Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Exp Med. Sep 20, 2025; 15(3): 107184
Published online Sep 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i3.107184
Published online Sep 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i3.107184
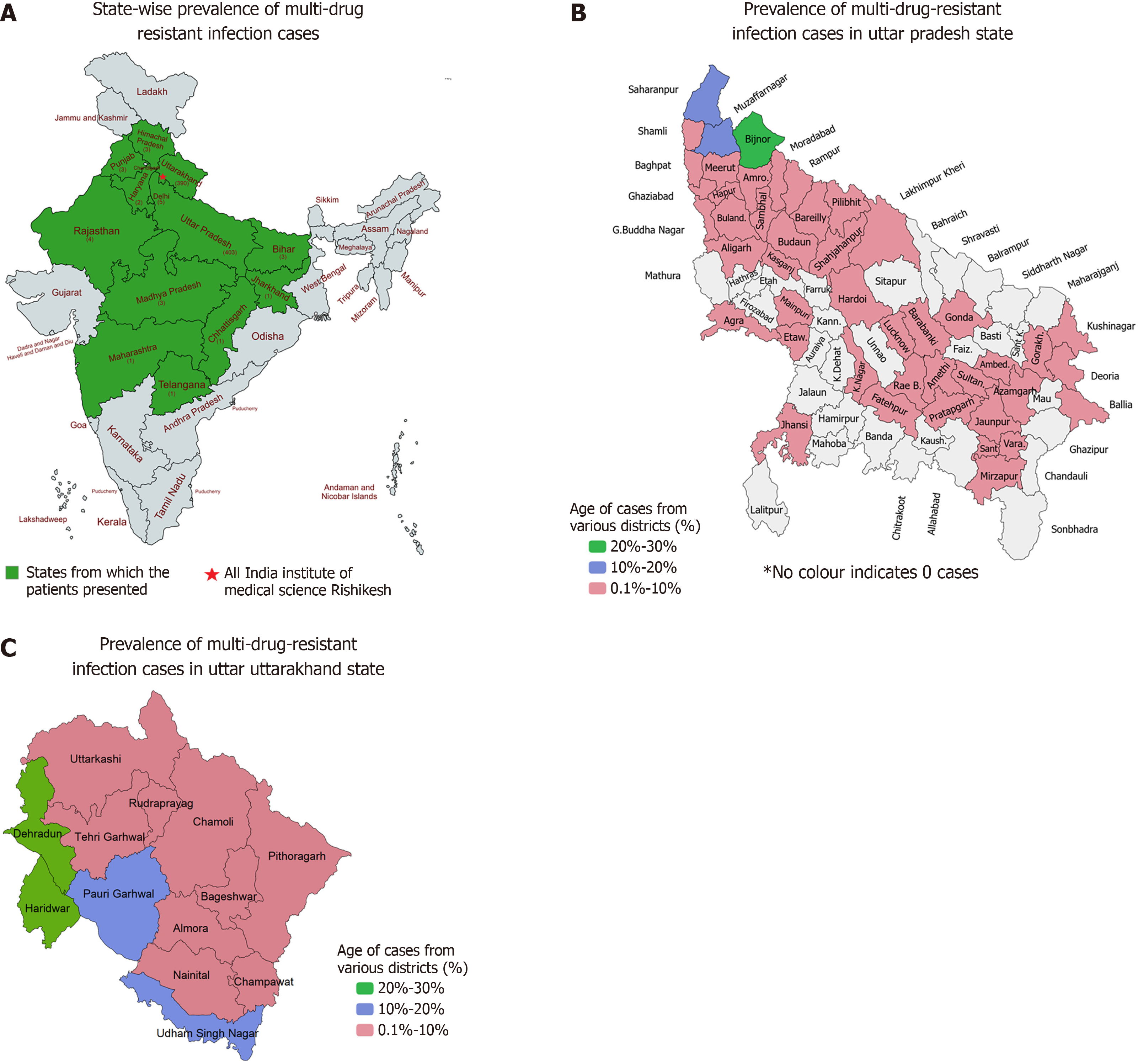
Figure 1 Demographic distribution of multidrug resistance infection cases.
