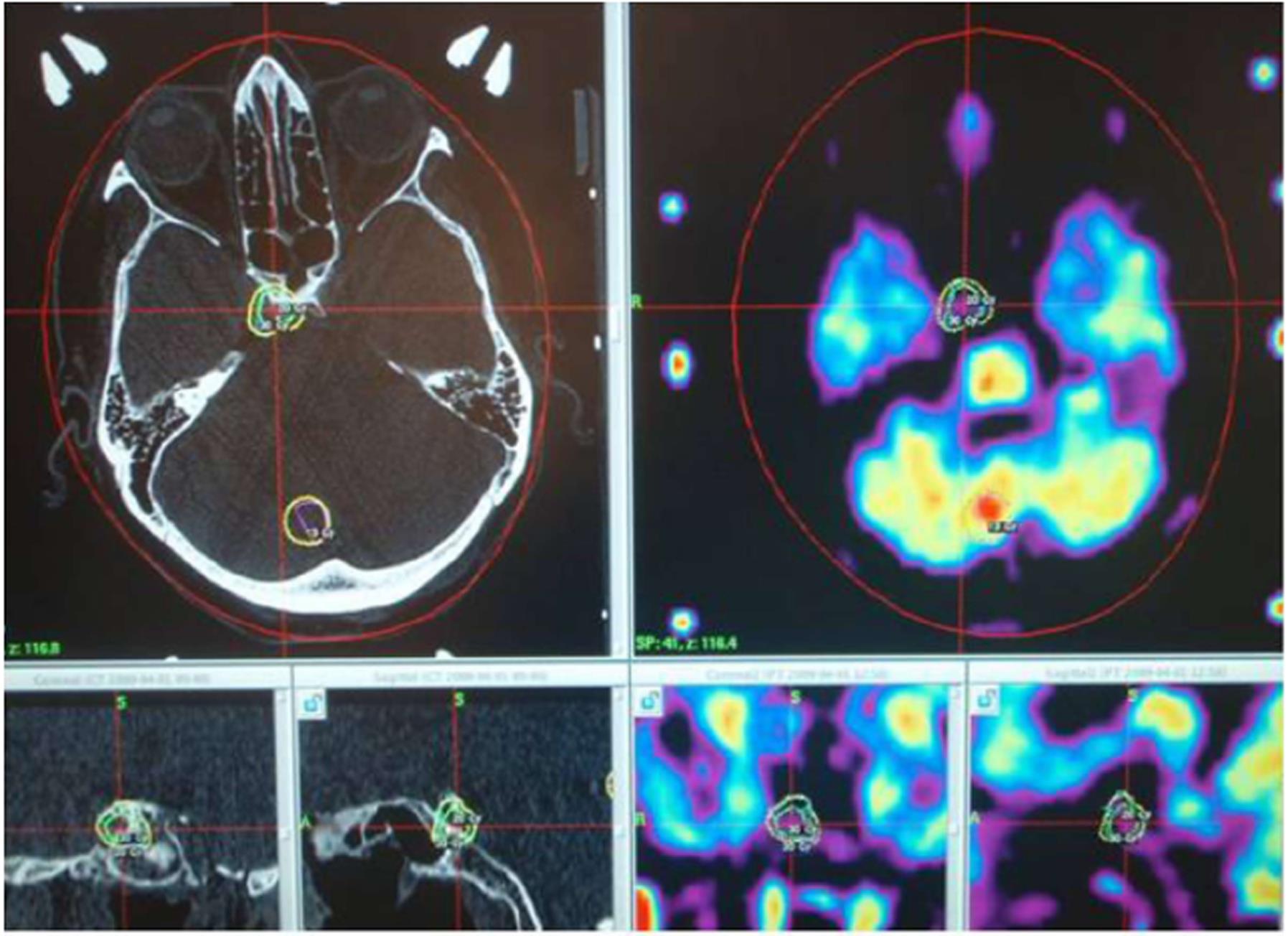
Figure 3 An example of computer planning for irradiation procedure of a residual pituitary adenoma, which was not completely removed from the parasellar space during a transnasal approach.
In the upper row are the axial views of CT and MRI-PET images with the tumor location. In the lower row from left to right: the frontal and sagittal views of CT and MRI-PET images. CT: Computed tomography; MRI-PET: Magnetic resonance imaging - positron emission tomography.
