Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Jun 19, 2025; 15(6): 106775
Published online Jun 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.106775
Published online Jun 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.106775
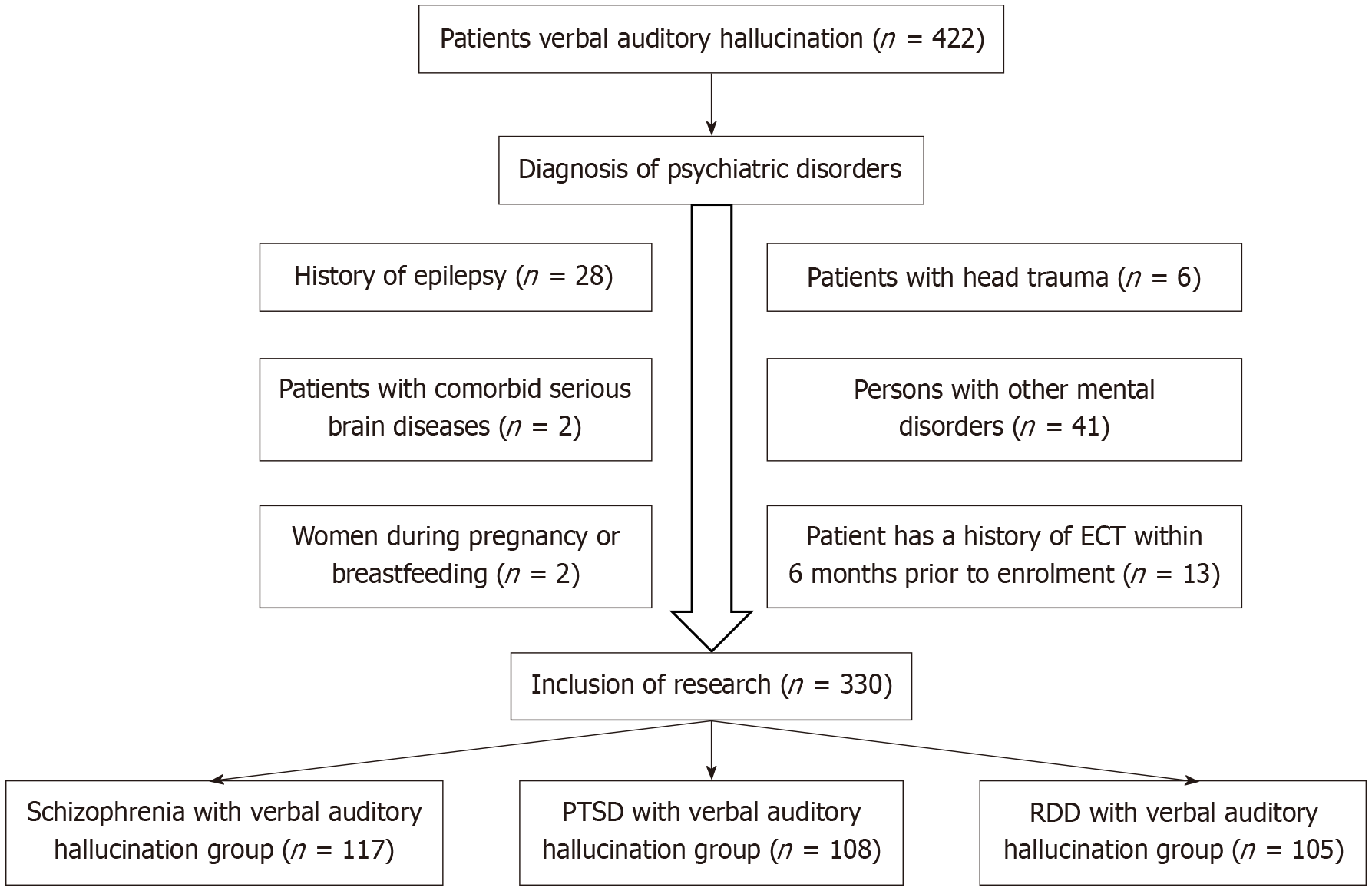
Figure 1 Flow chart of the study.
PTSD: Post-traumatic stress disorder; RDD: Recurrent depressive disorder.
