Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Sep 19, 2025; 15(9): 108465
Published online Sep 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i9.108465
Published online Sep 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i9.108465
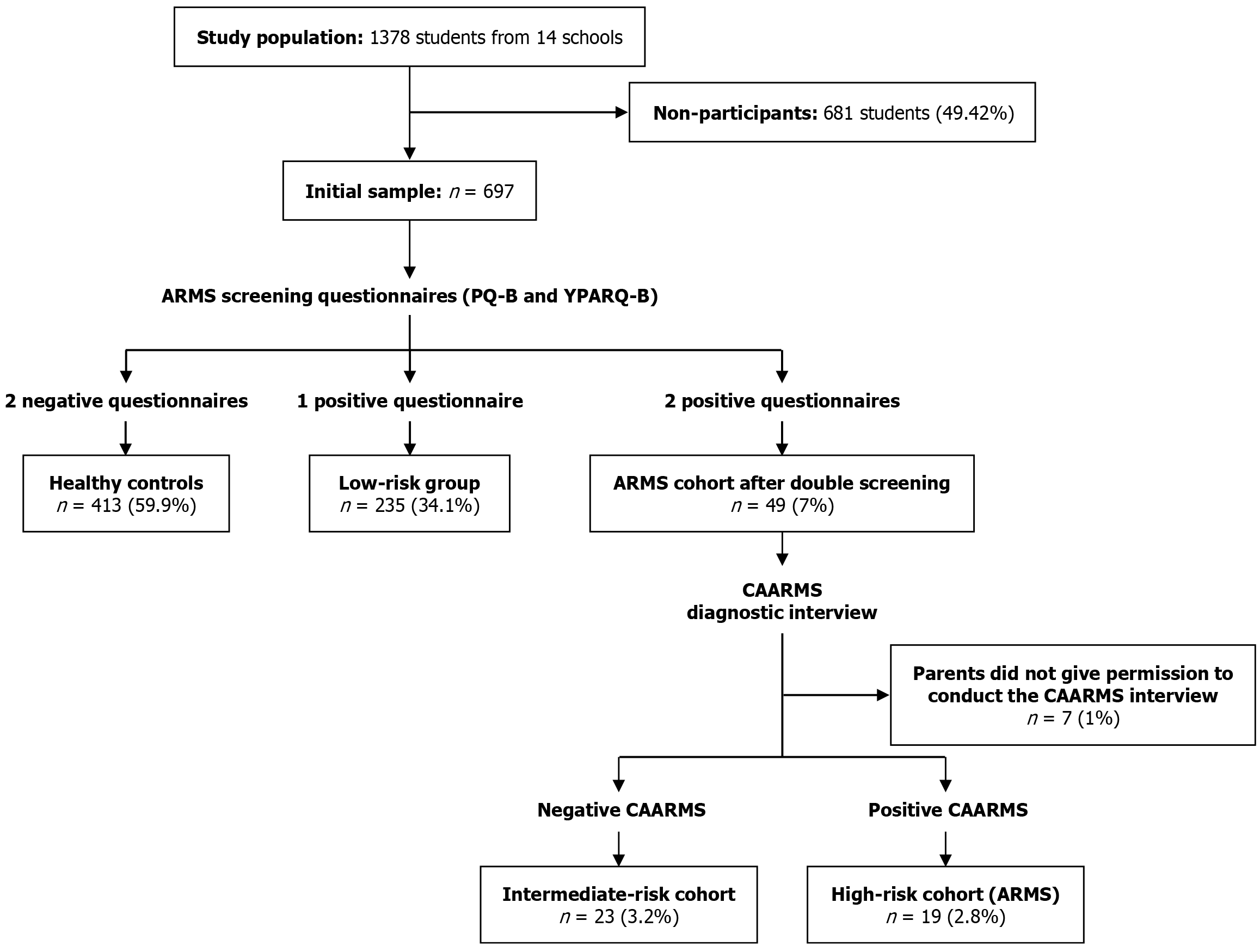
Figure 1 The sample selection process and its division into the four study groups.
