Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Orthop. Jul 18, 2017; 8(7): 536-544
Published online Jul 18, 2017. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v8.i7.536
Published online Jul 18, 2017. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v8.i7.536
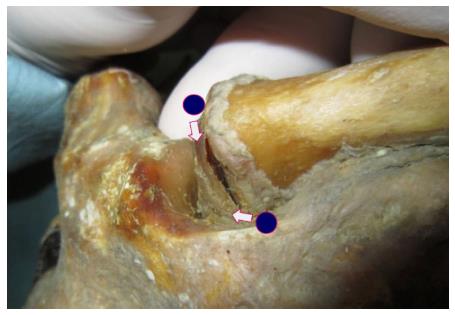
Figure 1 The two standard portals for sternoclavicular arthroscopy.
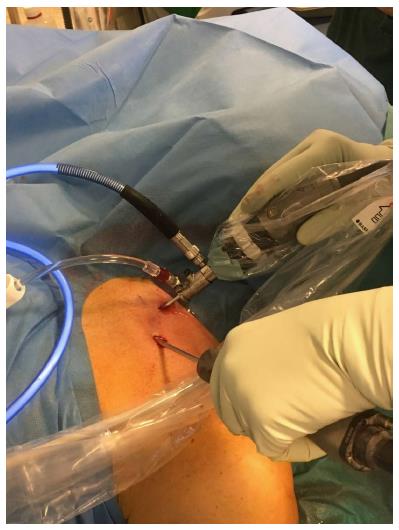
Figure 2 Sternoclavicular arthroscopy performed with the patient supine, using a 2.
7 mm arthroscope and a 4.0 mm shaver.
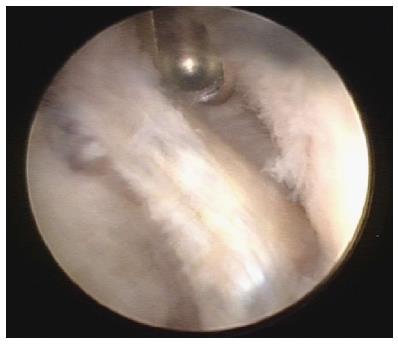
Figure 3 Arthroscopic view of the left sternoclavicular joint showing degenerative changes in the partially resected disc (in the middle) and chondral degeneration of the clavicular cartilage (right side of photo).
The shaver is introduced through the superior portal.
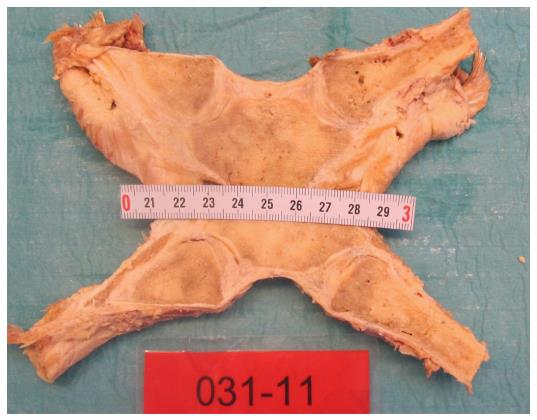
Figure 4 The sternoclavicular joints were divided frontally with a thin band saw so that both sternoclavicular joints were unfolded in the same section through the center of the discs.
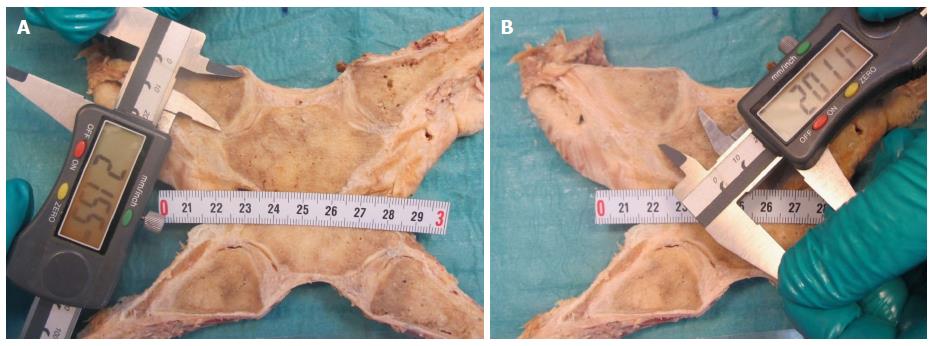
Figure 5 Measurement of the height of the articular cartilages (cranial-caudal) on the clavicle (A) and manubrium (B).