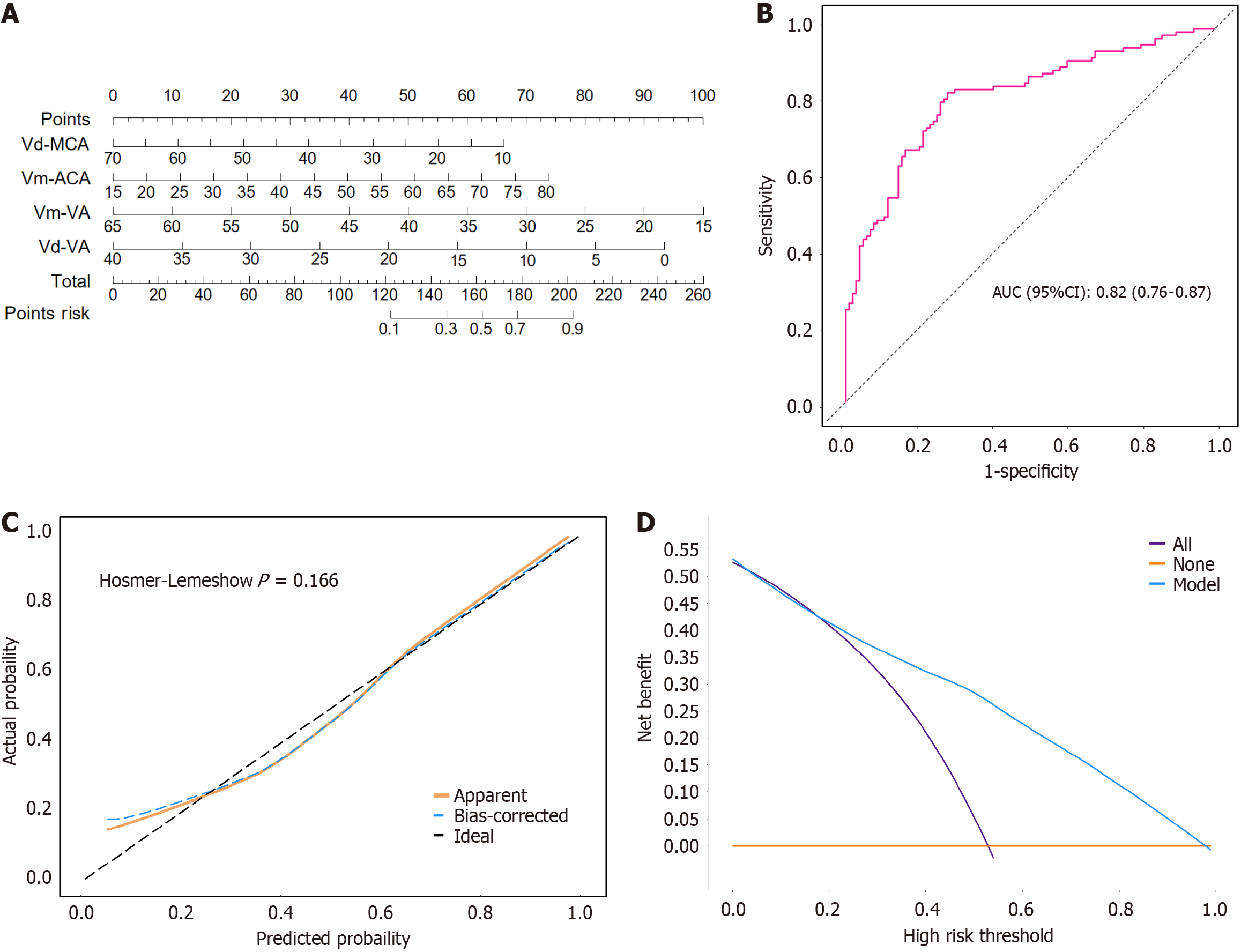
Figure 2 Construction and evaluation of model 1.
A: Nomogram; B: Receiver operating characteristic curve; C: Calibration curve; D: Decision curve analysis curves. MCA: Middle cerebral artery; VA: Vertebral artery; Vm: Mean velocity; Vd: End-diastolic velocity; AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval.