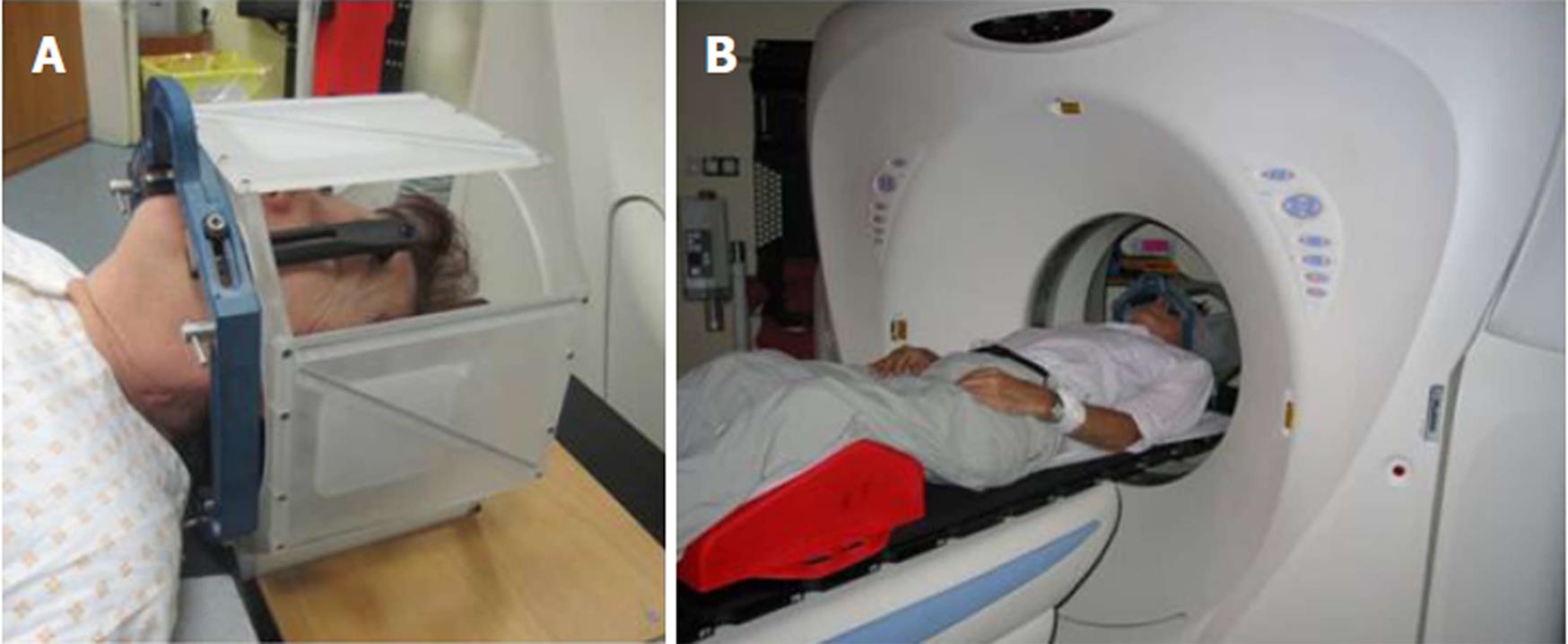
Figure 4 The stereotactic frame.
A: The stereotactic frame (BrainLab, Germany) with the localizer cube attached, mounted on the patient’s head with four screws that fix the frame onto the skull bone; B: The patient is brought into the CT machine prior to the combined CT imaging with the frame. CT: Computed tomography.
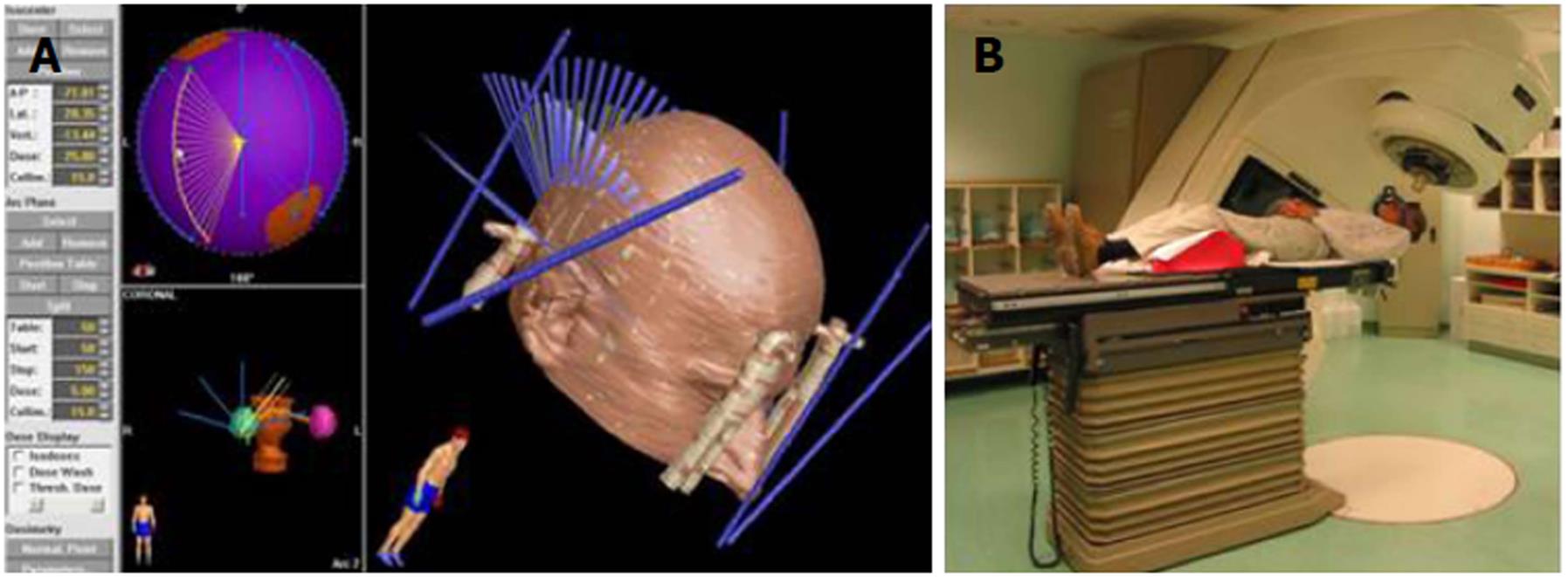
Figure 5 Irradiation with a linear accelerator.
A: A computer irradiation plan showing a localizer cube attached to the stereotactic frame (thick blue lines) (right image) and the direction of irradiation of the intracranial lesion with X-rays (thin blue lines). Small images on the left show the location of two intracranial lesions that are going to be irradiated; B: The patient is resting on the table with the head fixed in the stereotactic frame. The bed and gantry rotate about various axes, and this allows for irradiation by means of multiple trajectories intersecting at a certain point.
- Citation: Velnar T, Bosnjak R. Radiosurgical techniques for the treatment of brain neoplasms: A short review. World J Methodol 2018; 8(4): 51-58
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v8/i4/51.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v8.i4.51