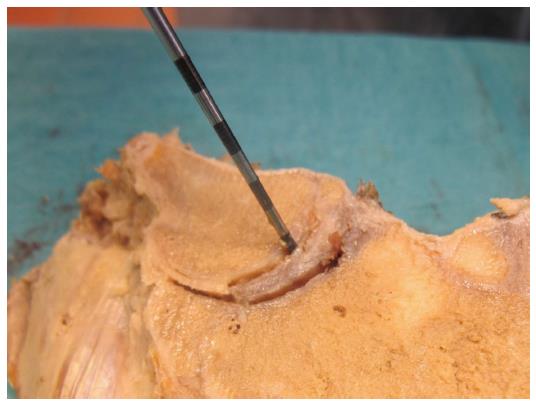
Figure 6 Probing the attachments of the intraarticular disc to the clavicle and first rib-manubrium junction as well as to the anterior and posterior capsule with a hooked arthroscopic probe.
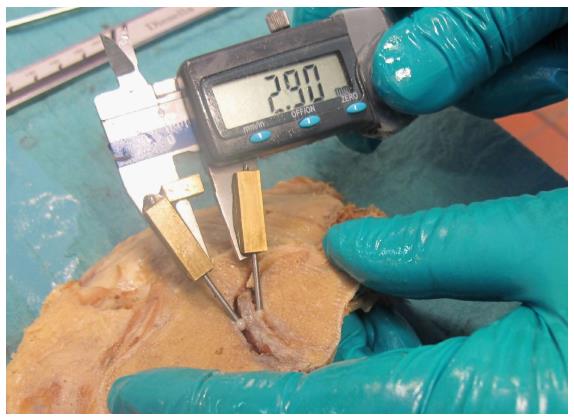
Figure 7 Measurement of the thickest and thinnest parts of the intraarticular discs with a calliper gauge.
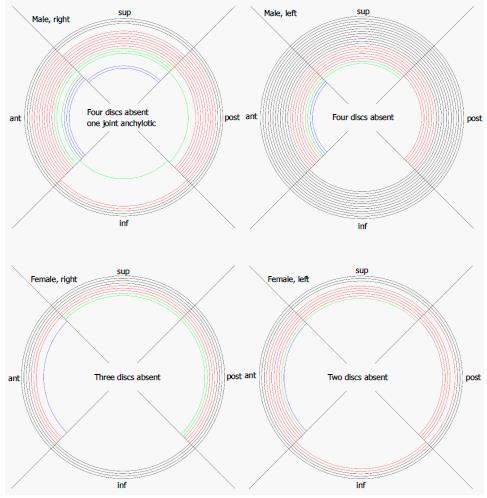
Figure 8 Graphic visualization of the attachments we found of the discs in left (left) and right (right) sternoclavicular joints of males and females.
Black lines: Full attachment of all four sectors; red lines: Attachment of three sectors; green lines: Attachment of two sectors; blue lines: Attachment of one sector only. inf: Inferior, sup: Superior; post: Posterior; ant: Anterior.
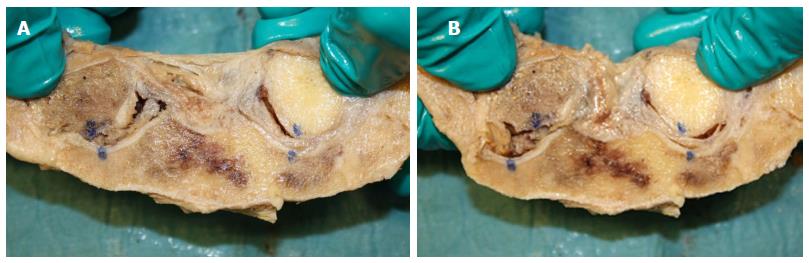
Figure 9 With inferior detachment (the sternoclavicular joint to the left) there was a substantial increase in supero-medial displacement of the medial clavicular end when a light medially directed push was applied to the lateral clavicle shaft (A: Light pull, B: Push).
With full attachment of the disc (as seen in the joint to the right) this displacement was much smaller. Blue dots were marked when no external forces were applied to the joints.
- Citation: Rathcke M, Tranum-Jensen J, Krogsgaard MR. Possibilities for arthroscopic treatment of the ageing sternoclavicular joint. World J Orthop 2017; 8(7): 536-544
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v8/i7/536.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v8.i7.536