Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Otorhinolaryngol. Nov 28, 2014; 4(4): 17-22
Published online Nov 28, 2014. doi: 10.5319/wjo.v4.i4.17
Published online Nov 28, 2014. doi: 10.5319/wjo.v4.i4.17
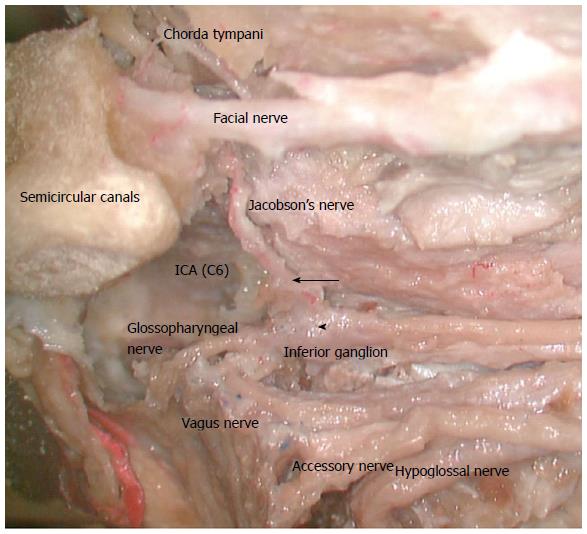
Figure 1 Image demonstrating the path of the glossopharyngeal nerve and the origin of the tympanic/Jacobson’s nerve (arrow) at the inferior ganglion (arrowhead).
(Used with permission from Dr. Takanori Fukushima, Professor of Neurosurgery, Duke University Medical Centre and Duke Raleigh Hospital). ICA: Internal Carotid artery.
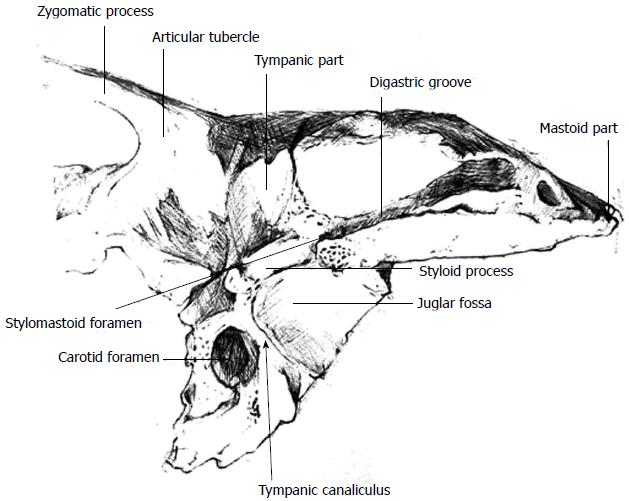
Figure 2 Illustration of the temporal bone demonstrating the relationship between the tympanic canaliculus, the carotid foramen and the jugular fossa.
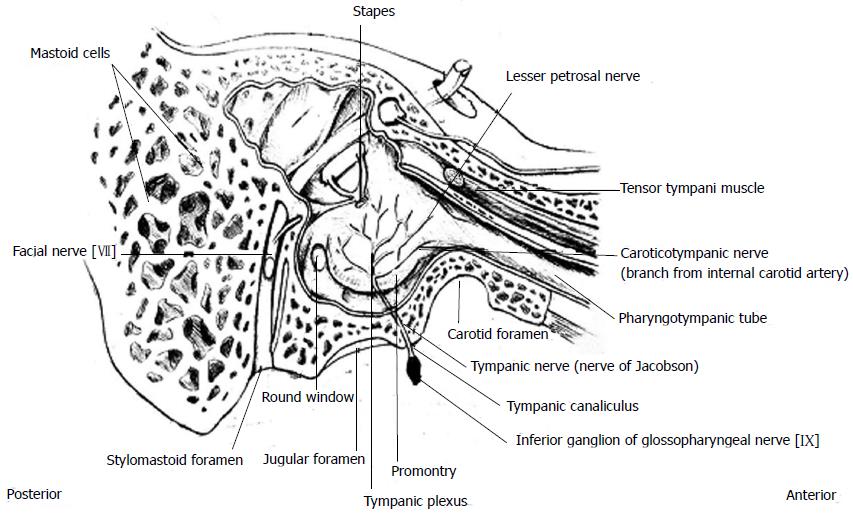
Figure 3 Schematic illustration of demonstrating the tympanic nerve from its origin (shaded in black), its course and its anatomical relations within the right middle ear.
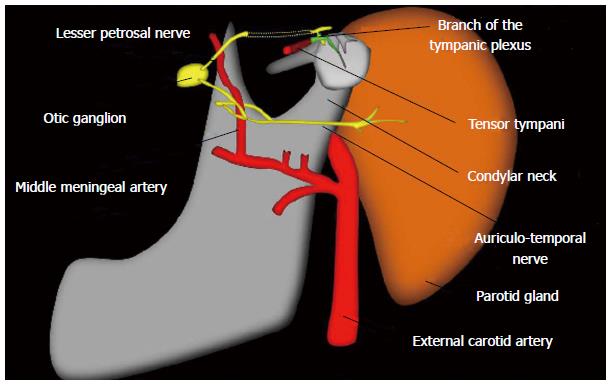
Figure 4 Illustration depicting the link between the tympanic plexus (formed by the tympanic nerve) and the parasympathetic supply to the parotid via the lesser petrosal nerve and the otic ganglion.
(Used with permission from Dr. José M. García Santos, MD, PhD, Head of the Radiology Department, University Hospital Morales Meseguer, Murcia, Spain).
- Citation: Kanzara T, Hall A, Virk JS, Leung B, Singh A. Clinical anatomy of the tympanic nerve: A review. World J Otorhinolaryngol 2014; 4(4): 17-22
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6247/full/v4/i4/17.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5319/wjo.v4.i4.17