Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Nephrol. Sep 6, 2016; 5(5): 461-470
Published online Sep 6, 2016. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v5.i5.461
Published online Sep 6, 2016. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v5.i5.461
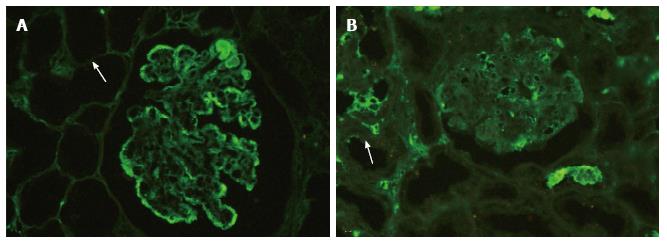
Figure 1 Examples of technically adequate and inadequate digestion.
A: Immunofluorescence staining on a paraffin embedded tissue section in a case of diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis after enzymatic digestion with proteinase K. Note the adequate digestion evidenced by disappearance of tubular epithelial cells (arrow) (FITC IgG, × 200); B: Immunofluorescence staining in a case with inadequate digestion with visible tubular epithelial cells (arrow). Note the antibody sticking to the surface of the capillary wall (FITC IgG, × 200). FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate.
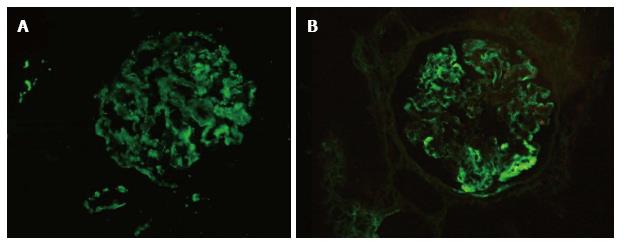
Figure 2 Comparable staining pattern on immunofluorescence on frozen and paraffin embedded tissue.
A case of dense deposit disease showing bright C3c deposition 3+ (0-3+ scale) on IF-F (A, FITC C3c, × 200). Note the comparative coarse granular capillary wall staining of C3c (3+) on paraffin embedded tissue section after enzymatic retrieval (B, FITC C3c, × 200). FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; IF-F: Immunofluorescence on fresh frozen tissue.
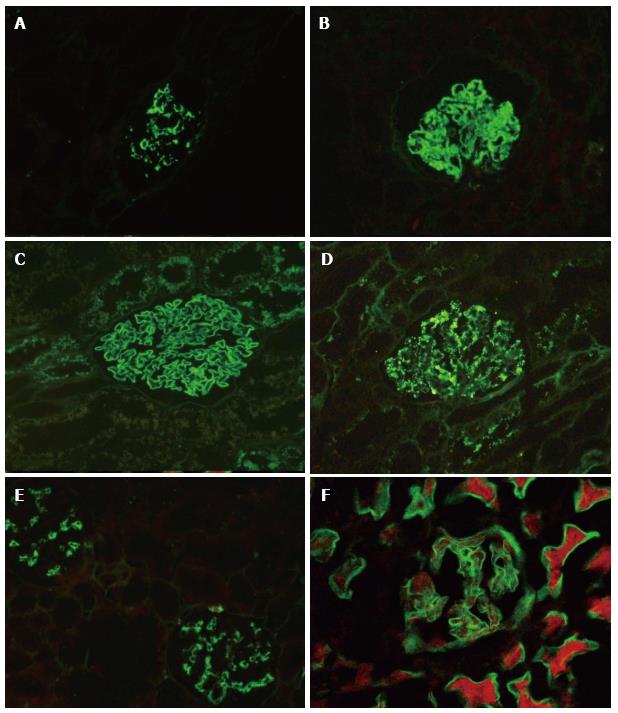
Figure 3 Glomerulonephritis diagnosed on immunofluorescence on paraffin.
A: IgA nephropathy: There is predominantly mesangial deposition of IgA (FITC IgA × 100); B: Class IV or diffuse lupus nephritis: Immunofluorescence reveals coarsely granular deposition of immunoglobulins in both mesangium and in the peripheral capillary wall (FITC IgG × 200); C: Membranous nephropathy: Immunofluorescence reveals fine granular capillary wall deposition of IgG (C, FITC IgG × 200); D: Post infectious glomerulonephritis: Garland pattern with elongated peripheral loop deposits is depicted, along with occasional mesangial deposits (D, FITC C3c, × 200); E: C1q nephropathy with mesangial deposition of C1q (FITC C1q × 100); F: Diabetic nephropathy with linear accentuation of glomerular capillary wall and tubular basement membrane (FITC IgG × 200). FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate.
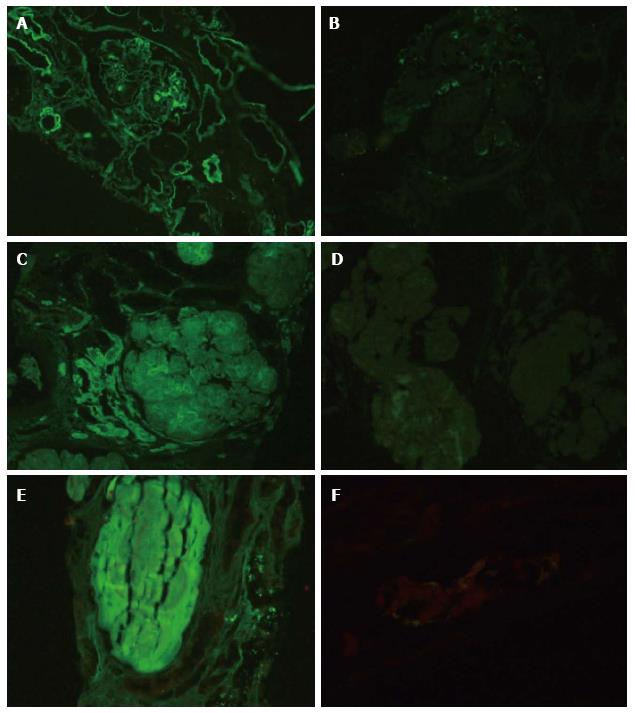
Figure 4 Immunofluorescence on paraffin to demonstrate monoclonal deposits.
A case of light chain deposition disease with kappa light chain restriction. There is nodular mesangial, capillary wall and tubular basement membrane deposition of kappa light chain (A, FITC kappa, × 100) while no deposition of lambda is noted (B, FITC lambda, × 200); C: A case of primary amyloidosis with lambda light chain restriction. The lambda deposition is noted in the mesangium (FITC lambda × 200); D: There is no deposition of kappa (D, FITC kappa × 200); E: A case of cast nephropathy with kappa light chain restriction. Note the brightly positive casts for kappa (FITC kappa × 200) with no traces of lambda (F, FITC lambda × 200). FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate.
- Citation: Singh G, Singh L, Ghosh R, Nath D, Dinda AK. Immunofluorescence on paraffin embedded renal biopsies: Experience of a tertiary care center with review of literature. World J Nephrol 2016; 5(5): 461-470
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v5/i5/461.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v5.i5.461