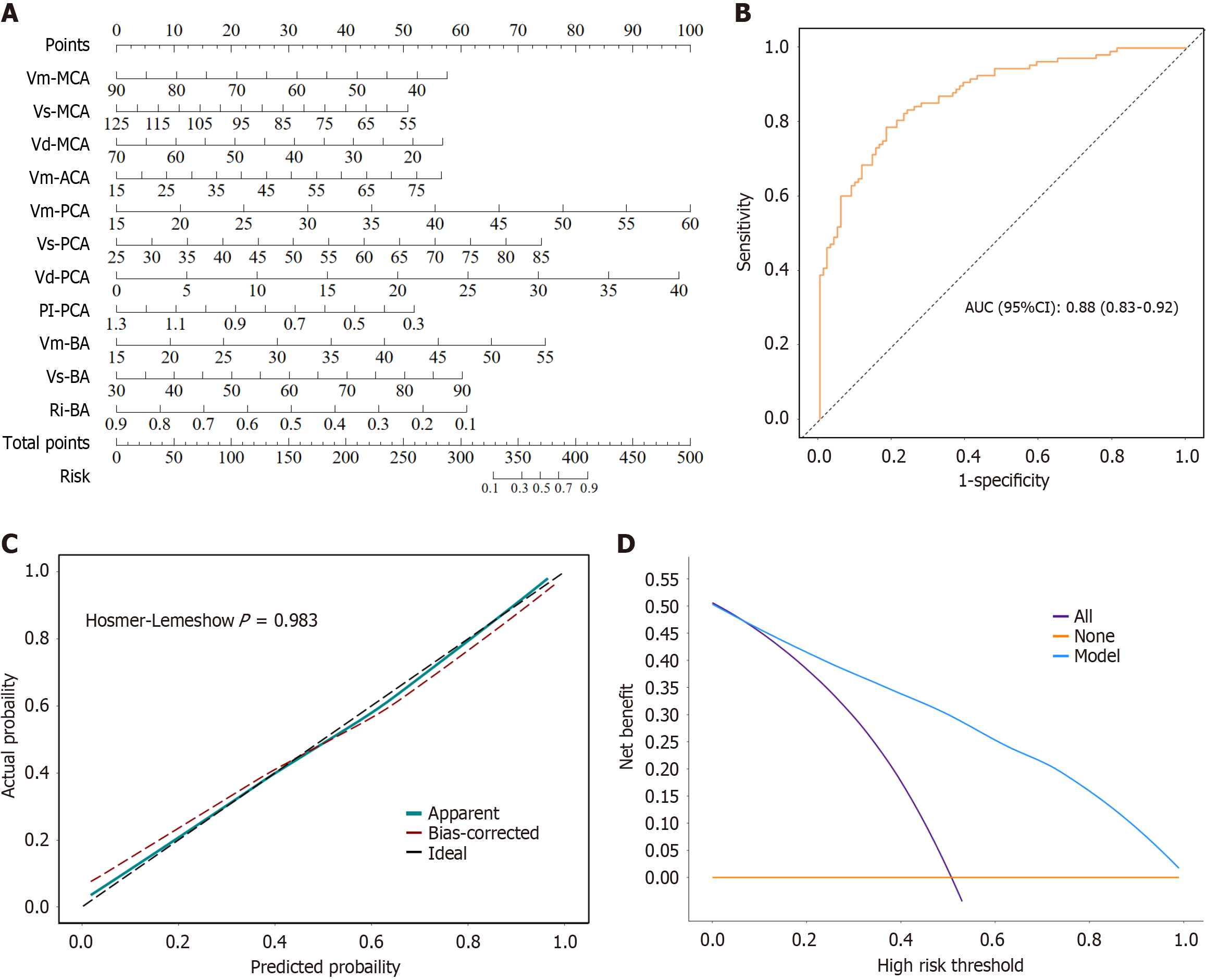
Figure 3 Construction and evaluation of model 2.
A: Nomogram; B: Receiver operating characteristic curve; C: Calibration curve; D: Decision curve analysis curves. MCA: Middle cerebral artery; ACA: Anterior cerebral artery; PCA: Posterior cerebral artery; BA: Basilar artery; Vm: Mean velocity; Vs: Peak systolic velocity; Vd: End-diastolic velocity; PI: Pulsatility index; RI: Resistance index; AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval.