A: State-wise proportion of cases (n = 820); B: District-wise distribution of cases in Uttar Pradesh (n = 820); C: District-wise distribution of cases in Uttarakhand (n = 820).
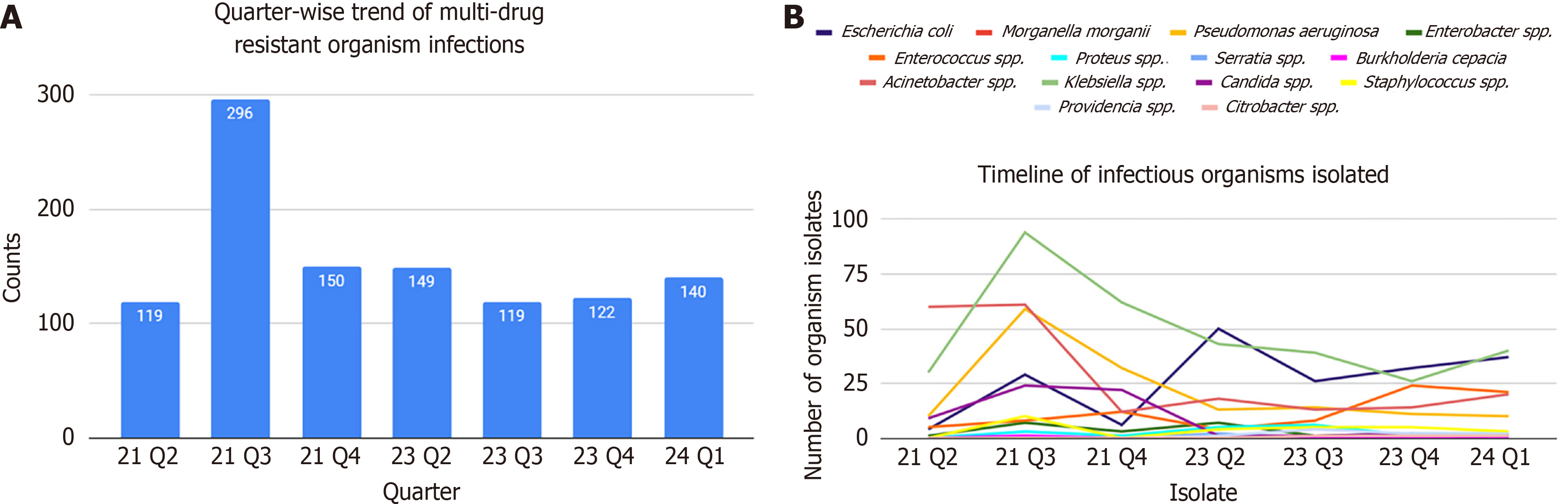
Figure 2 Trend in multidrug resistance organism infections.
A: Trend in the years 2021 and 2023; B: Genus-specific trend in isolates (n = 1106).