Thus, this study was carried out on a final sample of 690 individuals. The participants were divided into 4 groups: (1) Healthy controls: Who did not exceed the cut-off points on the Prodromal Questionnaire-Brief (PQ-B) or Youth Psychosis At-Risk Questionnaire Brief (YPARQ-B) (n = 413; 59.9% of the initial sample); (2) Low-risk group: Who exceeded the cut-off point in either the PQ-B or YPARQ-B, but not both (n = 235; 34.1%); (3) Intermediate-risk group: Who exceeded the cut-off points on both the PQ-B and YPARQ-B but did not meet any diagnostic criteria for the at-risk mental state (ARMS) on the comprehensive assessment of ARMS interview (n = 23; 3.2%); and (4) High-risk group (ARMS): Who exceeded the cut-off points of both the PQ-B and YPARQ-B and also met at least one diagnostic criterion for the ARMS in the comprehensive assessment of ARMS interview (n = 19; 2.8%). PQ-B: Prodromal Questionnaire-Brief; YPARQ-B: Youth Psychosis At-Risk Questionnaire Brief; CAARMS: Comprehensive assessment of at-risk mental state; ARMS: At-risk mental state.
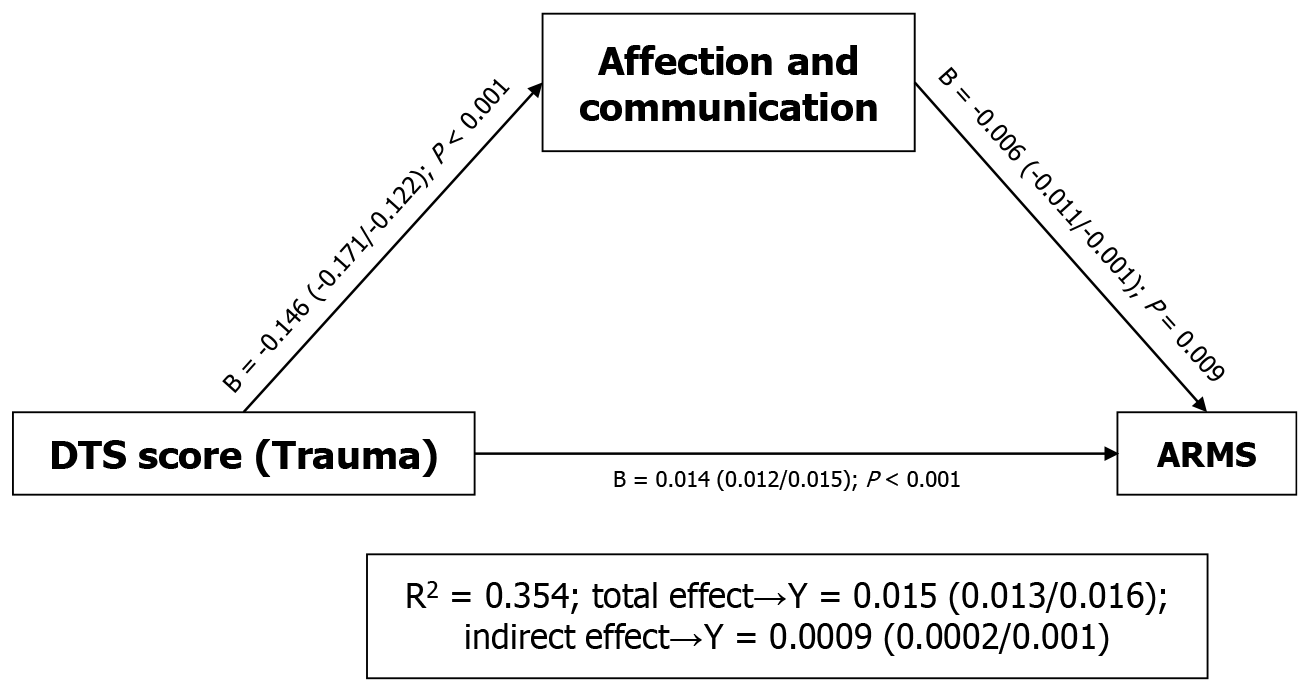
Figure 2 Model of how parental socialization (affection and communication) mediated the relationship between trauma (Davidson Trauma Scale score) and an at-risk mental state (group into which the participants had been classified).
DTS: Davidson Trauma Scale; ARMS: At-risk mental state.
- Citation: Jovani A, Moliner-Castellano B, Gimeno Vergara R, Benito A, Marí-Sanmillán MI, Castellano-García F, Haro G. Impact of childhood trauma and parental socialization on at-risk mental state in non-clinical adolescents. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(9): 108465
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i9/108465.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i9.108465