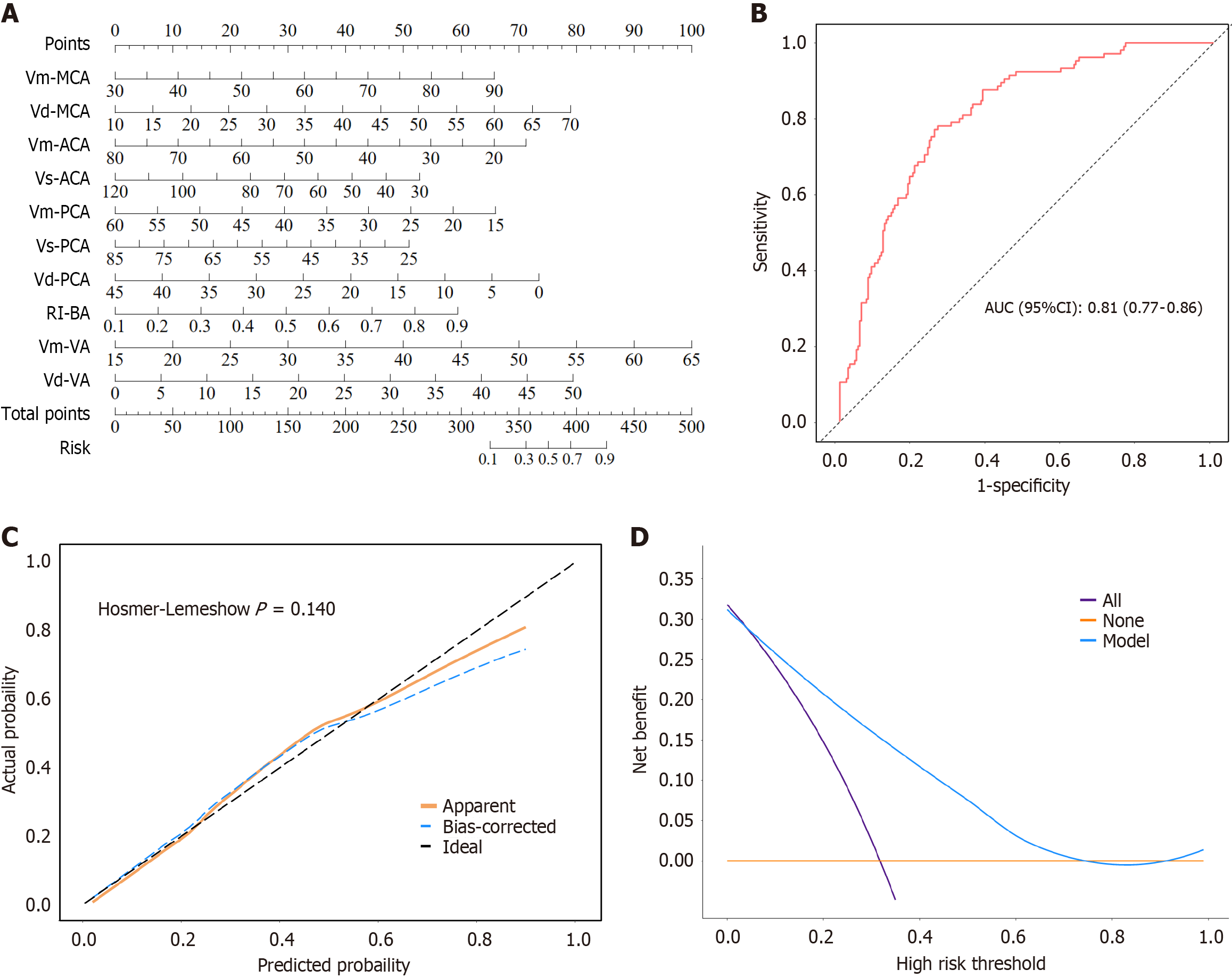
Figure 4 Construction and evaluation of model 3.
A: Nomogram; B: Receiver operating characteristic curve; C: Calibration curve; D: Decision curve analysis curves. MCA: Middle cerebral artery; ACA: Anterior cerebral artery; PCA: Posterior cerebral artery; BA: Basilar artery; VA: Vertebral artery; Vm: Mean velocity; Vs: Peak systolic velocity; Vd: End-diastolic velocity; AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval.
- Citation: Cai ZY, Chen C, Huang ZY, Ye XW, Jin XZ, Chen HR, Sha JM. Cerebral hemodynamic characteristics of patients with auditory verbal hallucinations and the construction of nomogram models. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(6): 106775
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i6/106775.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.106775