Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
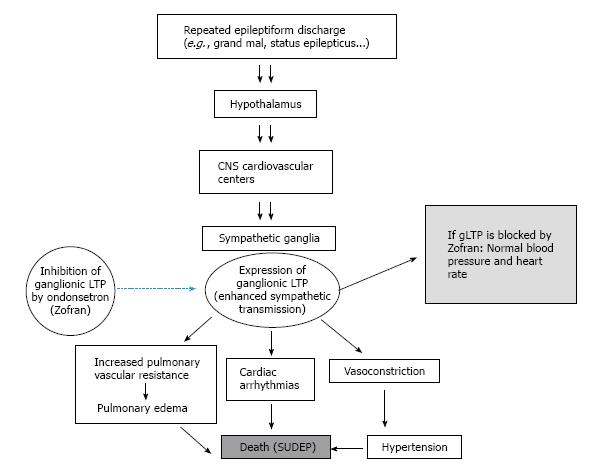
Figure 1 The hypothesis: In the whole animal, epileptic seizures provide the repetitive stimulation required for the expression of ganglionic long-term potentiation in sympathetic ganglia, resulting in increased peripheral resistance, hypertension and cardiopulmonary dysregulation leading to sudden death.
Blocking serotonin 5-HT3 receptor with antagonist (Zofran©) in ganglia has been shown to obviate the effect of gLTP. gLTP: Ganglionic long-term potentiation; CNS: Central nervous system; SUDEP: Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy.
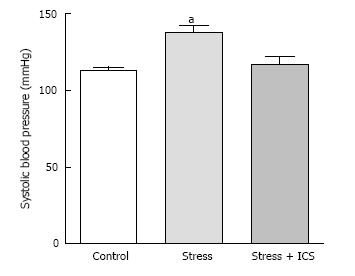
Figure 2 Tropisetron (ICS) normalizes established stress hypertension in psychosocially stressed male rats without affecting blood pressure in control (unstressed) rats measured at day 30 of continuous stress.
Blood pressure was measured by tail-cuff plethysmography. Similar results were obtained from female rats. Each point in each group is the mean ± SD from 5 male or female rats. (a) indicates significant difference from other groups (Adapted from ref. [29]).
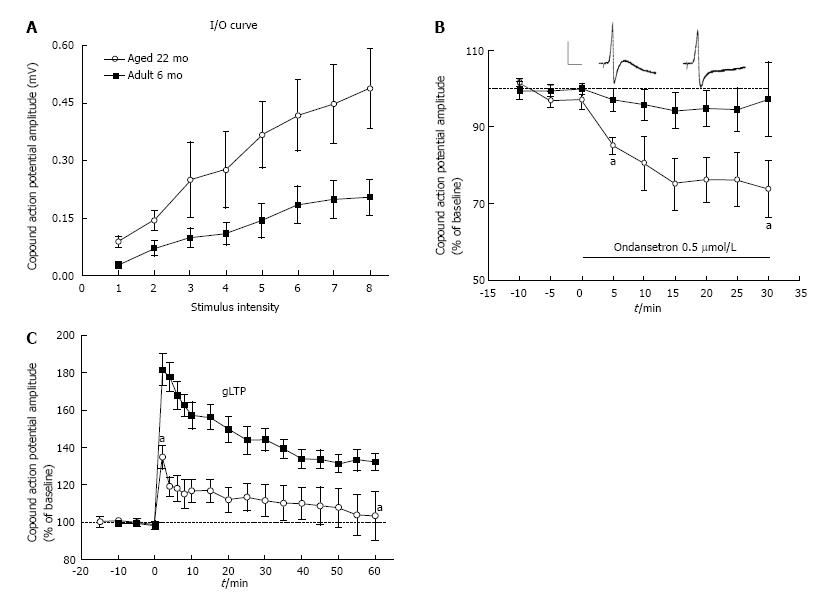
Figure 3 Expression of ganglionic long-term potentiation in sympathetic superior cervical ganglia in aged (22 mo) hypertensive rats.
A: Input/output curve (I/O) of aged animal ganglia compared to adult (6 mo) ganglia, indicating enhanced synaptic activity in the aged animal ganglia. Stimulus intensity numbers along the X-axis are arbitrary values, where 1 is the minimal and 8 the maximal response (CAP amplitude in mV). Each point from aged rats is significantly different from matching points of adult rats, and is the mean ± SEM from 5-7 ganglia; B: Inhibition of “baseline” ganglionic transmission in aged rats by a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist ondansetron (Zofran) as an indication of expression of gLTP in vivo. Zofran (0.5 μmol/L, solid horizontal line) decreased CAP baseline of ganglia isolated from aged but not of those isolated from adult rats. All points between the two “a“ are significantly different (P < 0.05) from corresponding point for adult rats. Each point in each series is the mean ± SEM from 5-7 ganglia. Inset: CAPs of aged rats before and after application of drug; calibration 0.5 mV/20 ms; C: High frequency stimulation (HFS: 20 Hz/20 s, at 0 time) of the preganglionic nerves evoked robust gLTP in ganglia excised from adult rats. Identical protocol in ganglia from aged rats produced no gLTP. Each point represents the mean ± SEM from 5 ganglia. Adapted from ref. [35]. gLTP: Ganglionic long-term potentiation; CAP: Compound action potential.
- Citation: Alkadhi KA. Long-term potentiation in autonomic ganglia: Potential role in cardiovascular disorders. World J Pharmacol 2016; 5(2): 51-58
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3192/full/v5/i2/51.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5497/wjp.v5.i2.51