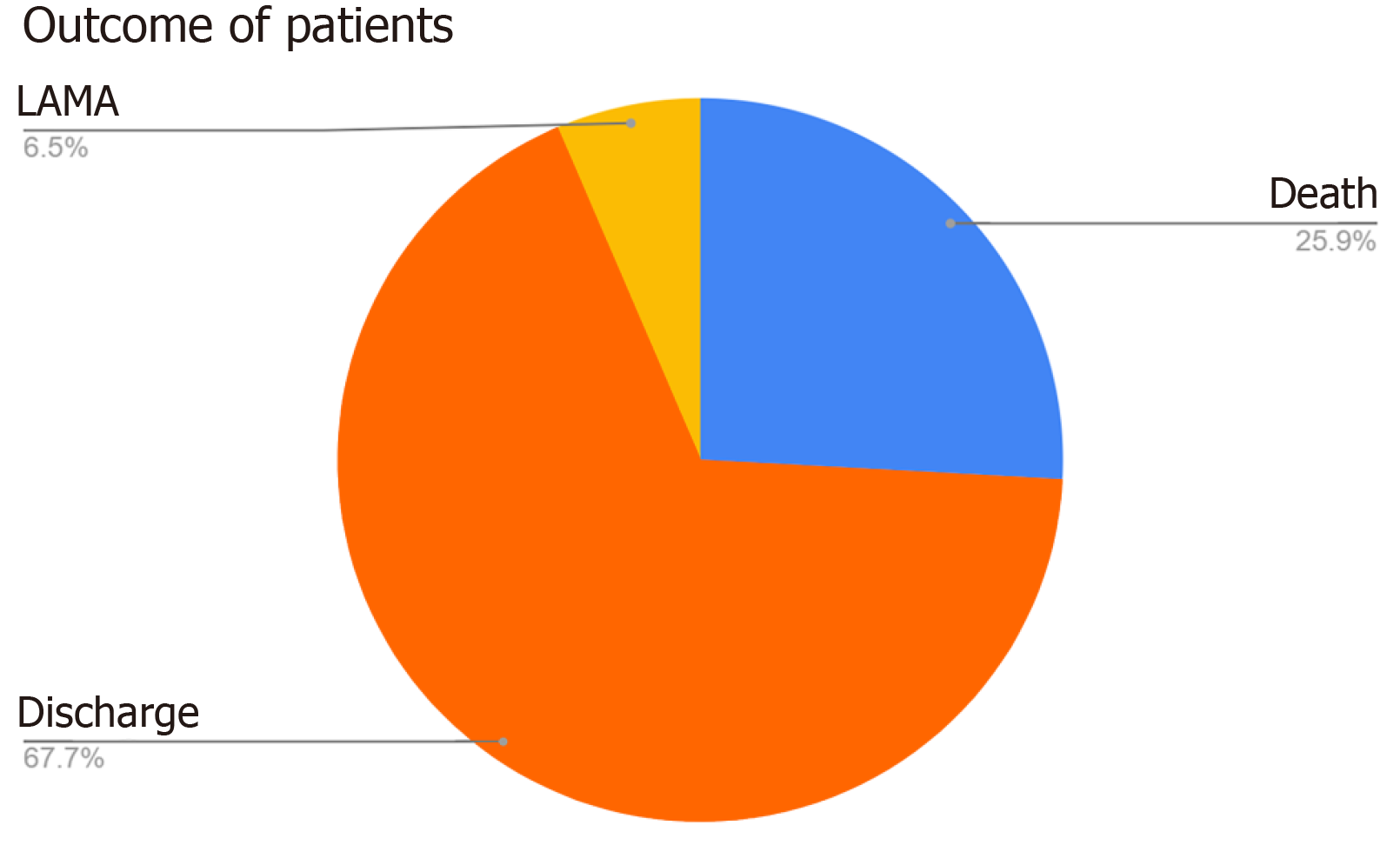
Figure 3 Outcome of multidrug resistance infection cases (n = 820).
LAMA: Leave against medical advice.
- Citation: Singh H, Patel AA, Pandy P, Omar BJ, Prasad A, Singh V, Sharma P, Bairwa M, Sihag RK, Tiwari A, Rajput D, Kulshrestha M, Saini S, Kumar A, Sarkar B, Duggal B, Agarwal A, Kaeley N, Dhingra G, Mahala P, Yesodharan V, Chauhan H, Kumari D, Choudhary S, Sharma AK, Yadav R, Panda PK. Burden of multi-drug-resistant organisms in a tertiary healthcare institute in North India: Implications for regional public health. World J Exp Med 2025; 15(3): 107184
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v15/i3/107184.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v15.i3.107184